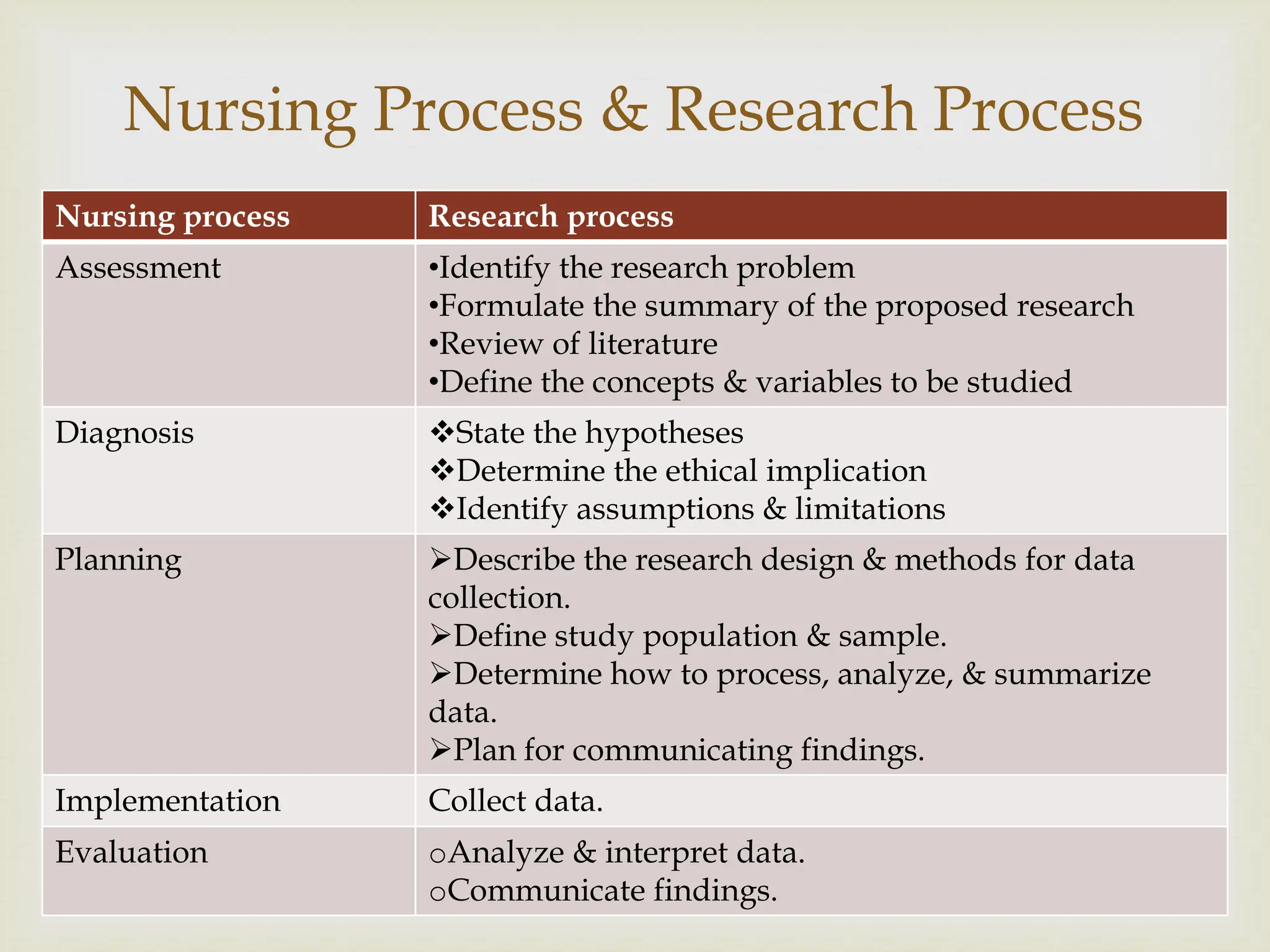
The document outlines the fundamentals of scientific research, emphasizing systematic inquiry to enhance knowledge through structured methods and empirical evidence. It distinguishes between quantitative and qualitative research approaches, as well as the differences between basic and applied research, each with its own methodologies and purposes. Additionally, it discusses the nursing research process and its significance in improving nursing practices and education.