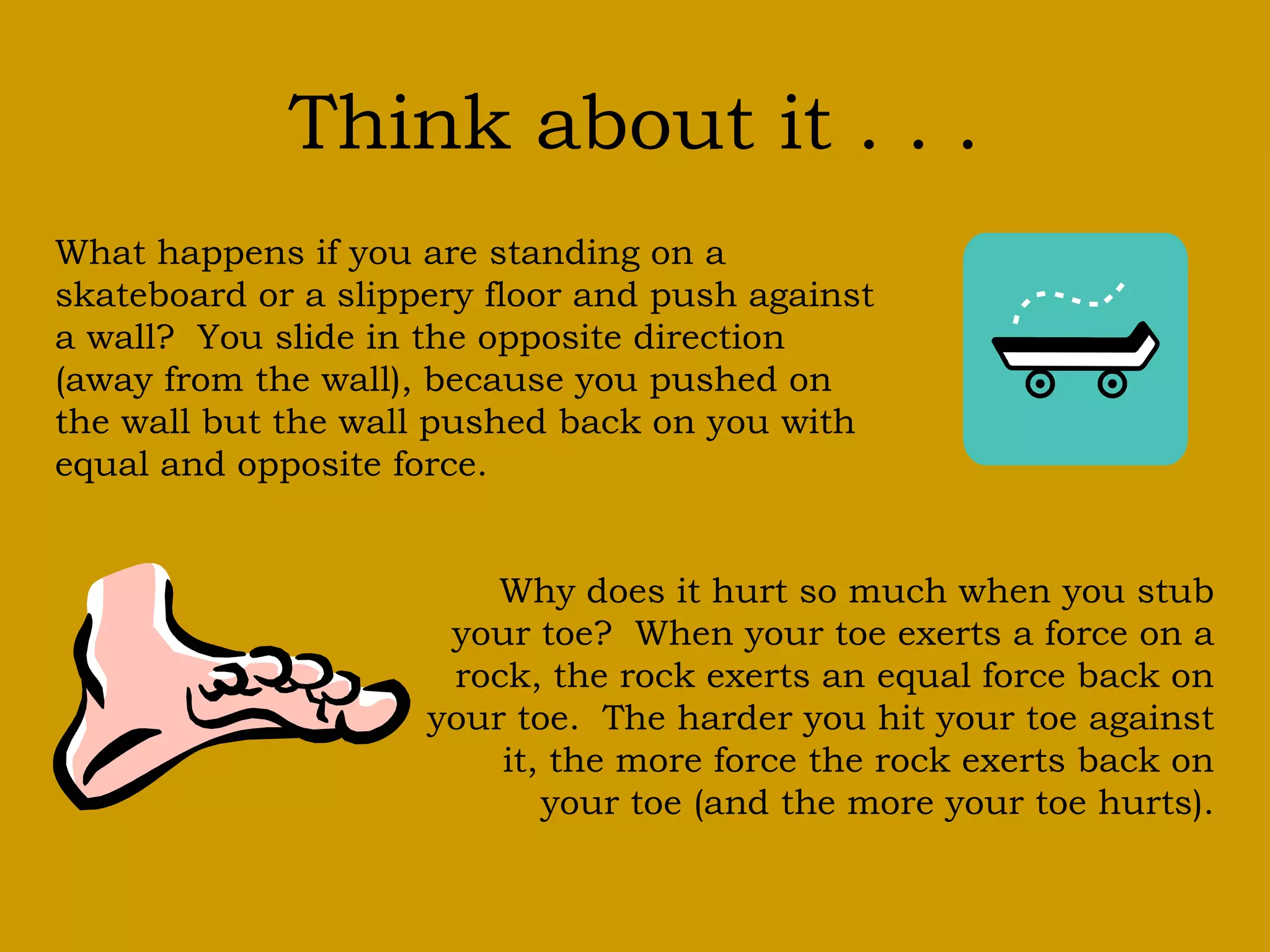
Sir Isaac Newton discovered three laws of motion that describe how objects move. The first law states that objects at rest will stay at rest and moving objects will keep moving unless acted on by an unbalanced force. The second law says that the force on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration. The third law explains that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.