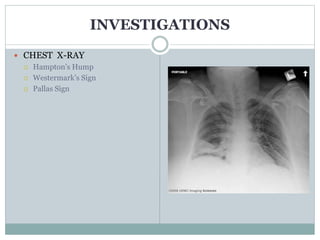
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a common and potentially fatal cardiovascular condition caused by blood clots in the lungs. The document discusses the classification, pathophysiology, risk factors, clinical features, diagnostic testing and management of PE. Key points include that PE has a 15% fatality rate if untreated, but mortality decreases to around 10% with anticoagulation therapy. Rapid risk stratification and treatment of high-risk PE cases with thrombolysis, surgery or other interventions is important for reducing mortality.