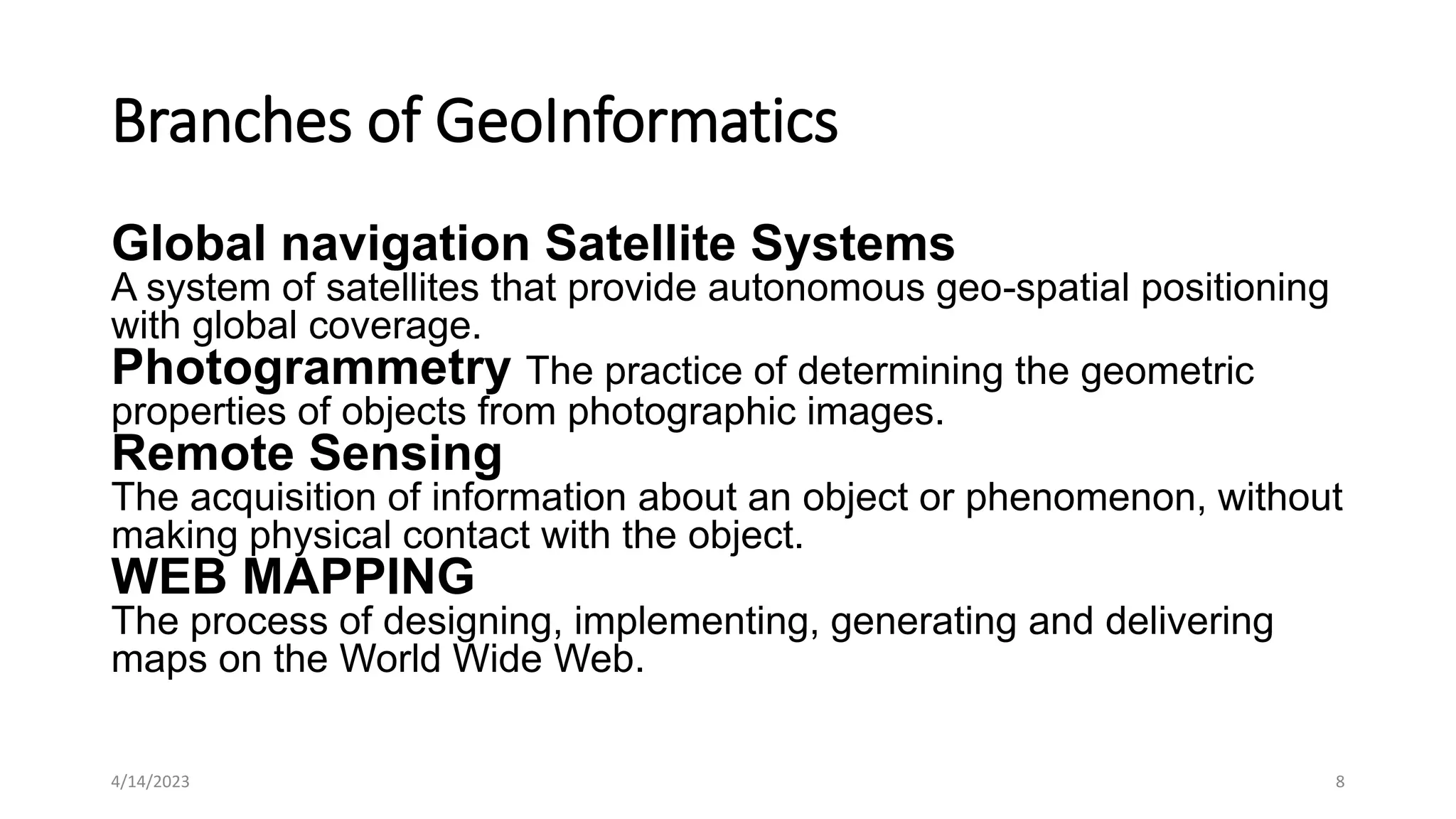
Geoinformatics is the science dealing with spatial information including its capture, classification, storage, processing, portrayal and dissemination. It uses tools and technology to acquire, analyze and visualize data about Earth's features from space. This geospatial information is used to solve problems in geography, geosciences and engineering. Geoinformatics includes remote sensing, mapping, modeling, database development and uses computation and visualization to analyze geoinformation.