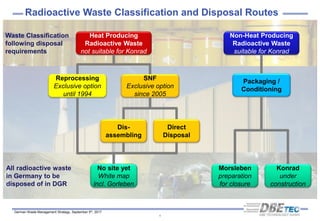
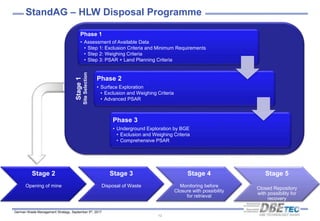
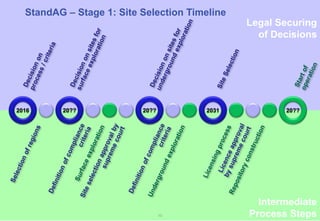
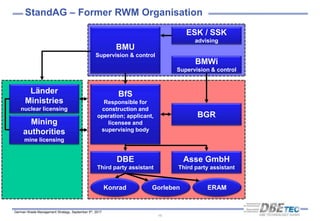
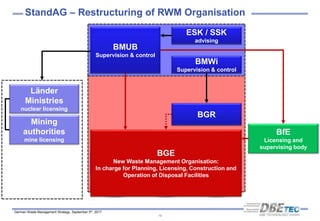
The document summarizes Germany's radioactive waste management strategy. It provides an overview of radioactive waste streams in Germany and discusses the political background. It describes the commissions and acts that guide the strategy, including the site selection process for a repository. It outlines the organizations involved, such as the Federal Office for the Safety of Nuclear Waste Management and the Federal Organization for Disposal, which were established to implement the strategy and oversee site selection.











![German Waste Management Strategy, September 5th, 2017
Regional
Conferences
Regional
Conferences
Regional
Conferences
Regional
Conferences
Regional
Conferences
StandAG – Involved Bodies in Site Selection
Federal Assembly
Federal Diet
Federal
Government
BMUB
BfE
Federal Office for the Safety
of Nuclear Waste Management
Representative
for Participation
Scientific
Advisory Board
BGE
(Federal WMO)
General Public
Local Affected
Public
Regional
Conferences
Symposia
‘Subregions‘ and
‘Council of Regions‘
National
Accompanying
Body
Societal Support
for Site Selection
Technical Support
for Site Selection
17
[Disposal Commission]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04vonberlepsch520170905tvbwmo-status-germany-170915181220/85/04-German-Waste-Management-Strategy-17-320.jpg)


