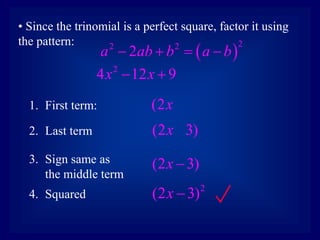
The document discusses factoring perfect square trinomials. A perfect square trinomial is a trinomial that is the result of squaring a binomial. To factor a perfect square trinomial, both the first and last terms must be perfect squares and the middle term must be 2 times the product of the binomial terms. If these conditions are met, the trinomial can be factored by reversing the process of squaring the binomial. Several examples demonstrate how to determine if a trinomial is a perfect square trinomial and how to factor it if so.