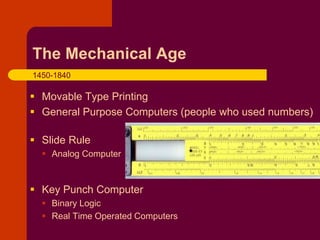
The document discusses the history of the Information Age from ancient times to the present. It divides this history into four periods: the Pre-Mechanical period from 3000 BC to 1450 AD, which saw the development of writing systems and early calculation tools; the Mechanical period from 1450-1840 that brought movable type printing and slide rules; the Electro-Mechanical period from 1840-1940 that introduced technologies like the telegraph, telephone, and early computers; and the modern Electronic/Information period from 1940 onward, where electronic computers were developed and advanced through generations using newer technologies like integrated circuits.