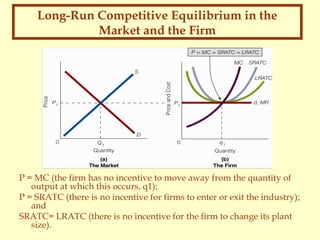
This document discusses the concept of perfect competition. It defines perfect competition as a market with many small buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, perfect information, and free entry and exit. Under perfect competition, each firm is a price taker and faces a horizontal demand curve. In the short run, a perfectly competitive firm will produce where price equals marginal cost to maximize profits or minimize losses. In the long run, the market reaches equilibrium when no firms want to enter or exit and each firm produces at the lowest point on its long-run average total cost curve.