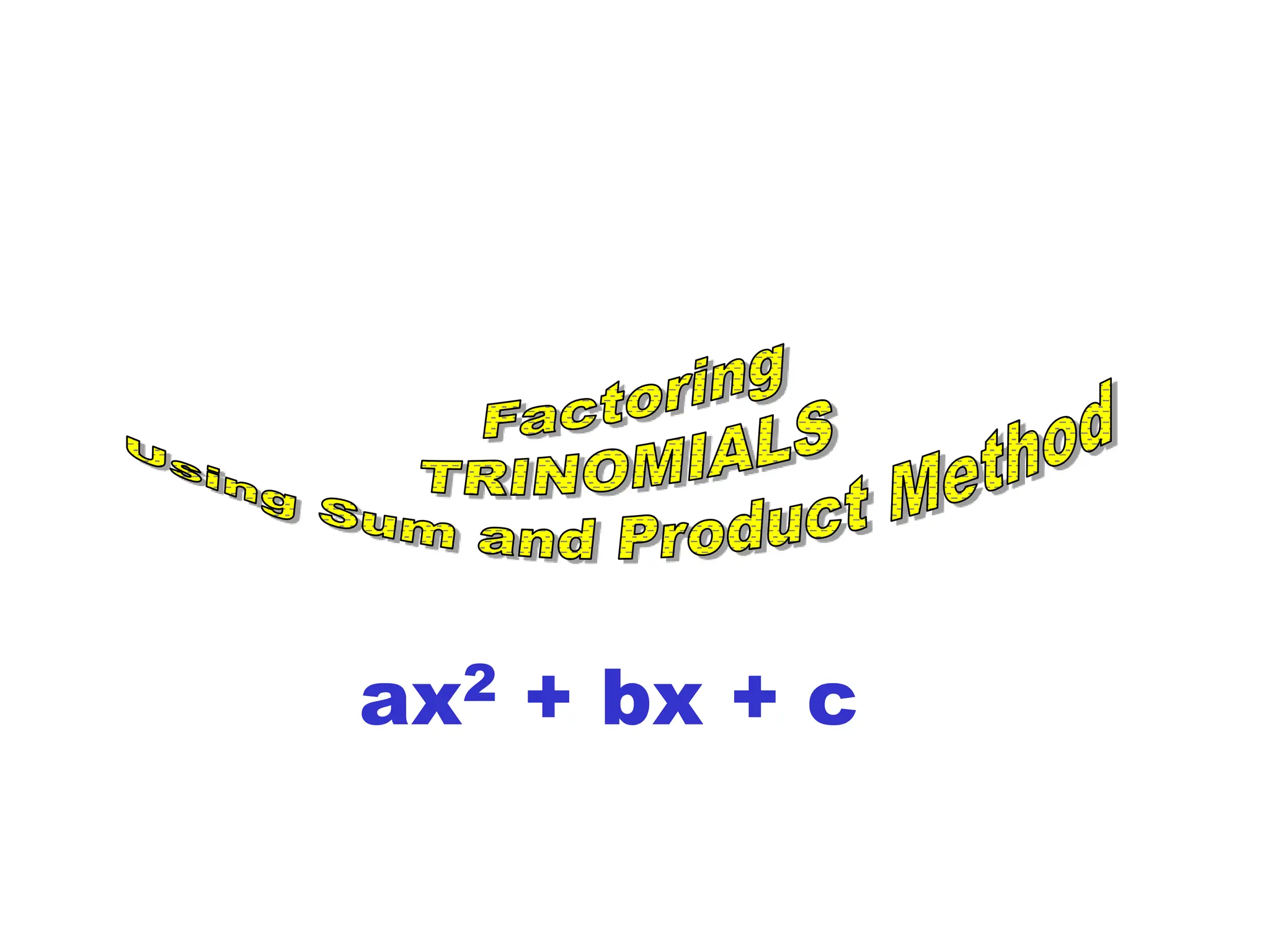
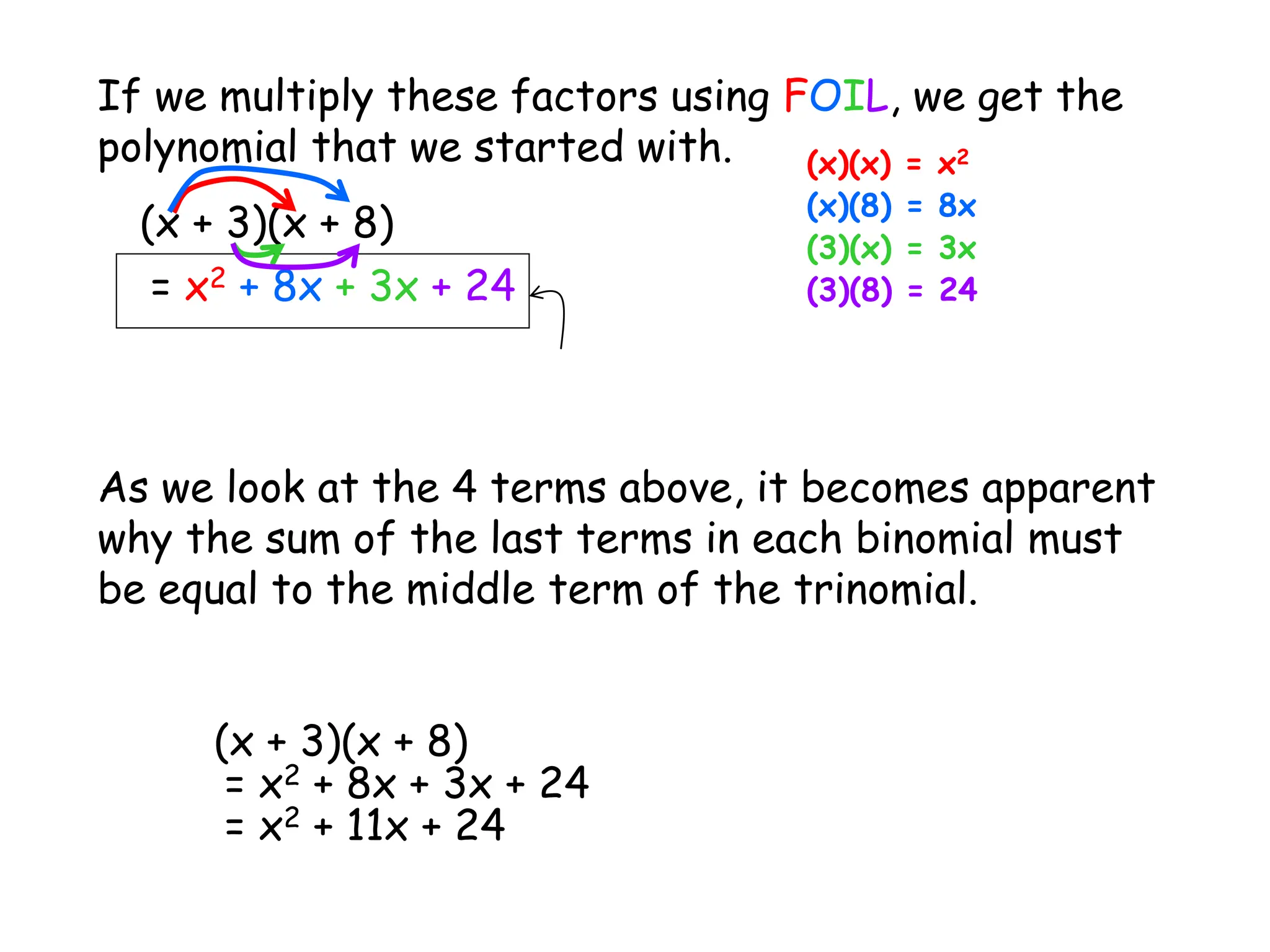
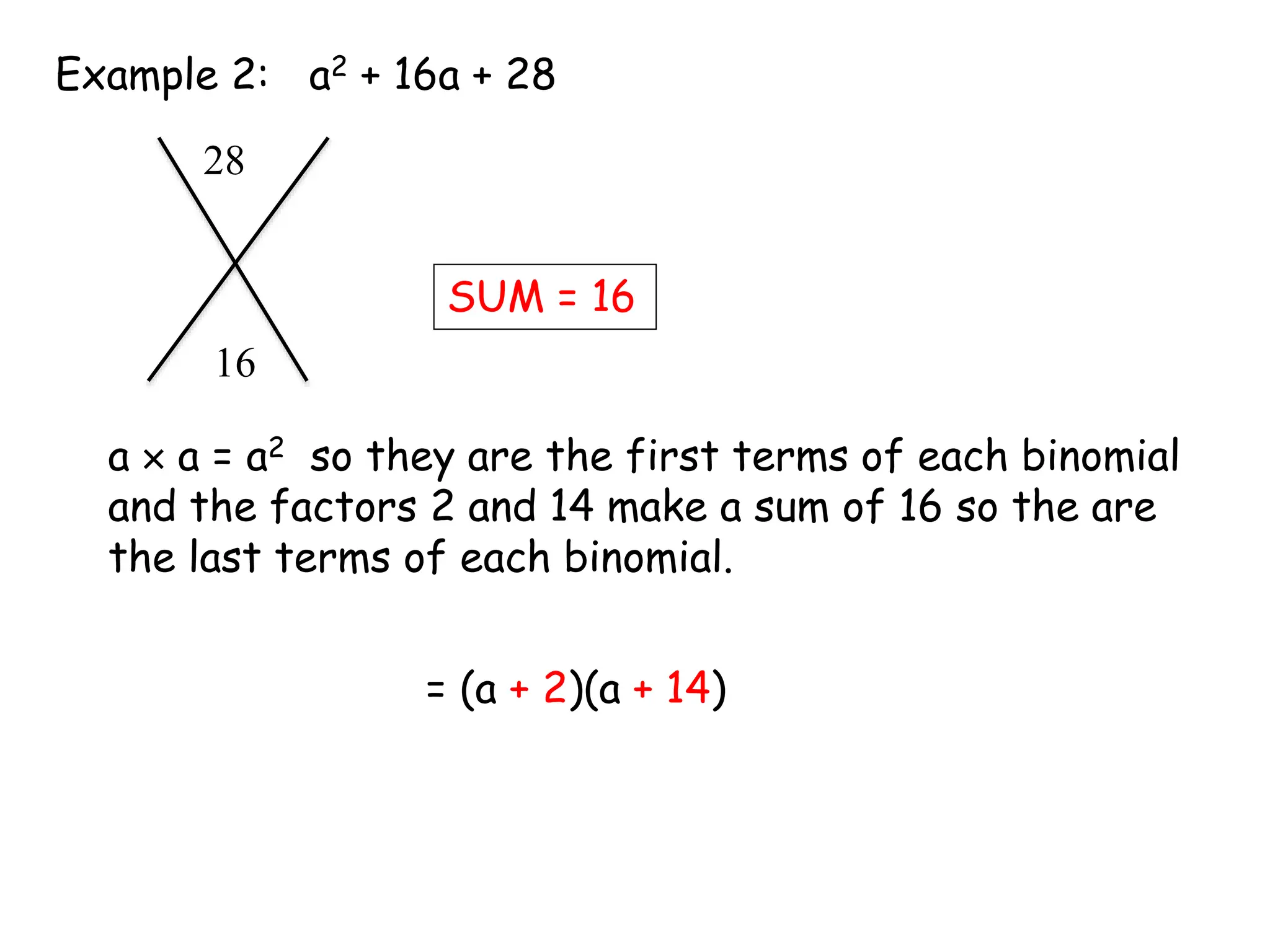
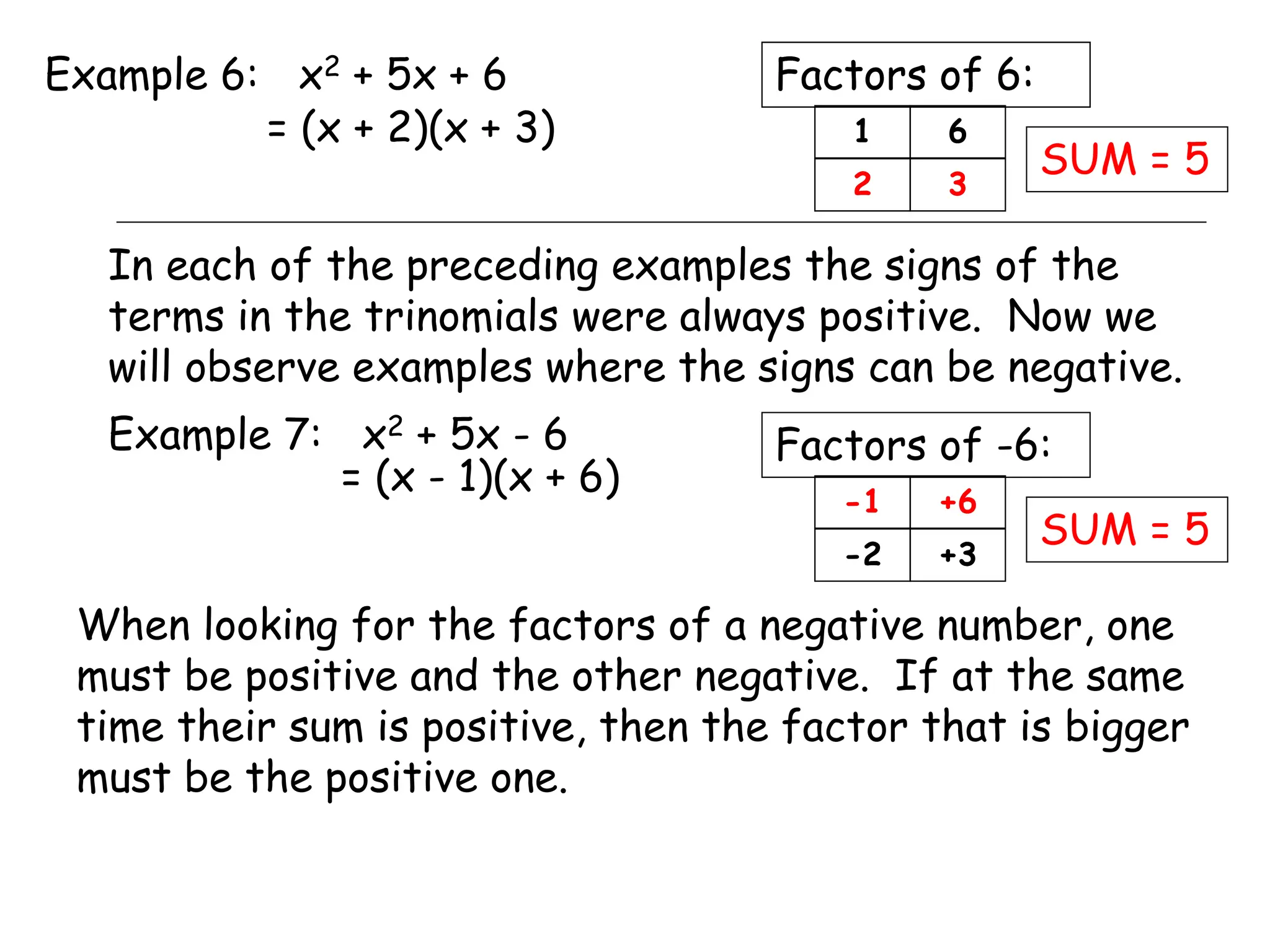
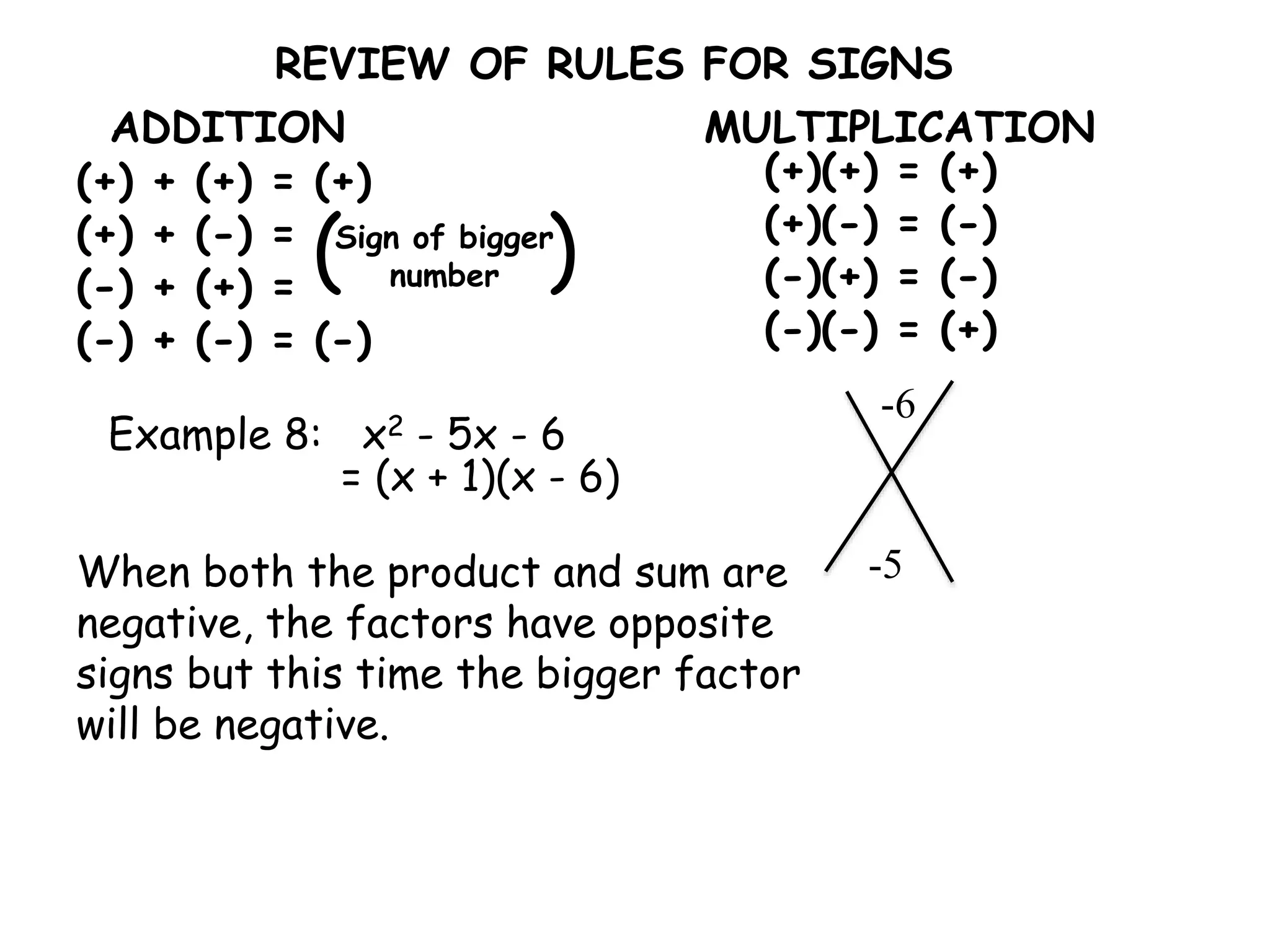
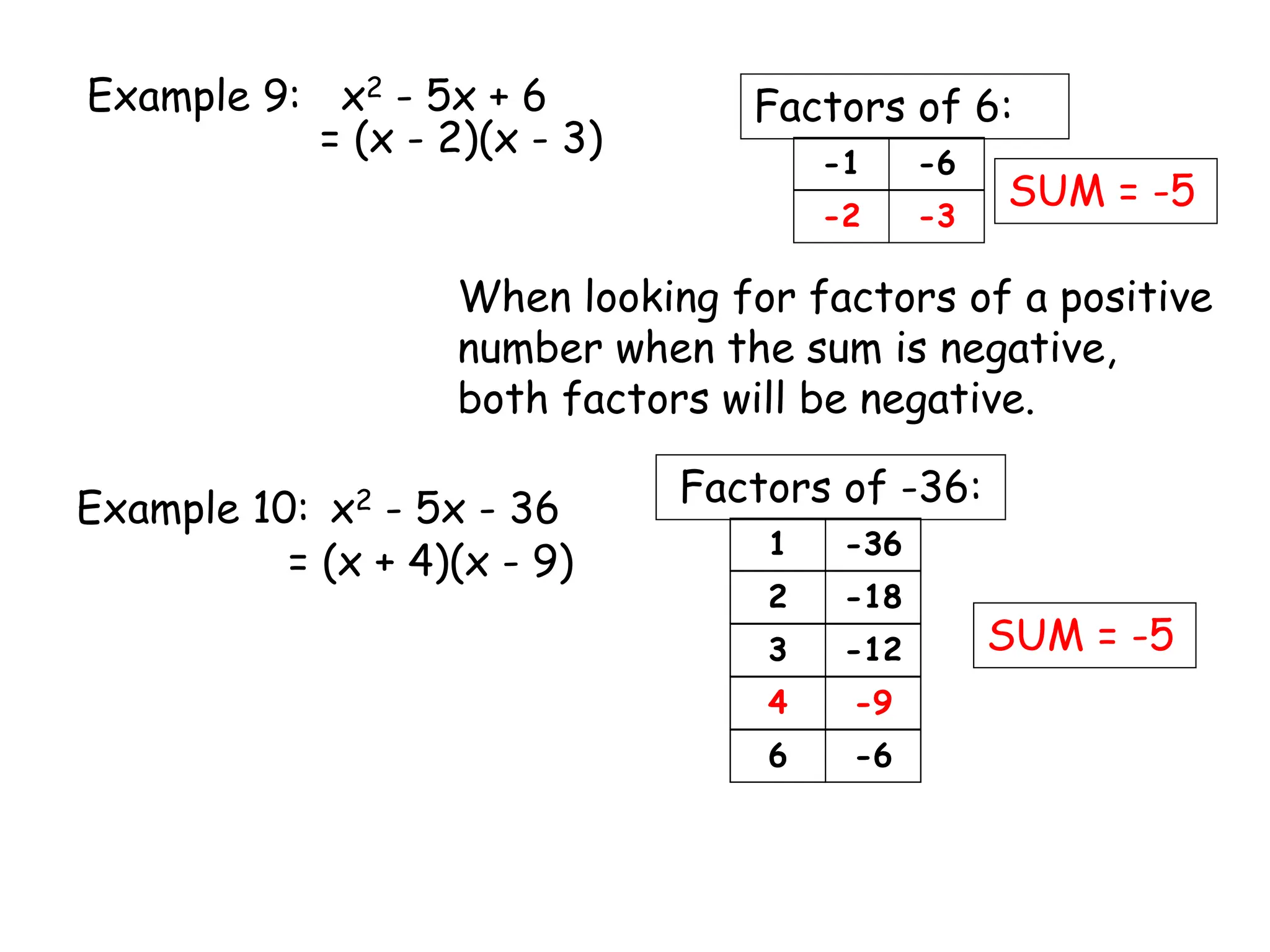
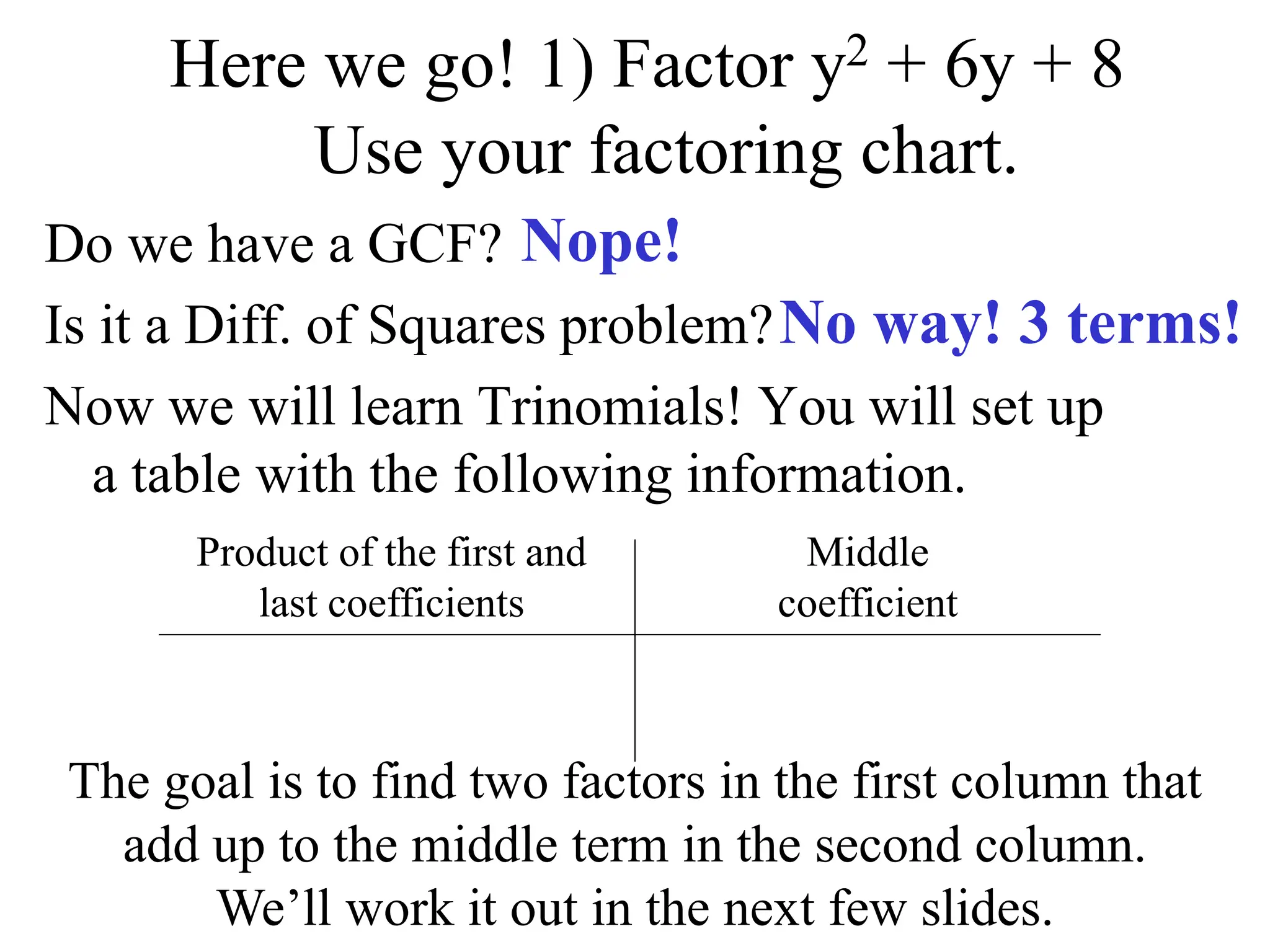
This document provides examples and instructions for factoring trinomials of the form ax2 + bx + c. It explains that the factors of c must have a sum of b and a product of ac. Several examples are worked through step-by-step to show how to set up a "MAMA table" to find the appropriate factors and then group the terms of the trinomial accordingly. The document also discusses how the signs of the factors change depending on the signs of b and c. Rules for determining the signs in different cases are presented.





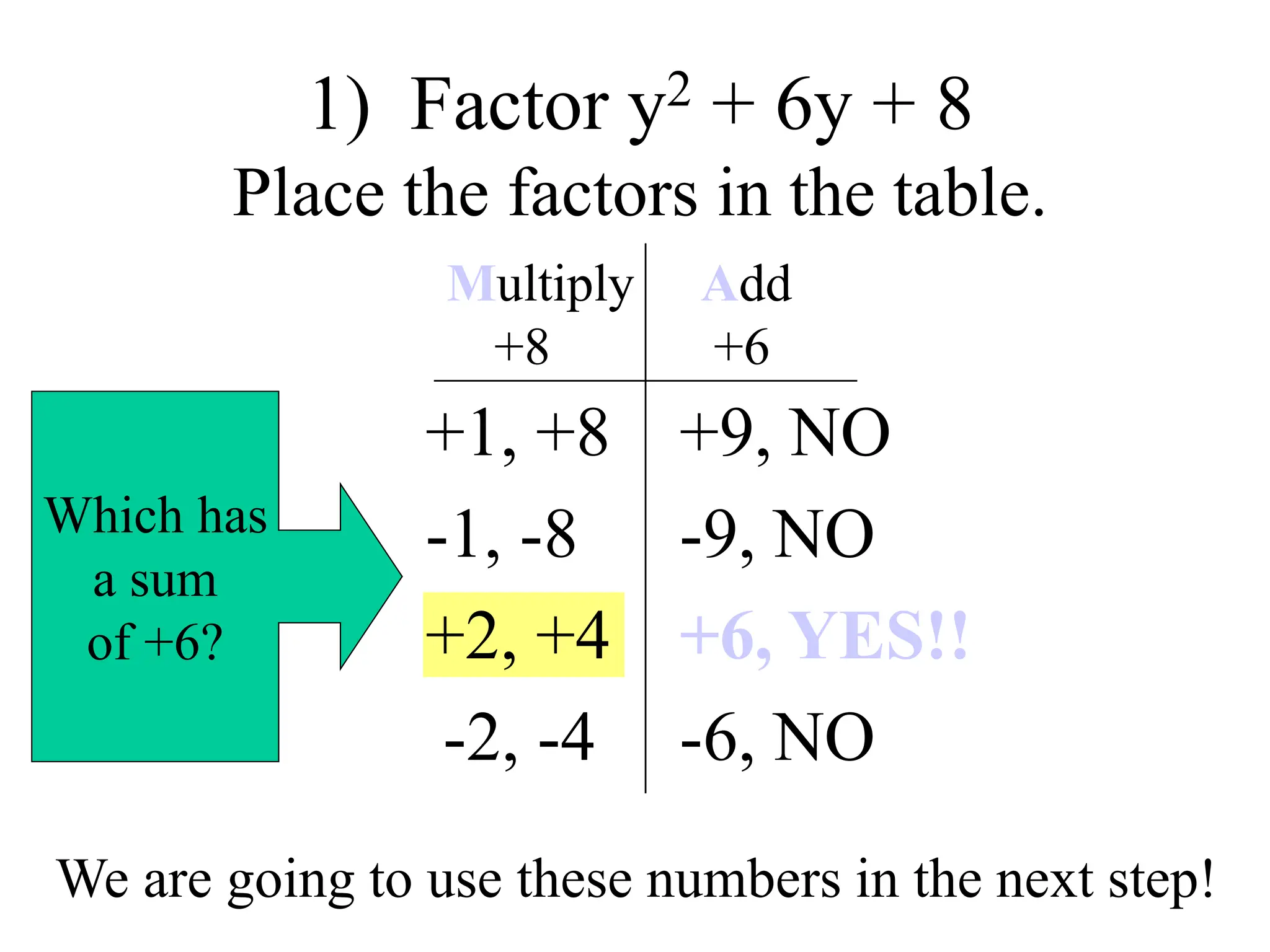





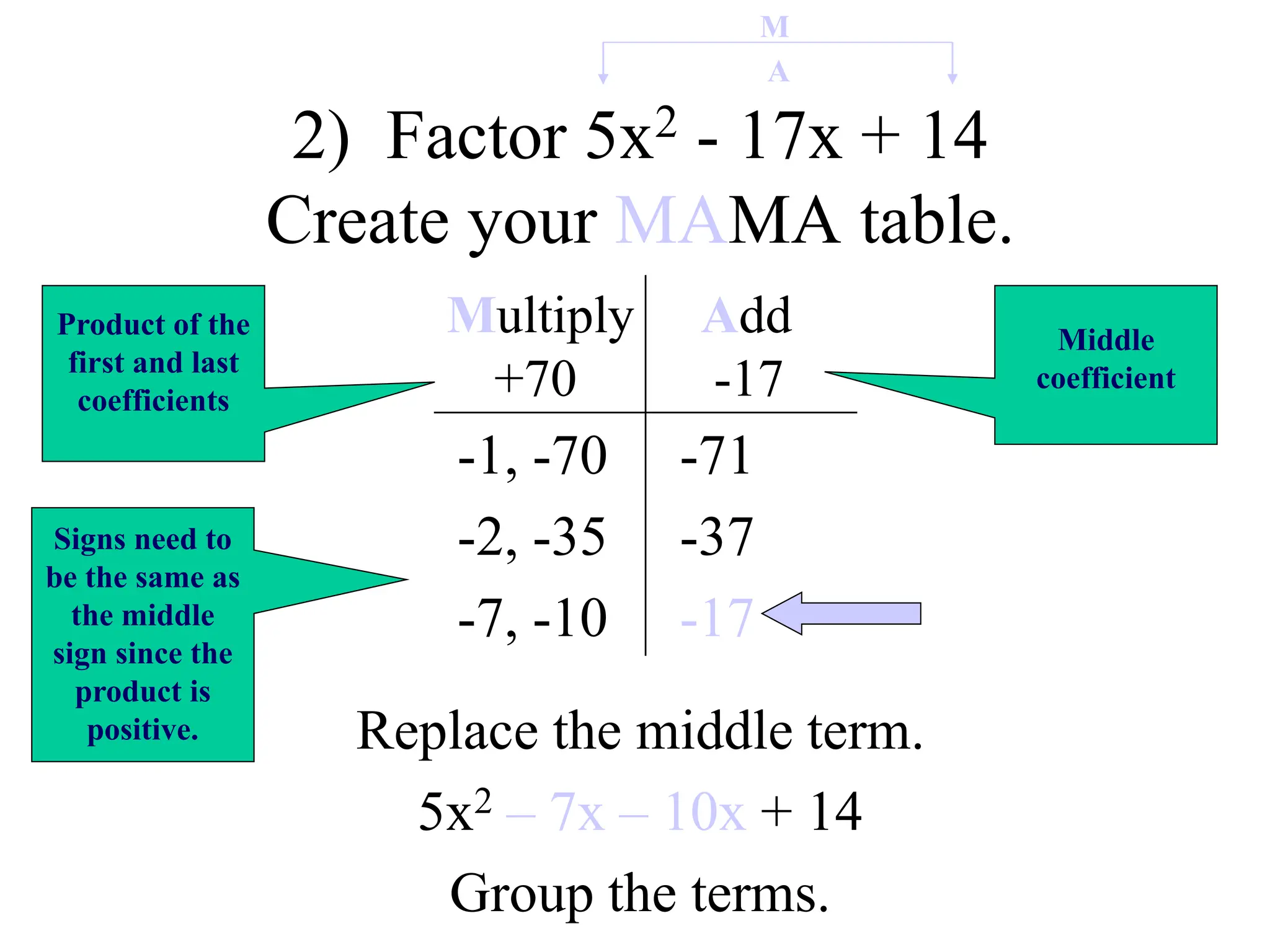



![2) Factor 2x2 - 14x + 12
Multiply Add
+6 -7
Find the GCF!
2(x2 – 7x + 6)
Now do the MAMA table!
-7
-5
Signs need to
be the same as
the middle
sign since the
product is
positive.
Replace the middle term.
2[x2 – x – 6x + 6]
Group the terms.
-1, -6
-2, -3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/factoringtrinomials-240204145800-9f119813/75/factoring-trinomials-ppt-24-2048.jpg)
![2[(x2 – x)(– 6x + 6)]
Factor out the GCF
2[x(x – 1) -6(x – 1)]
The parentheses are the same! Weeedoggie!
2(x – 6)(x – 1)
Don’t forget to follow your factoring chart when
doing these problems. Always look for a GCF
first!!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/factoringtrinomials-240204145800-9f119813/75/factoring-trinomials-ppt-25-2048.jpg)