1. The document discusses mathematical modeling concepts including direct, inverse, and joint variation. It provides examples of how to write equations for each type of variation given data points.
2. An example is worked out showing how to find the constant of variation k given direct variation data points and then using k to write the direct variation equation.
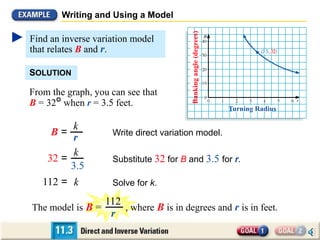
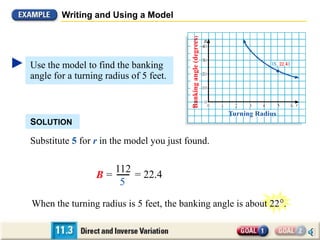
3. The document also shows how to apply concepts of direct and inverse variation to model the banking angle of a turning bicycle based on its turning radius. The model equation is derived and used to calculate the banking angle for a given turning radius.