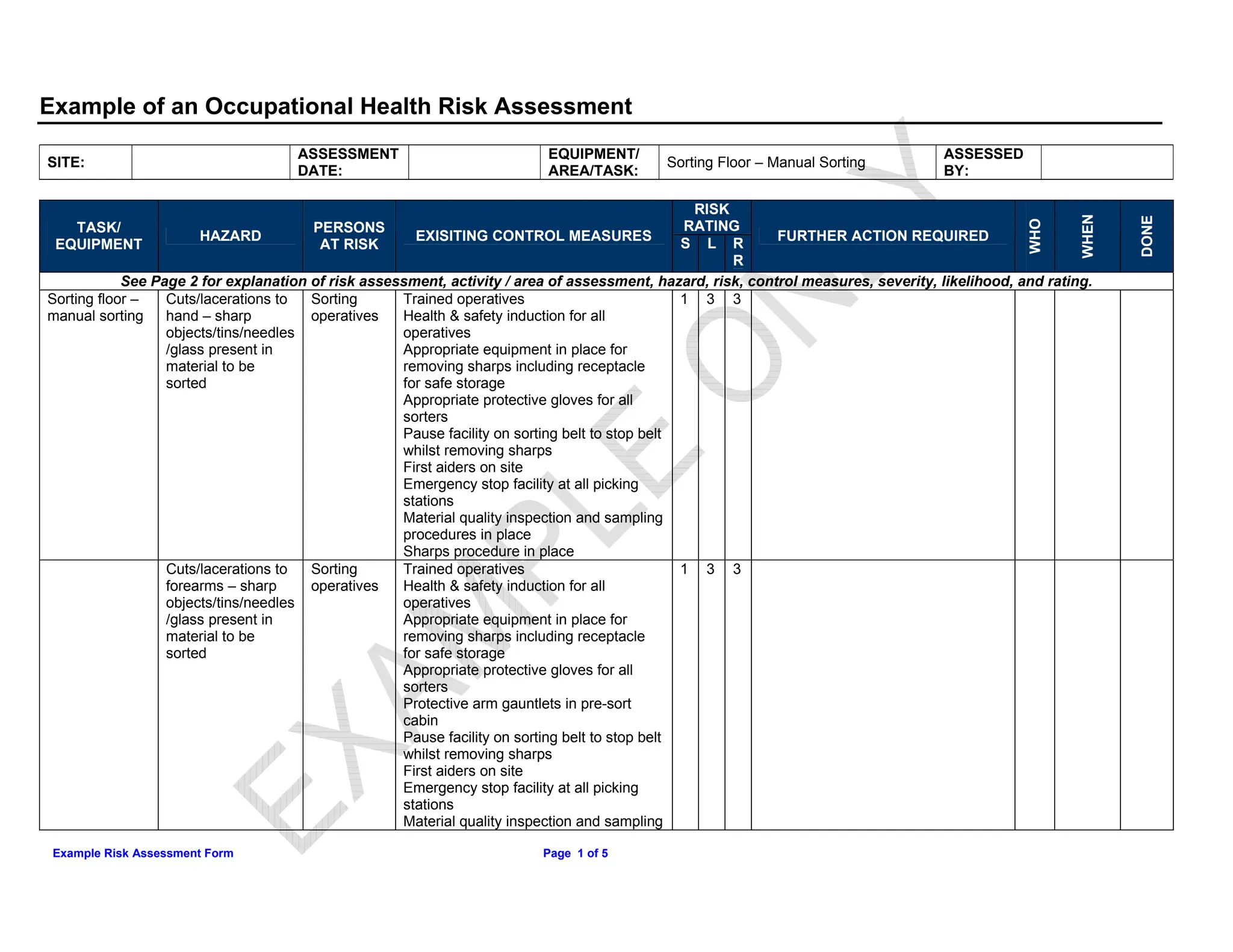
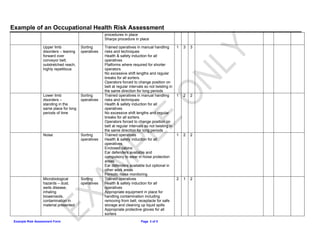
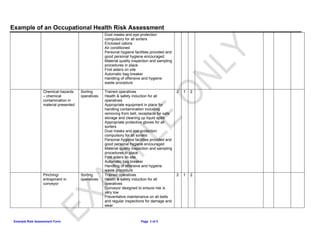
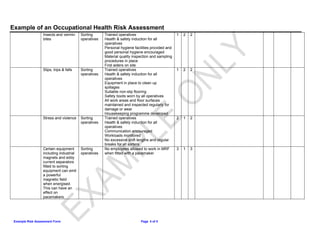
This document summarizes an occupational health risk assessment for a manual sorting floor. It identifies several potential hazards for sorting operatives including cuts, upper limb disorders, noise exposure, and slips/trips. For each hazard, it lists existing control measures like training, personal protective equipment, safety procedures. It then rates the severity, likelihood, and overall risk of each hazard on a scale of 1-3. Hazards rated 3 or higher may require further action to reduce the risk.