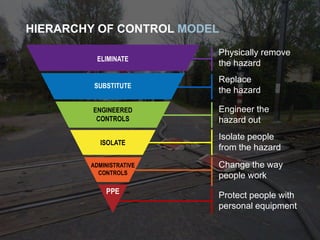
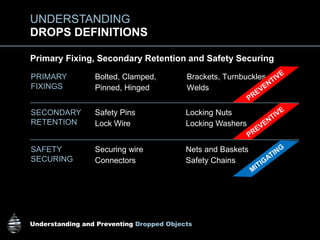
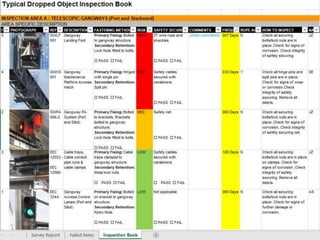
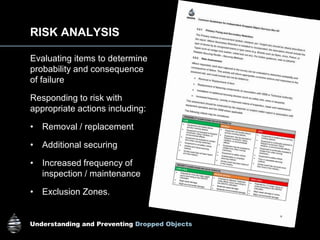
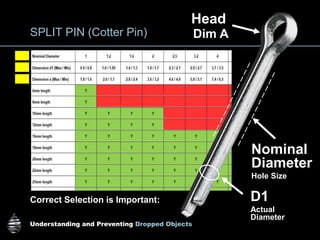
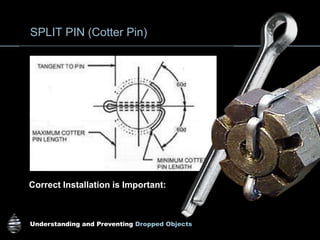
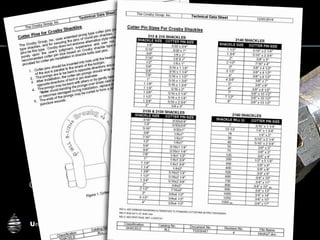
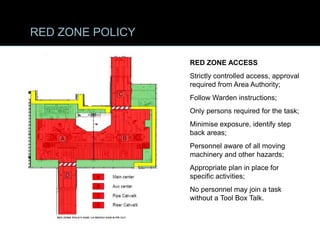
The document provides comprehensive guidelines on understanding, preventing, and controlling dropped objects in various operational environments. It outlines risk assessment strategies, inspection protocols, and preventive measures, including securing methods and training processes, to mitigate the hazards associated with dropped objects. Key emphasis is placed on the hierarchy of control, safety securing practices, and the importance of continuous awareness and training among personnel.