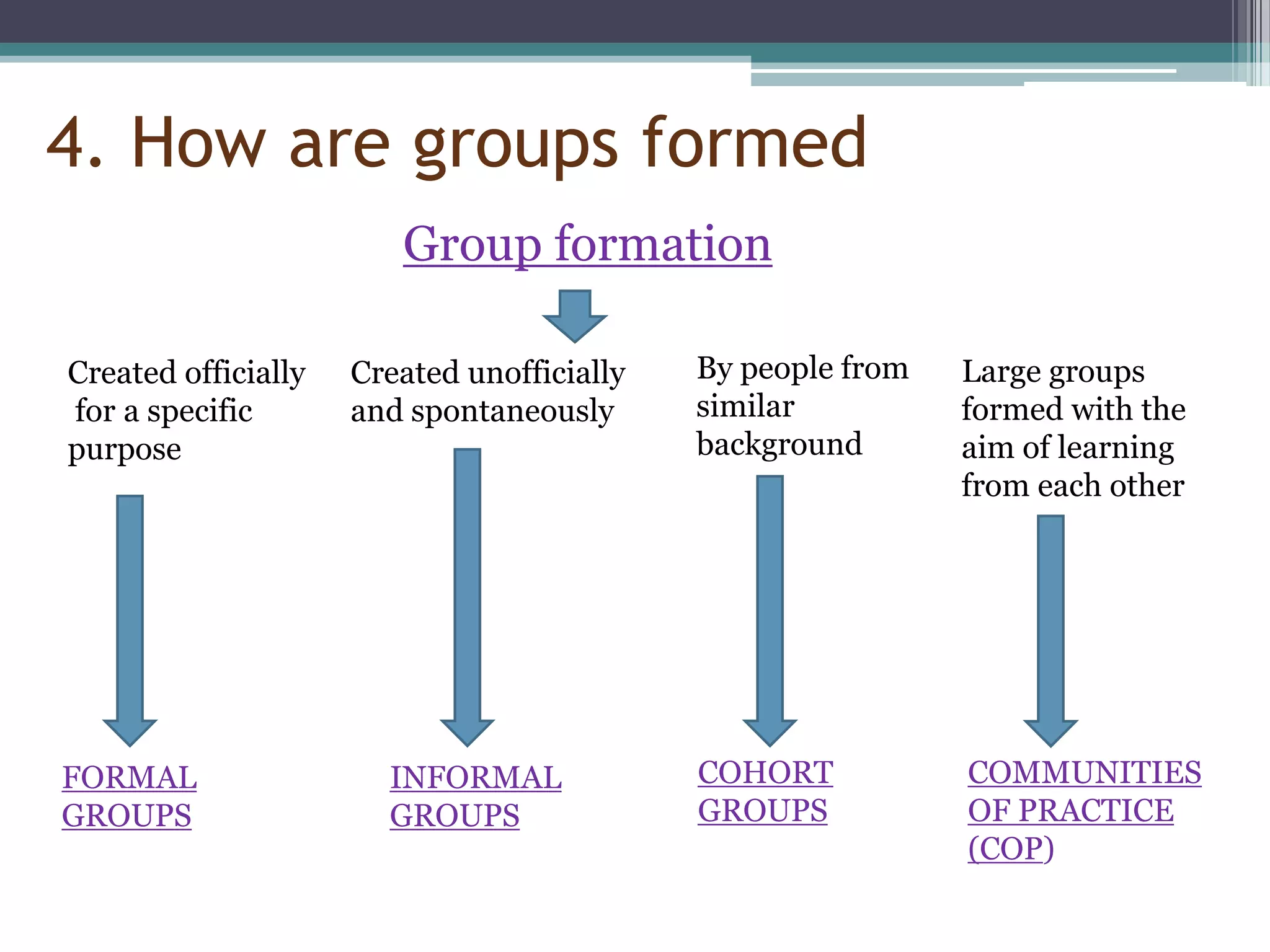
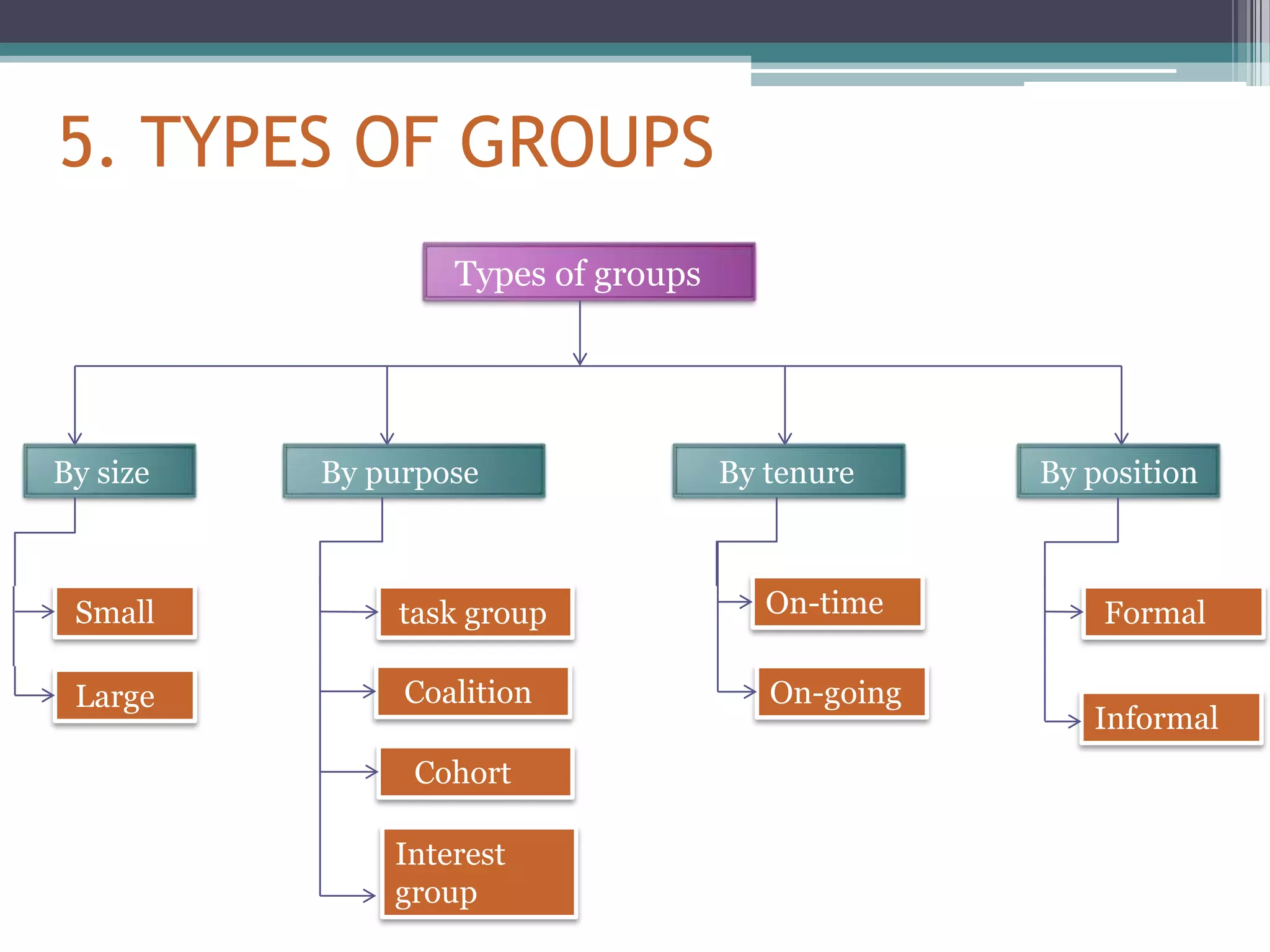
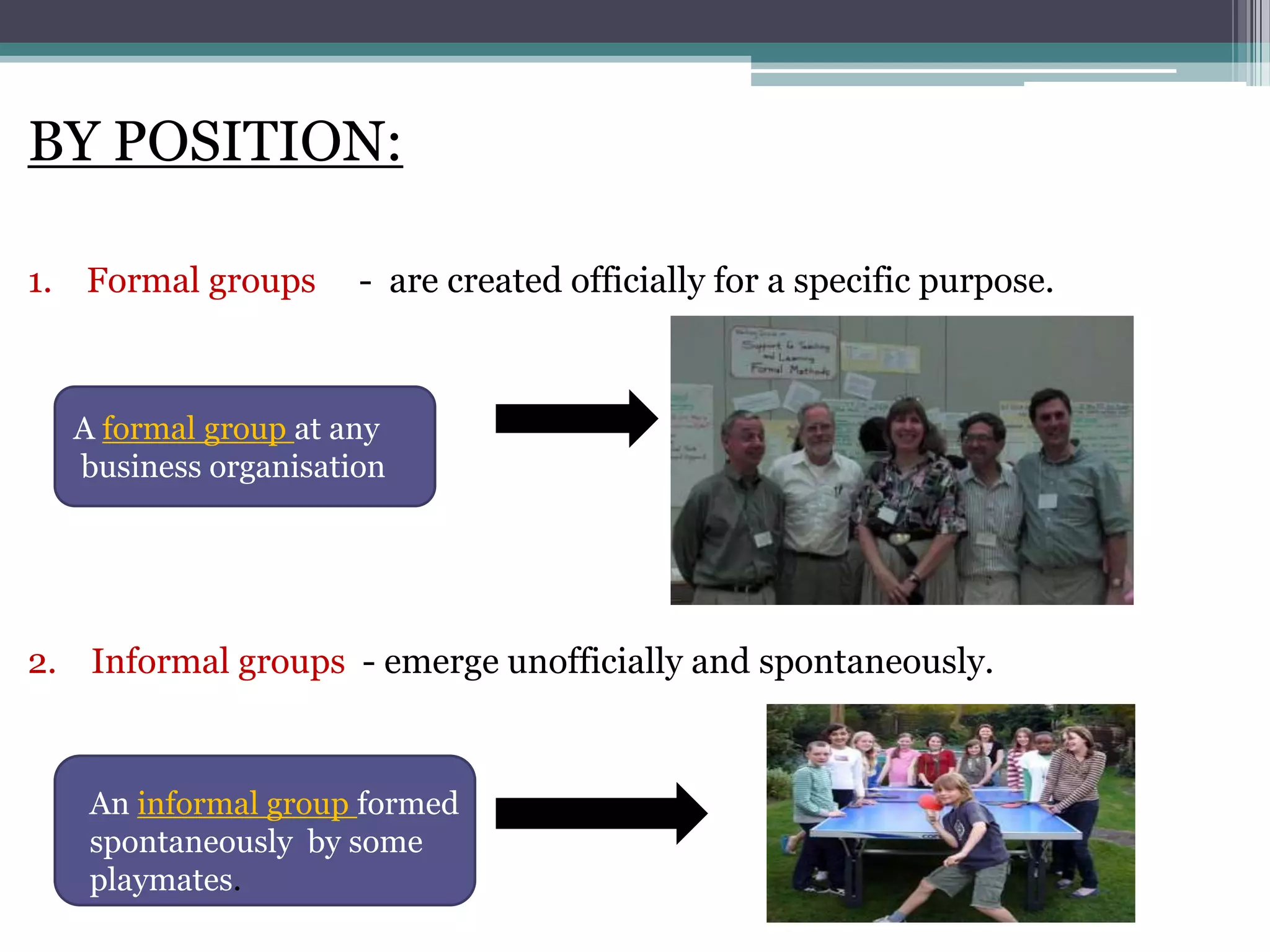
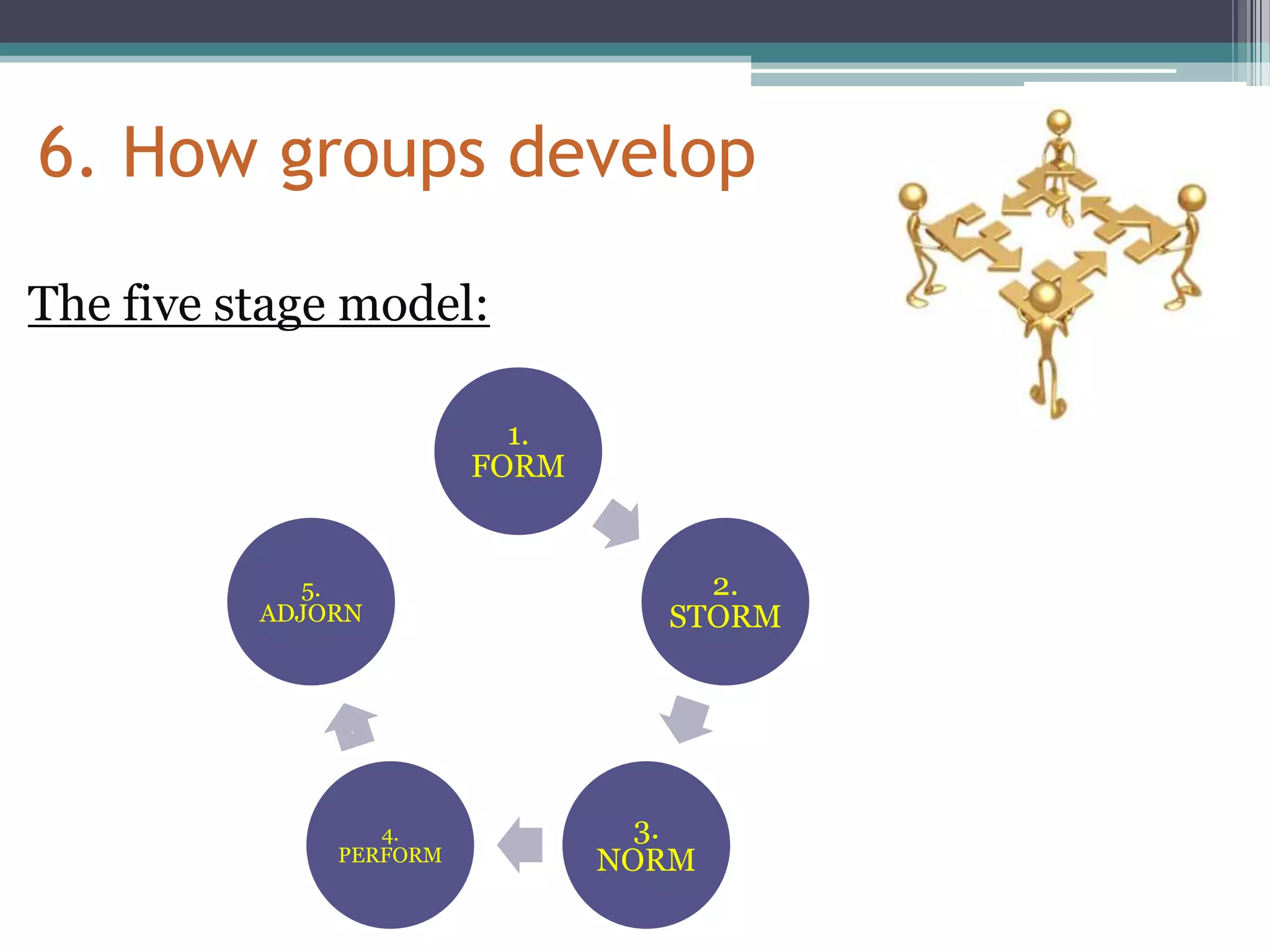
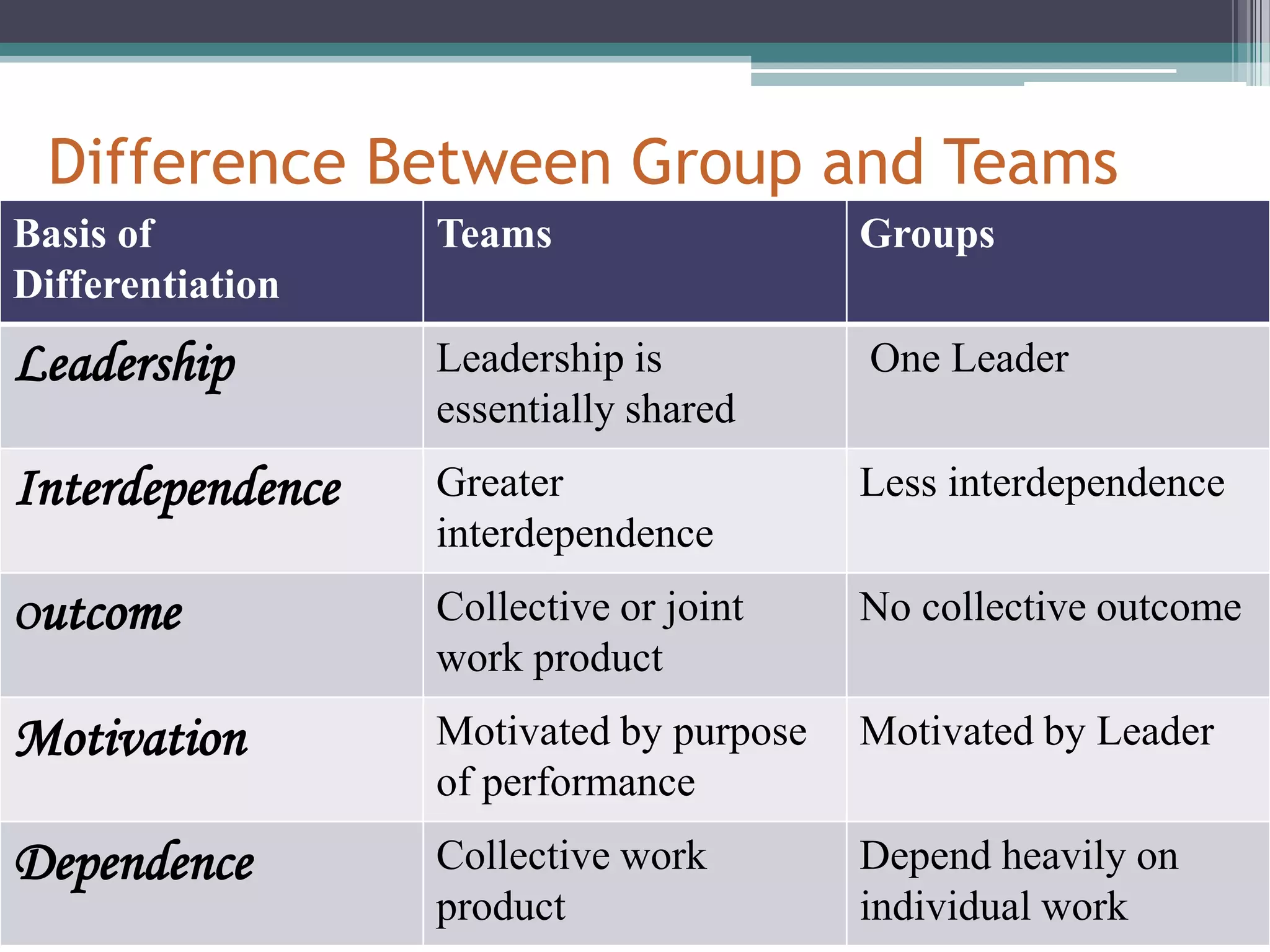
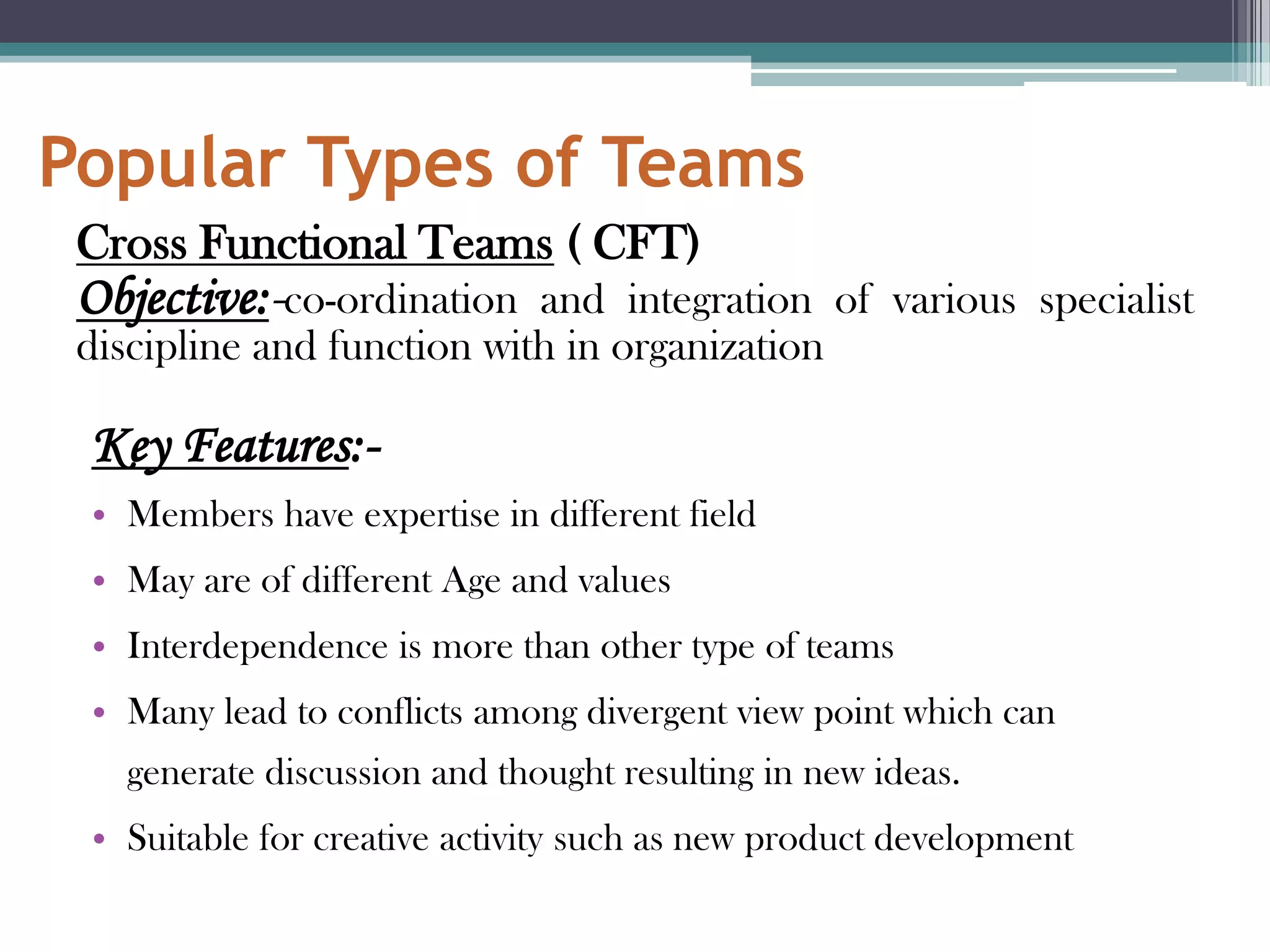
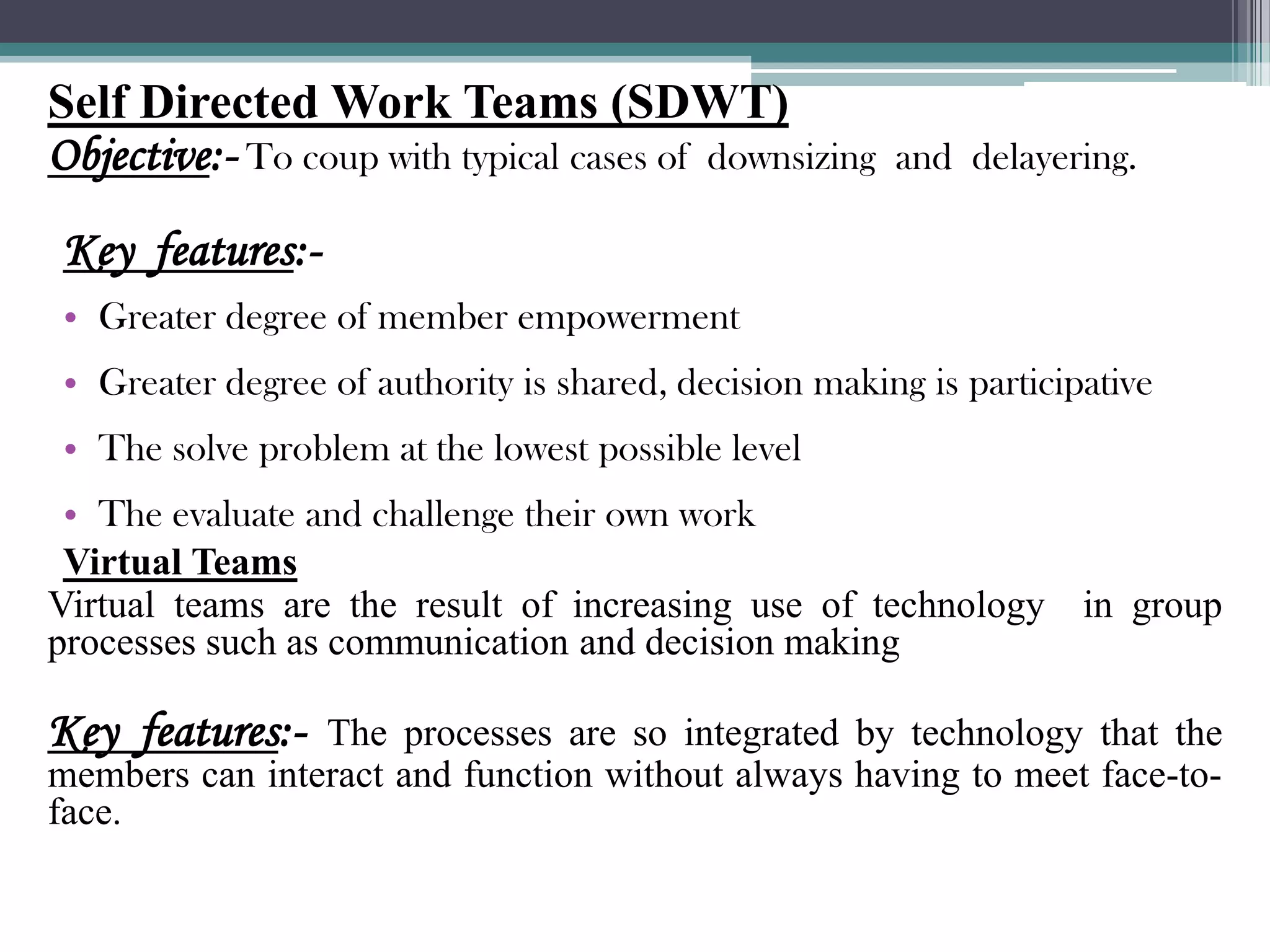
This document provides an overview of groups and teams. It discusses what groups and teams are, the importance of groups, how groups are formed, types of groups, and Tuckman's five stage model of group development. Specifically, it defines a group as people working together to achieve a common task, while defining a team as a small group working together to achieve a specific goal. It outlines various types of groups including formal vs informal, task groups, and cohorts. Lastly, it discusses Tuckman's five stages of group development - forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning.