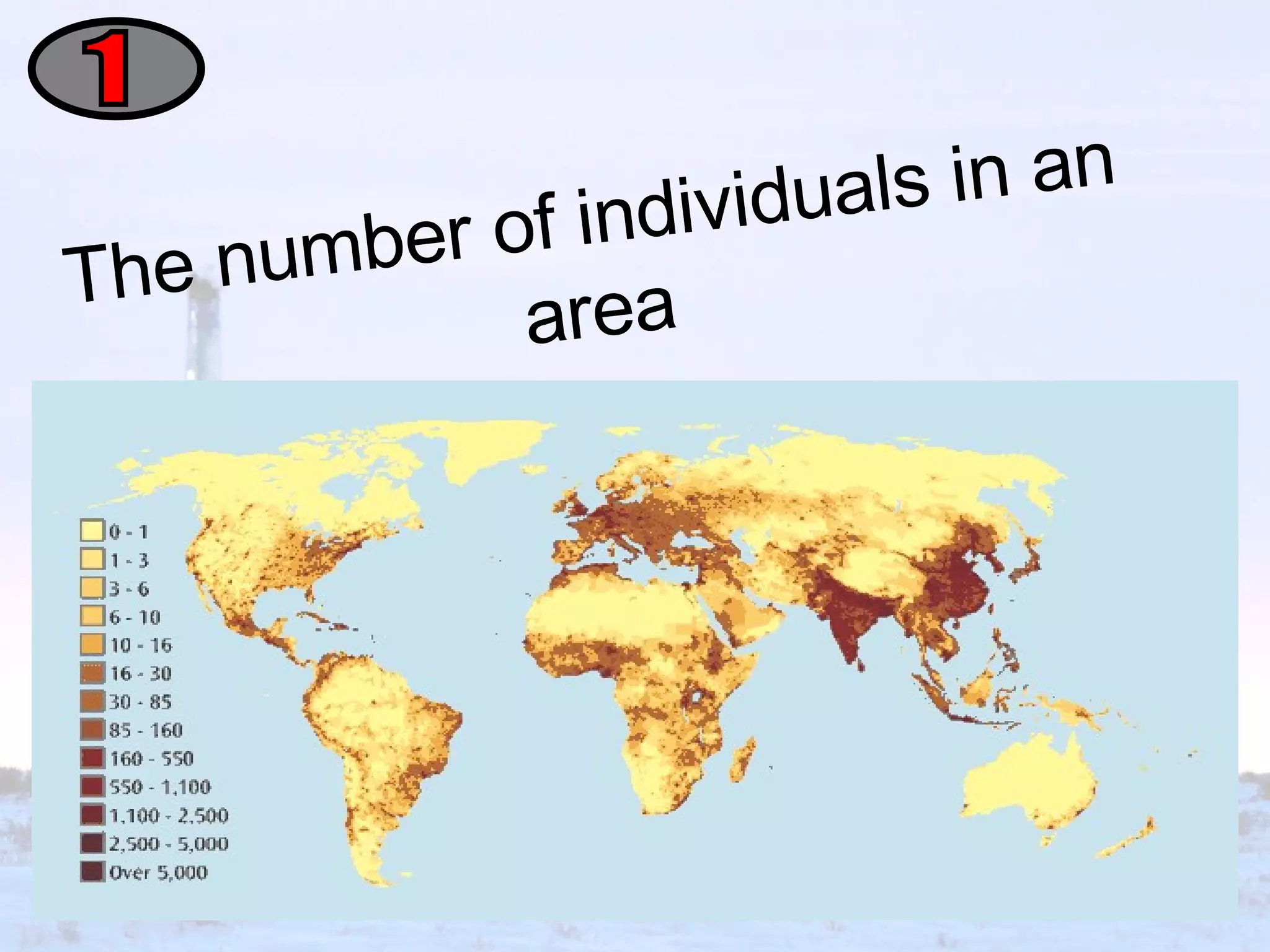
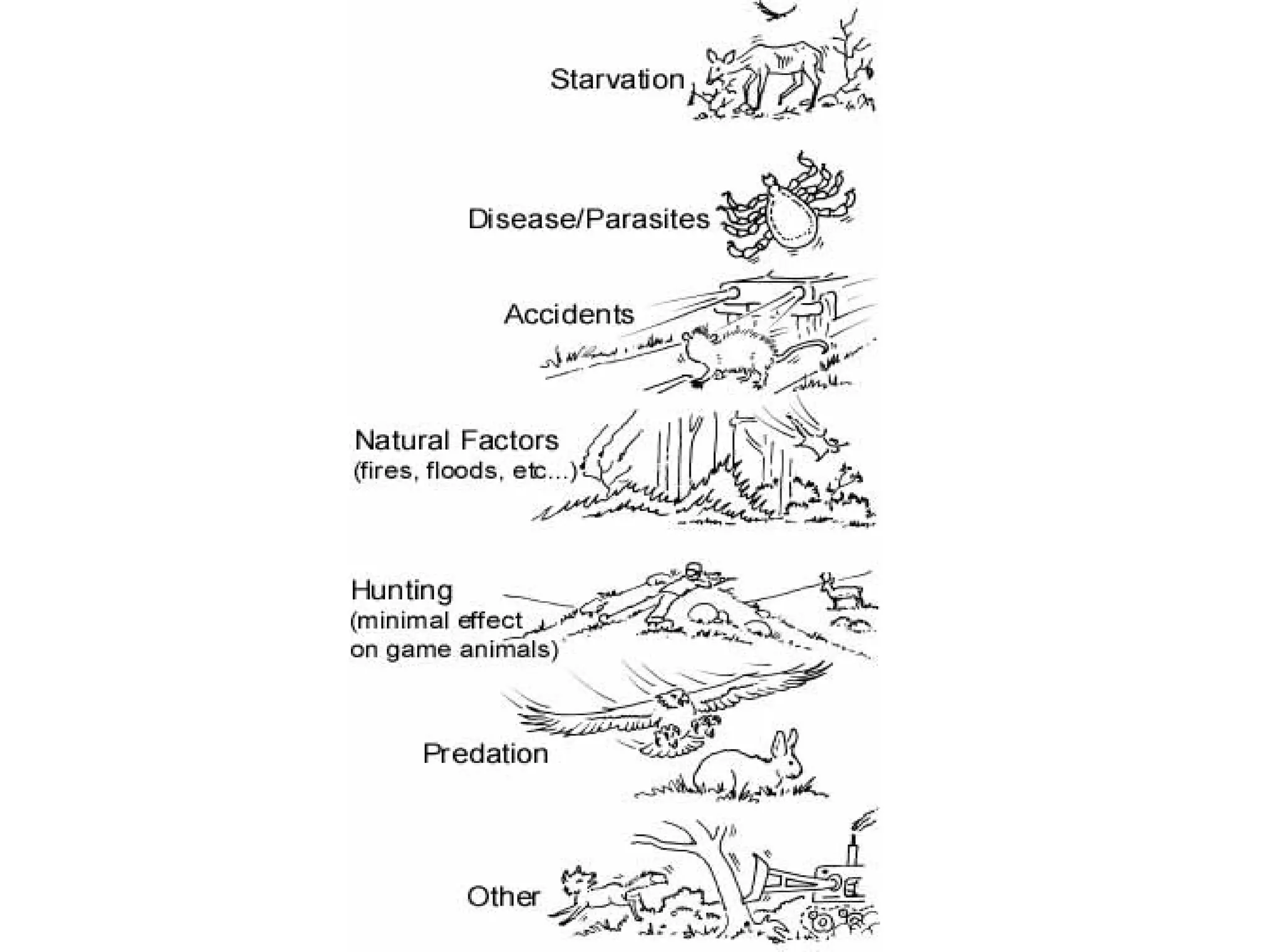
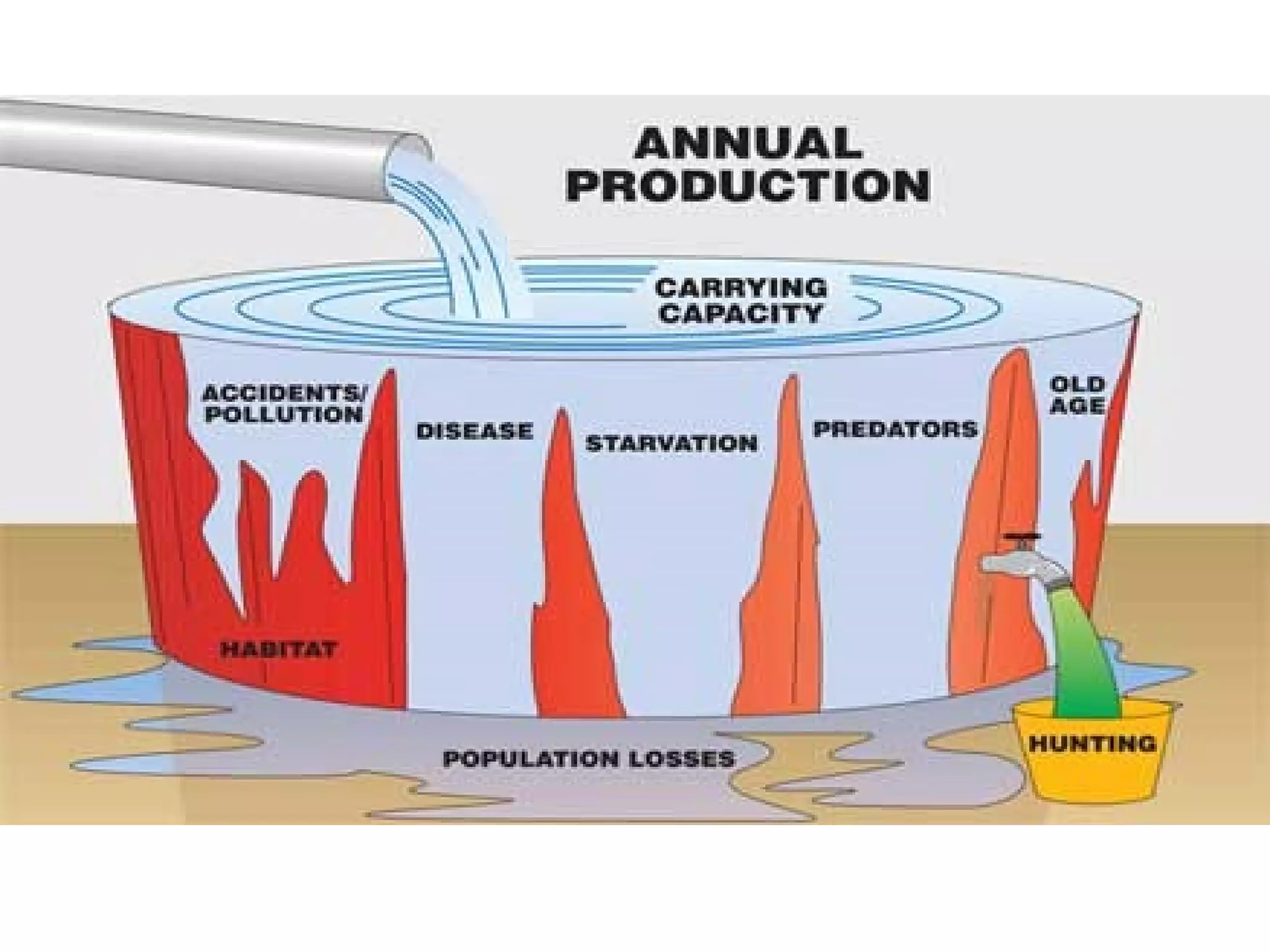
This document discusses key concepts related to studying populations. It defines population density as the number of individuals in an area. It explains that ecologists estimate population sizes through direct observation like counting, indirect observation of signs, or sampling a small area and extrapolating. An estimate is an approximation based on reasonable assumptions. Sampling is used when counting every member is not possible. Populations change size due to new members entering or leaving through birth, death, immigration, and emigration. Birth rate is the number of births and death rate is the number of deaths over a period of time. Limiting factors prevent population growth, such as food, space, and weather conditions. Carrying capacity is the largest population an environment can support.