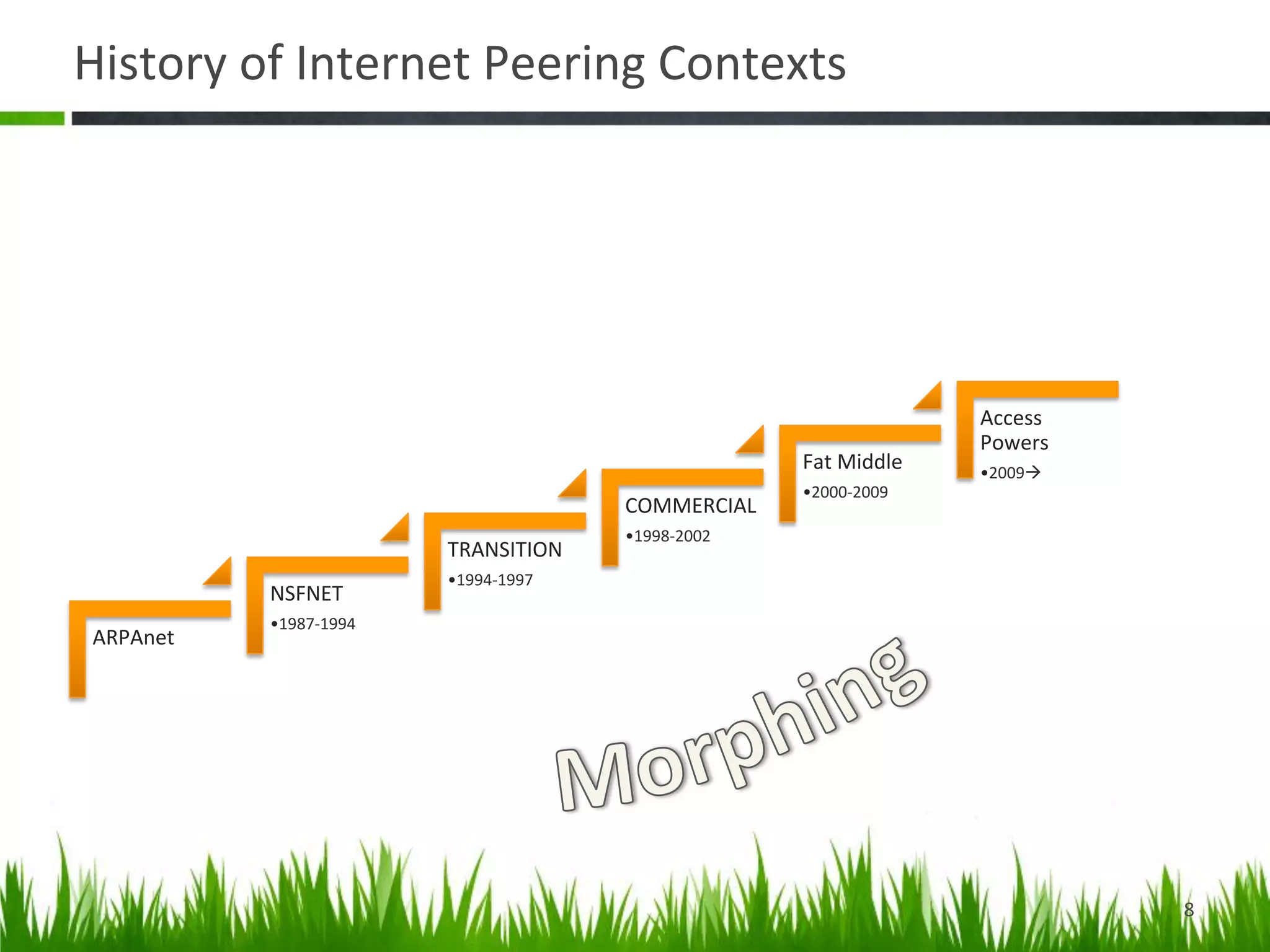
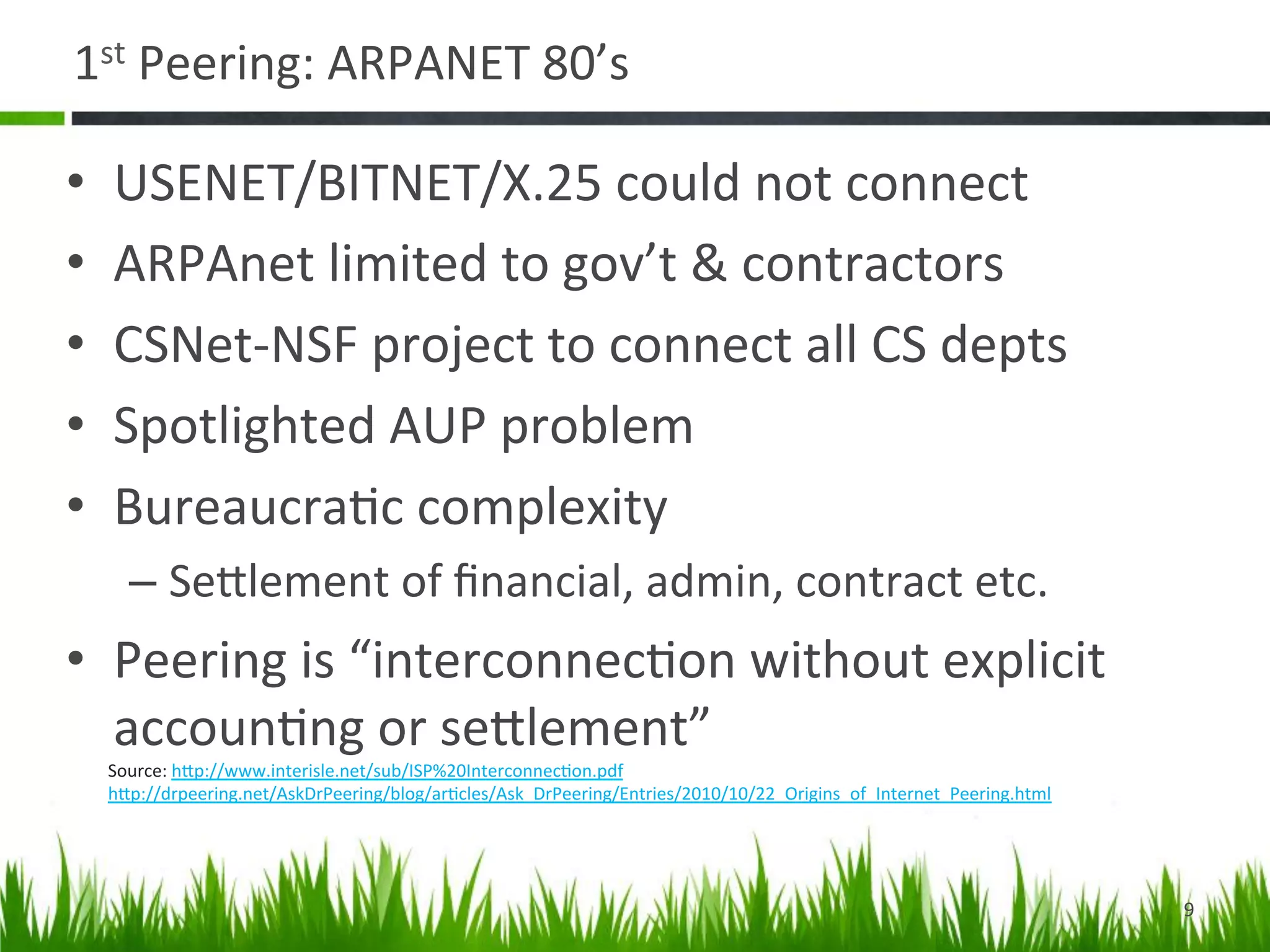
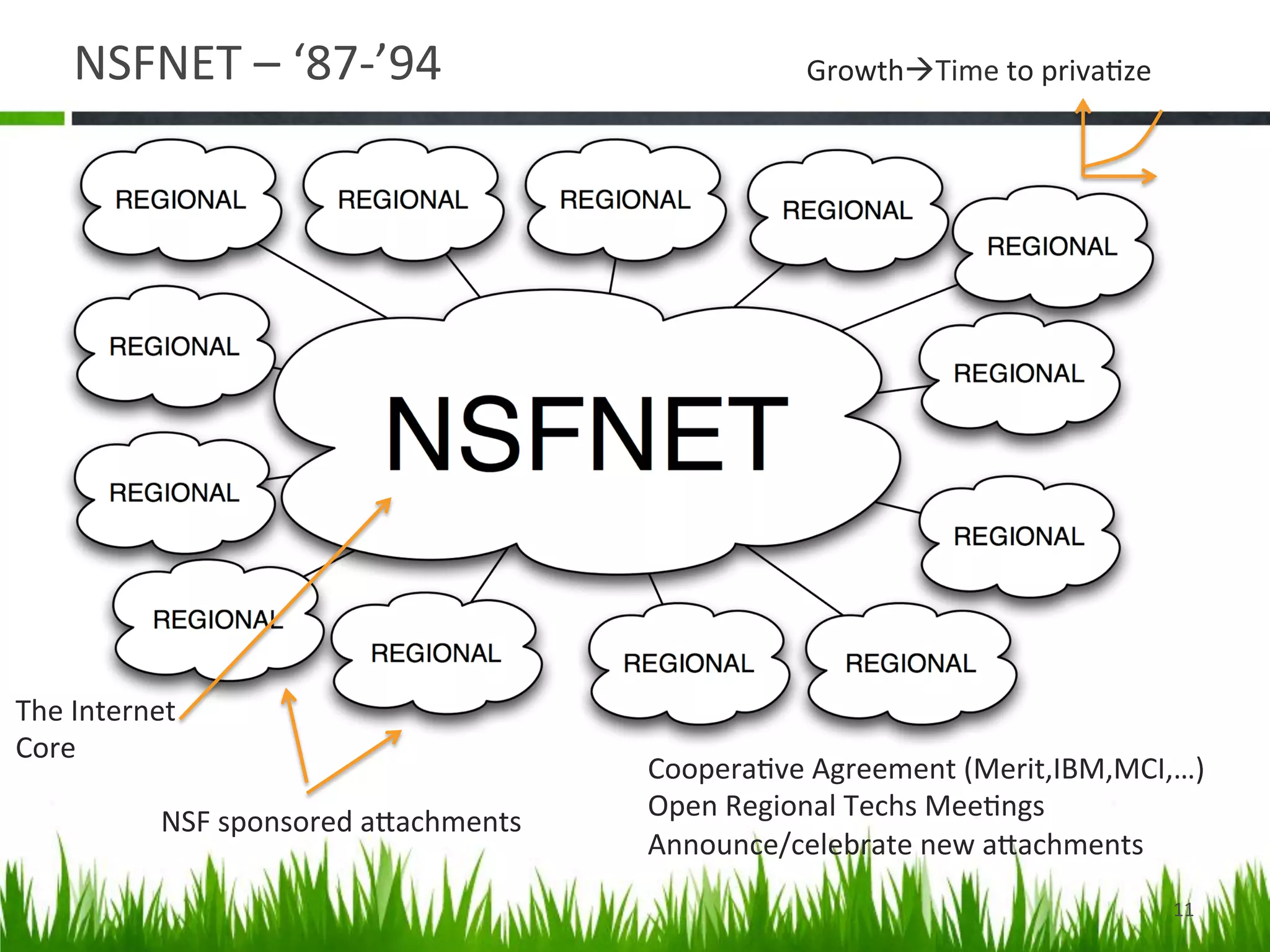
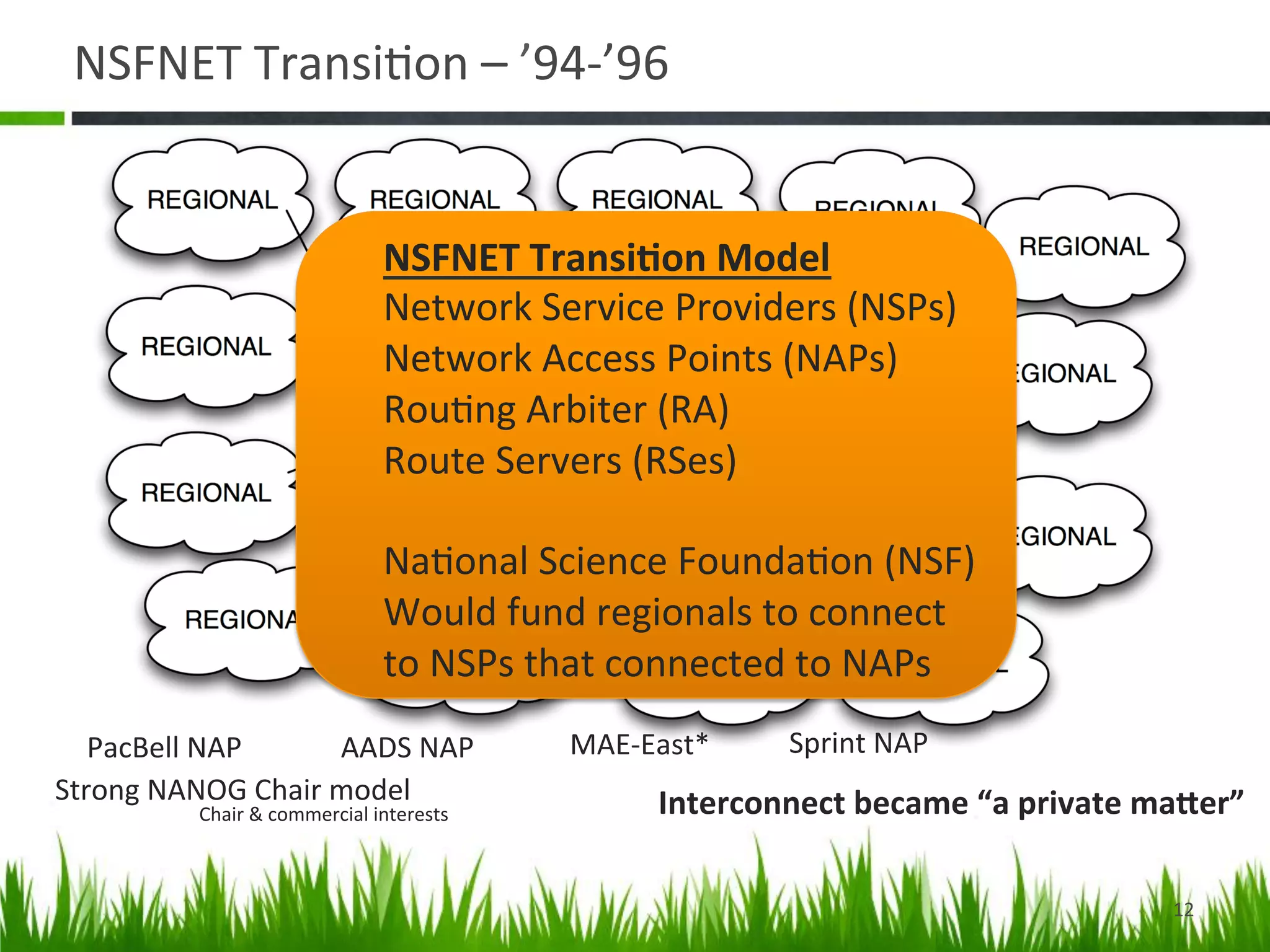
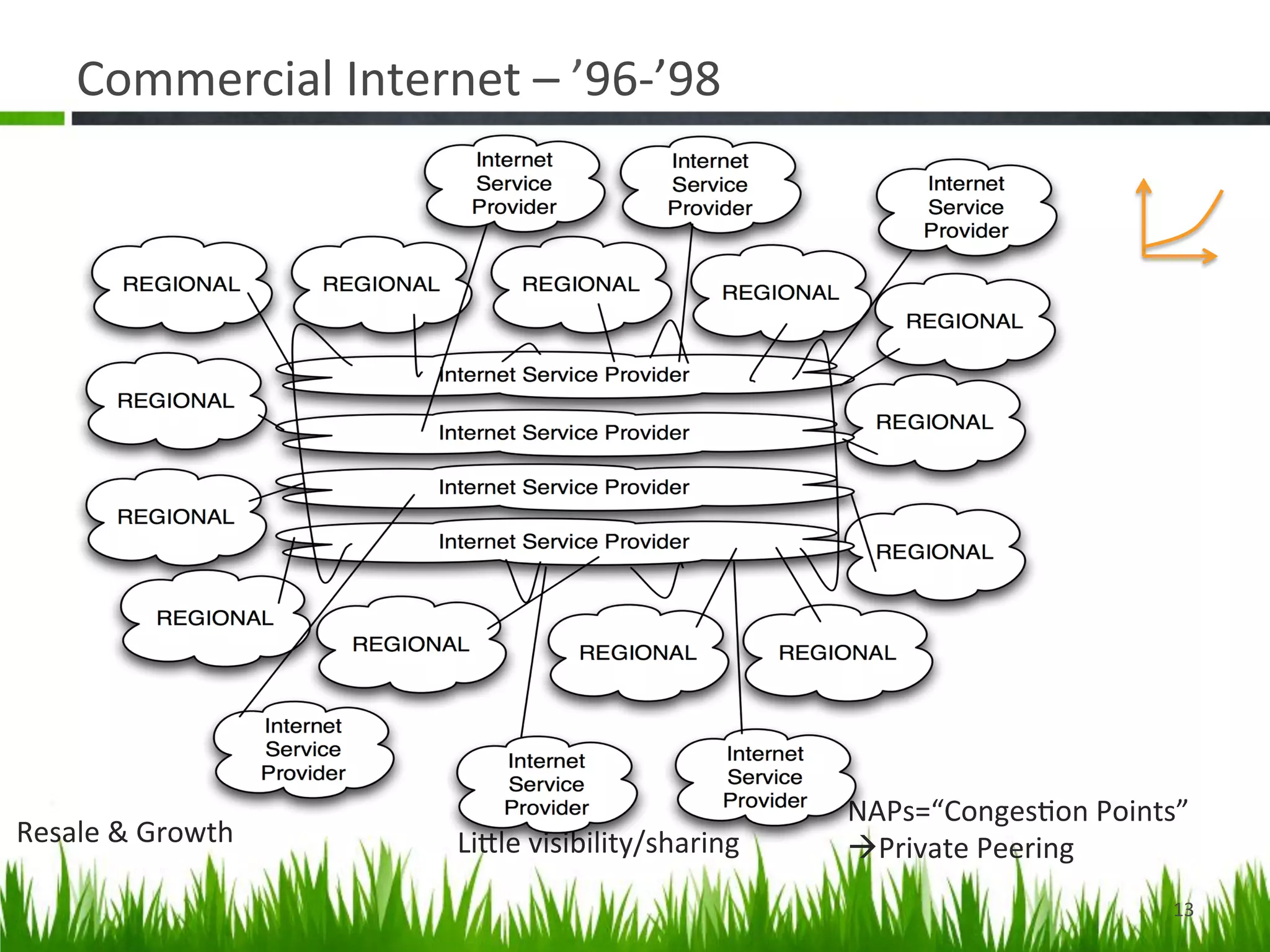
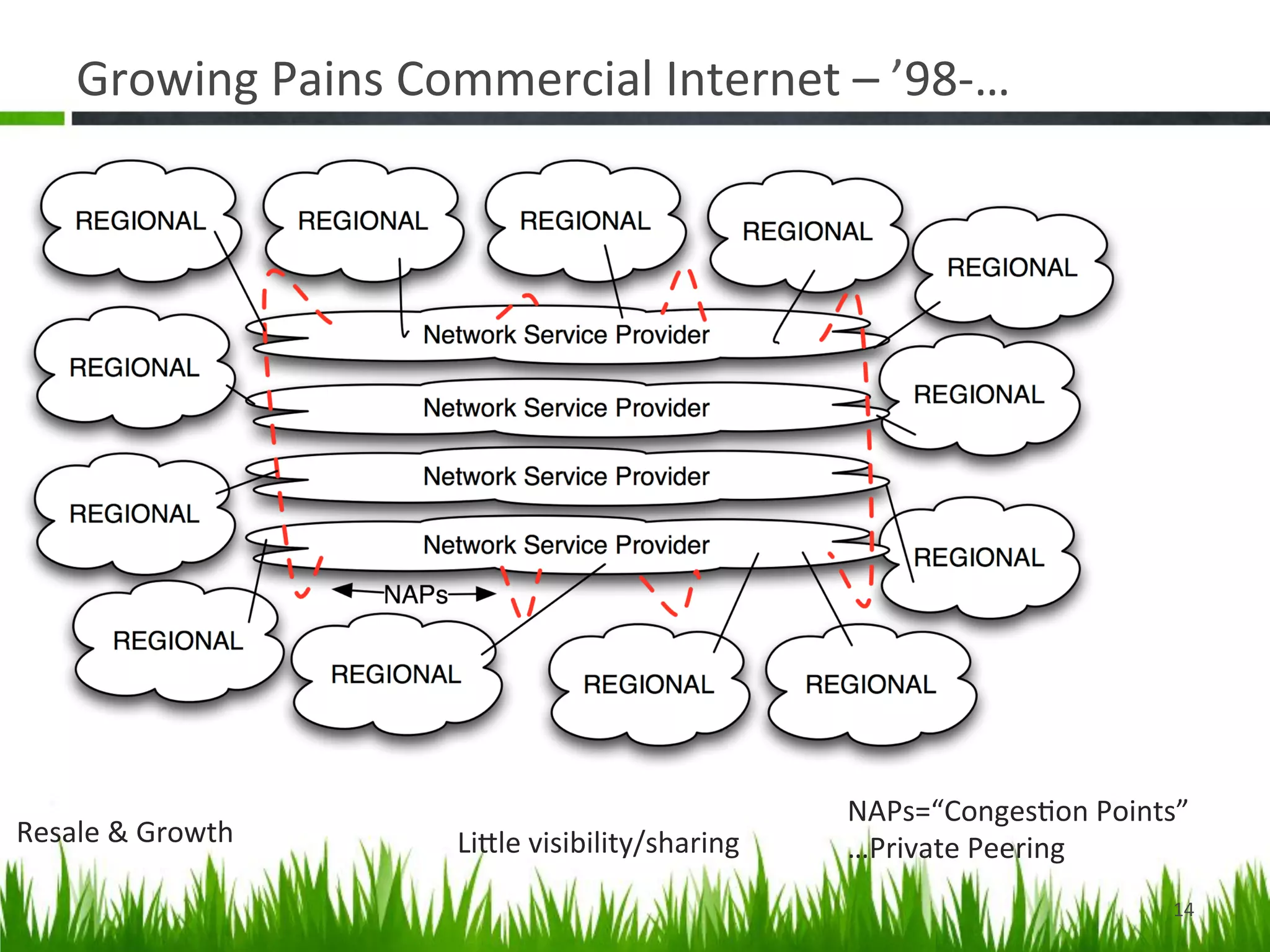
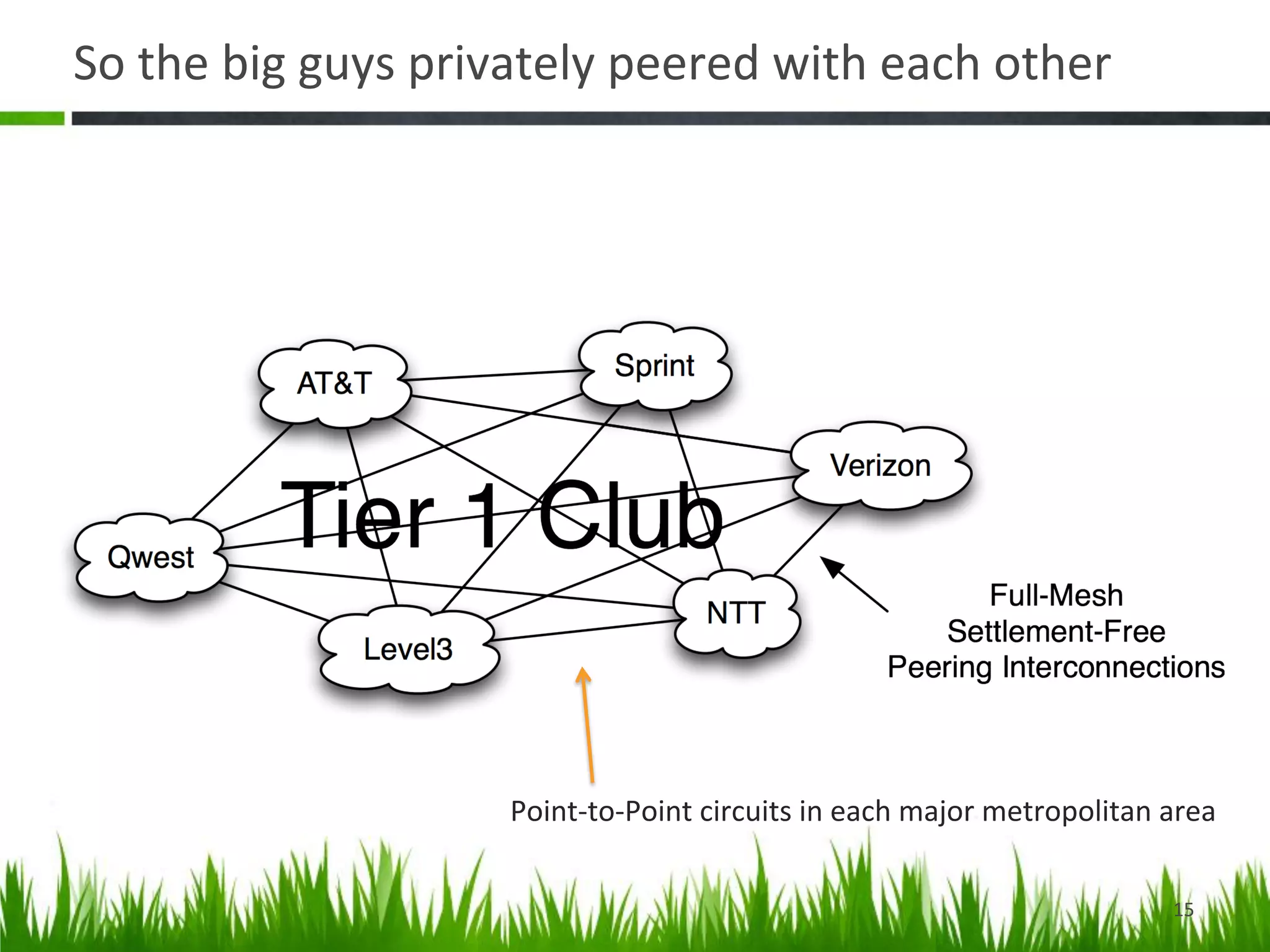
The document provides a historical perspective on the evolution of internet peering. It describes how peering began in the 1980s between ARPANET and other networks to connect organizations. It then discusses the NSFNET period from 1987-1994 when the National Science Foundation operated the backbone. In the 1994-1996 transition period, peering moved to Network Access Points but these became congested. By the late 1990s, large ISPs moved to private peering arrangements via direct connections due to these issues. This led to the current global internet peering ecosystem with no central coordination.