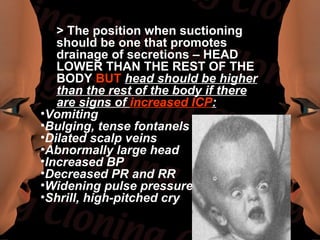
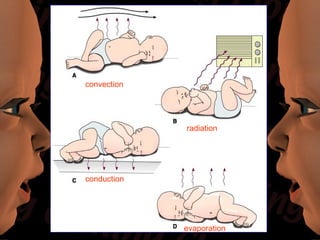
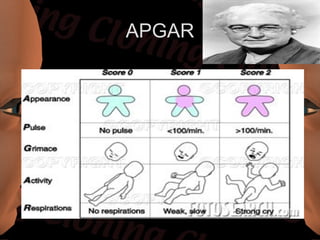
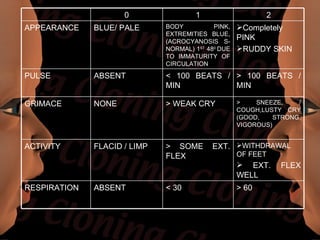
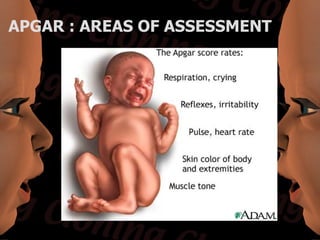
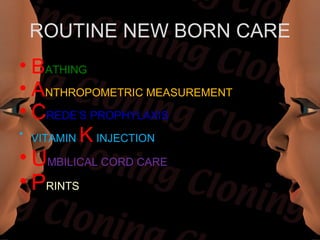
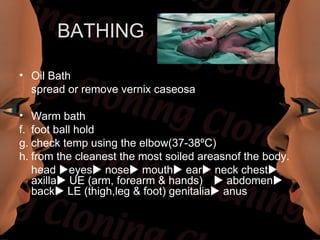
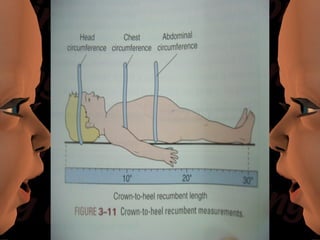
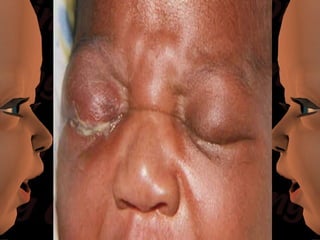
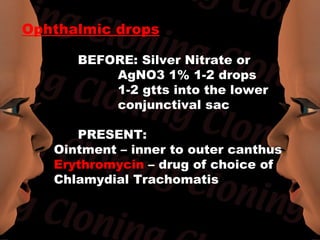
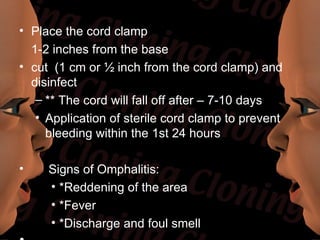
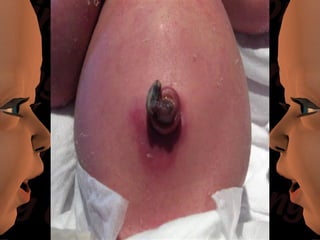
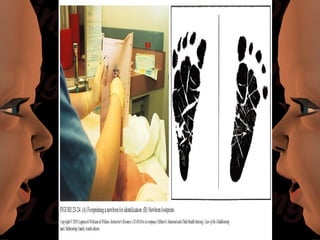
Newborn care involves immediate attention to the airway, temperature regulation, and Apgar scoring. Essential procedures include suctioning the mouth before nose, maintaining proper temperature, and assessing vital signs via Apgar. Routine care consists of bathing, measurements, Vitamin K injection, umbilical cord care, and identification/record keeping. The nurse focuses on meeting the newborn's physiologic and psychological needs while supporting healthy family bonding and education.