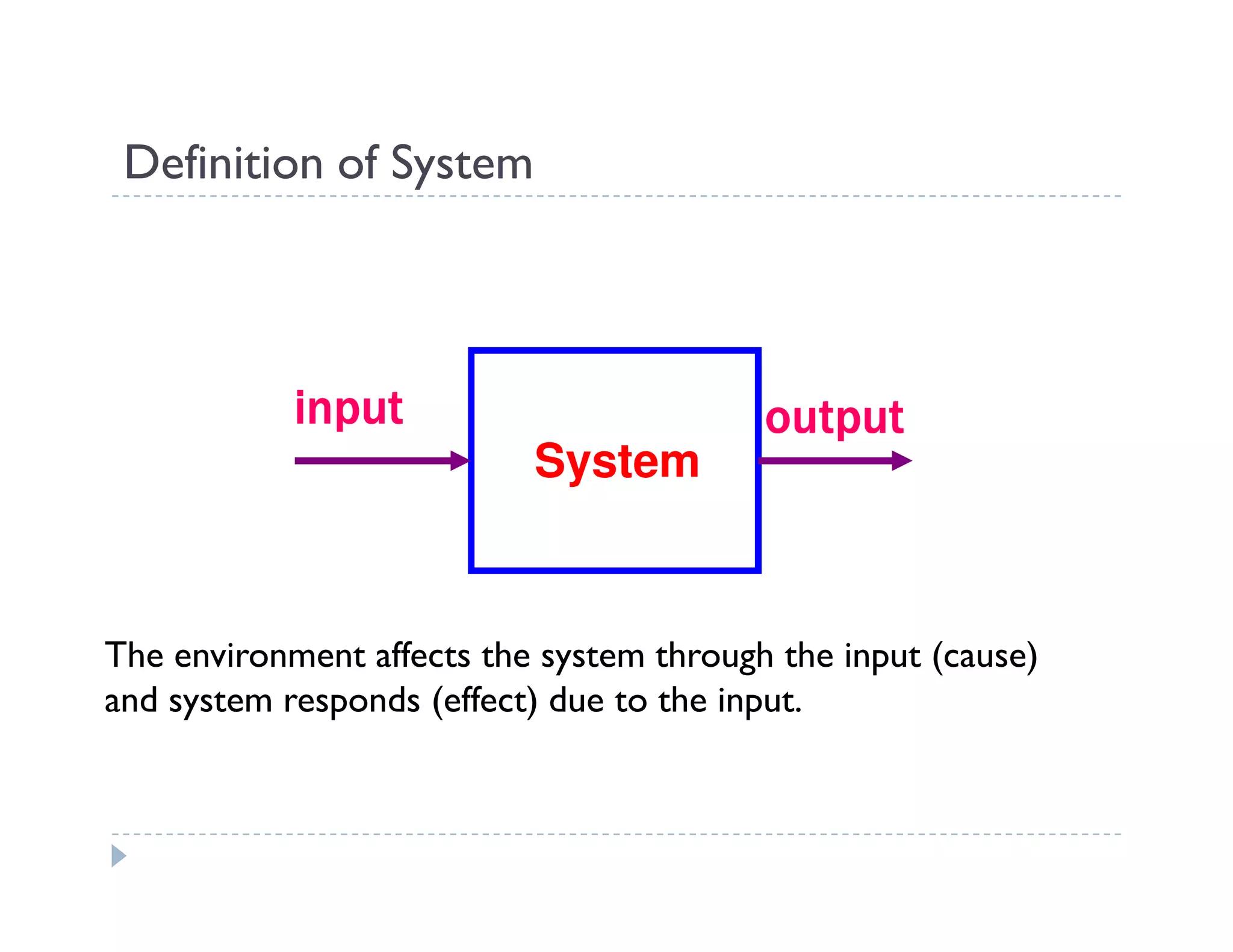
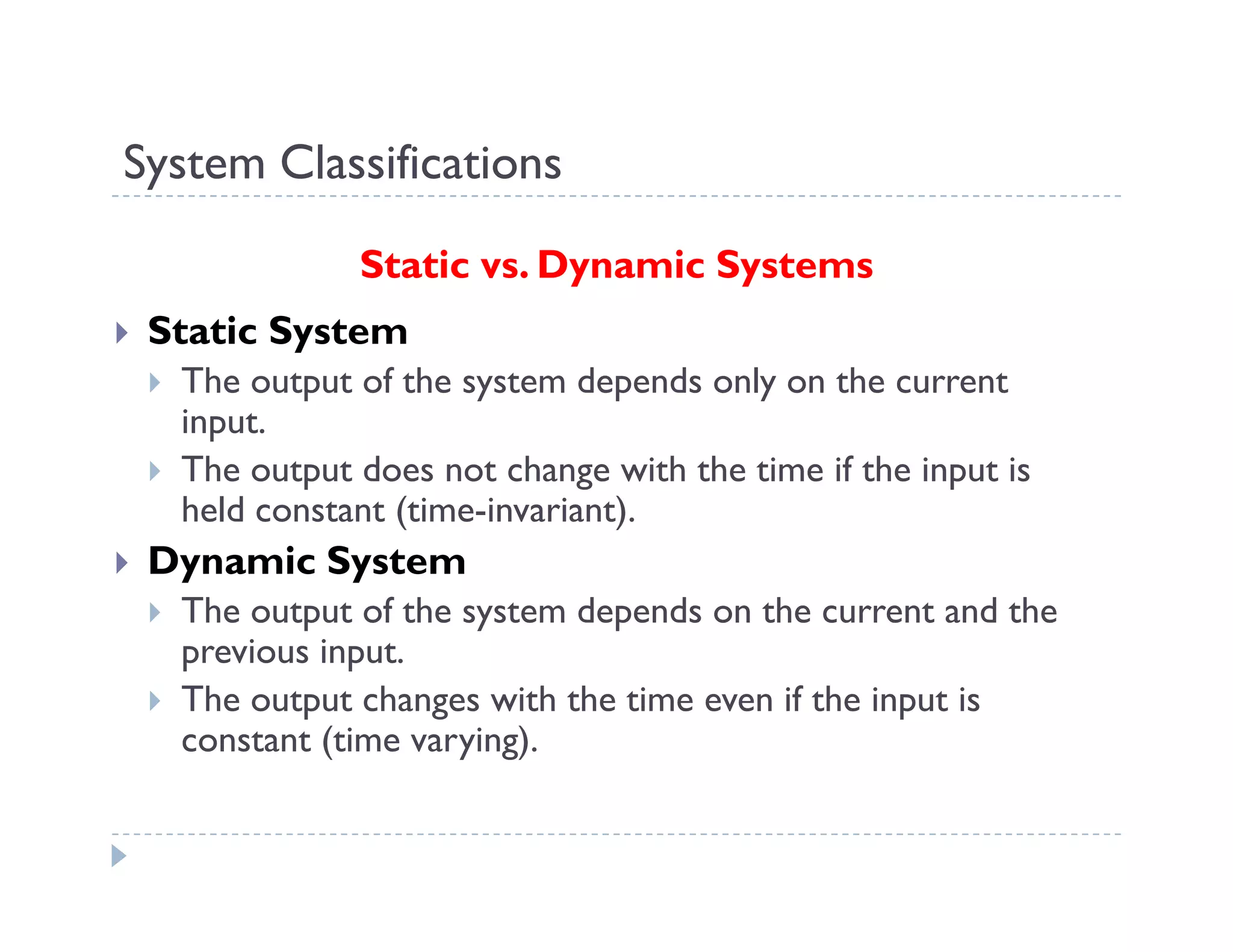
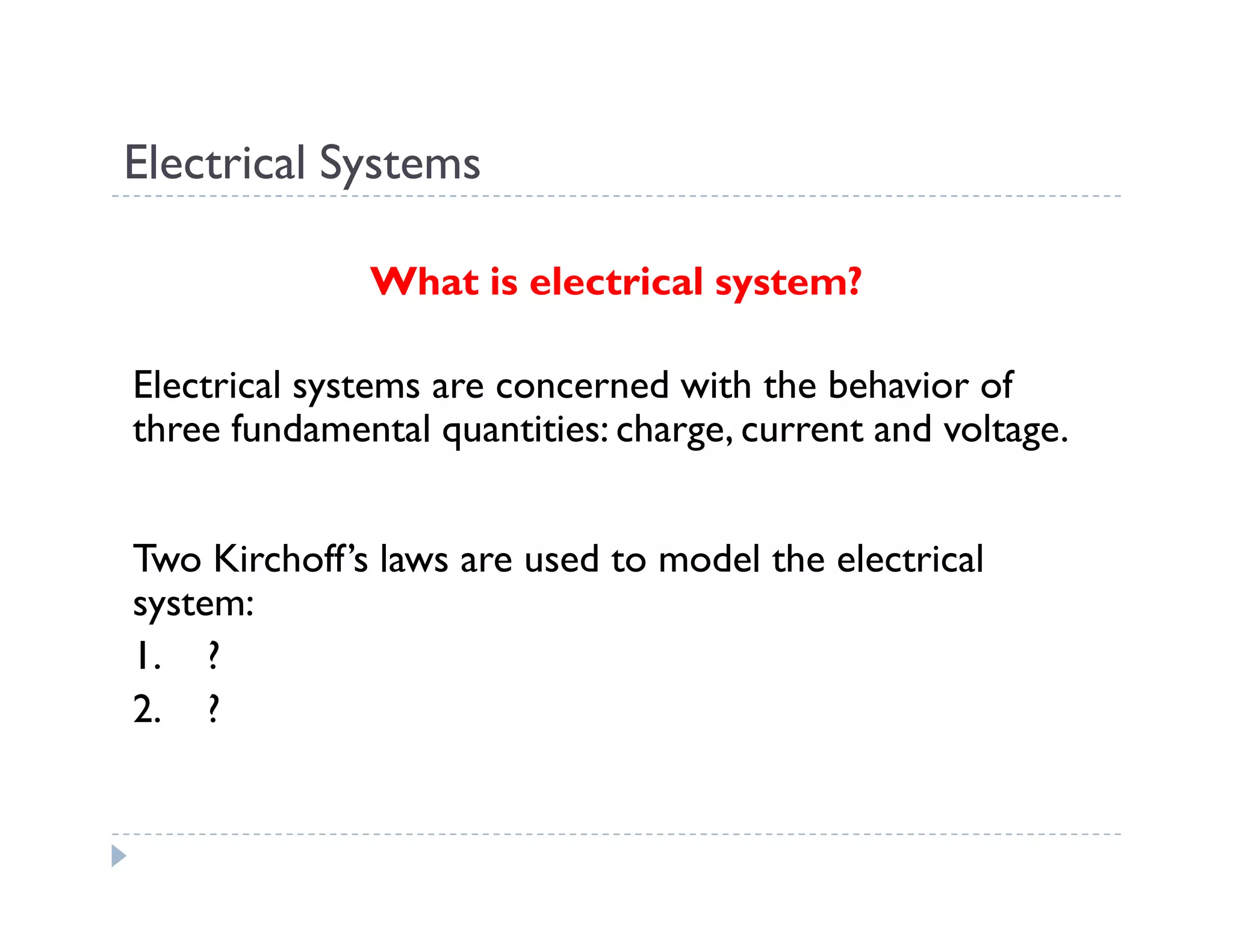
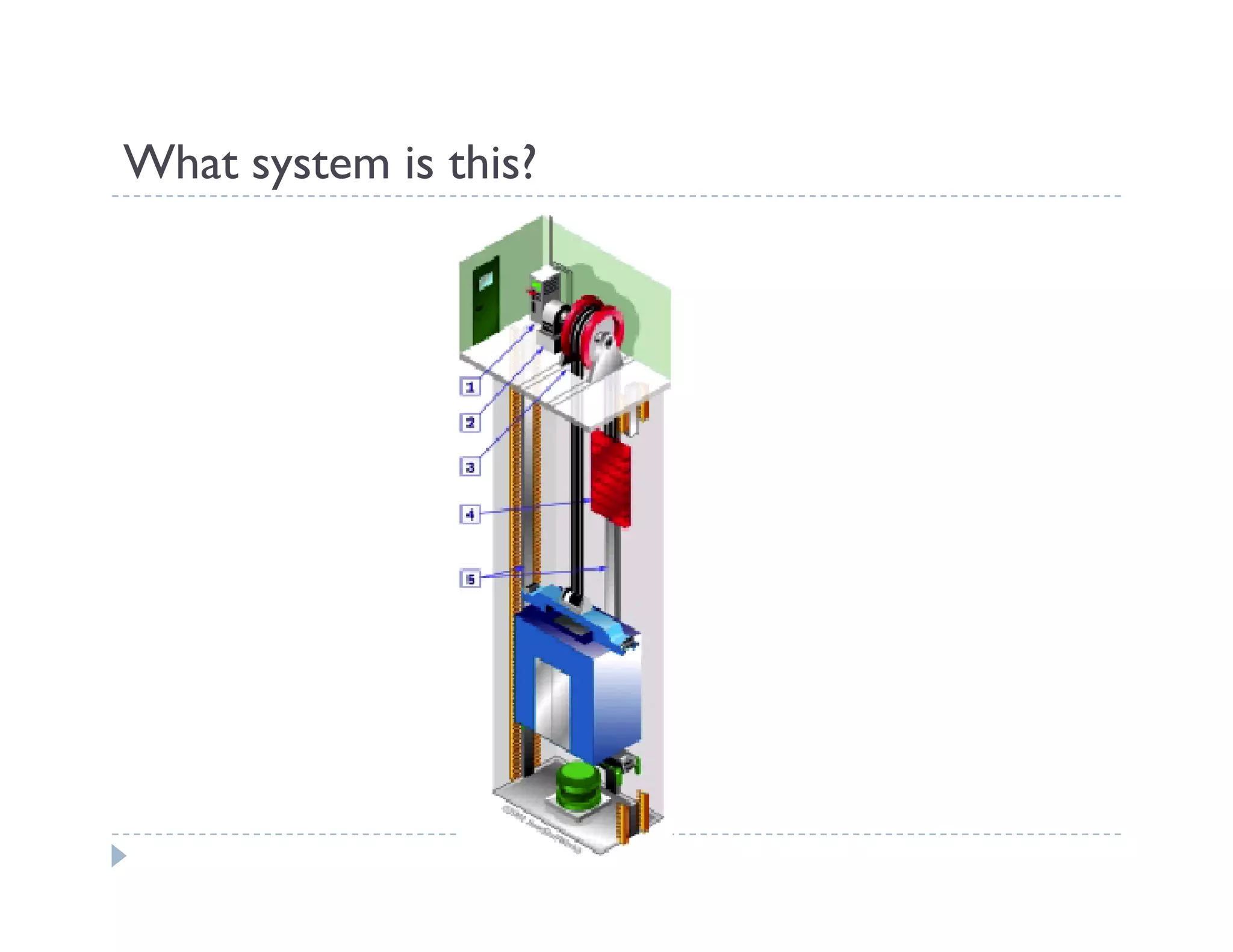
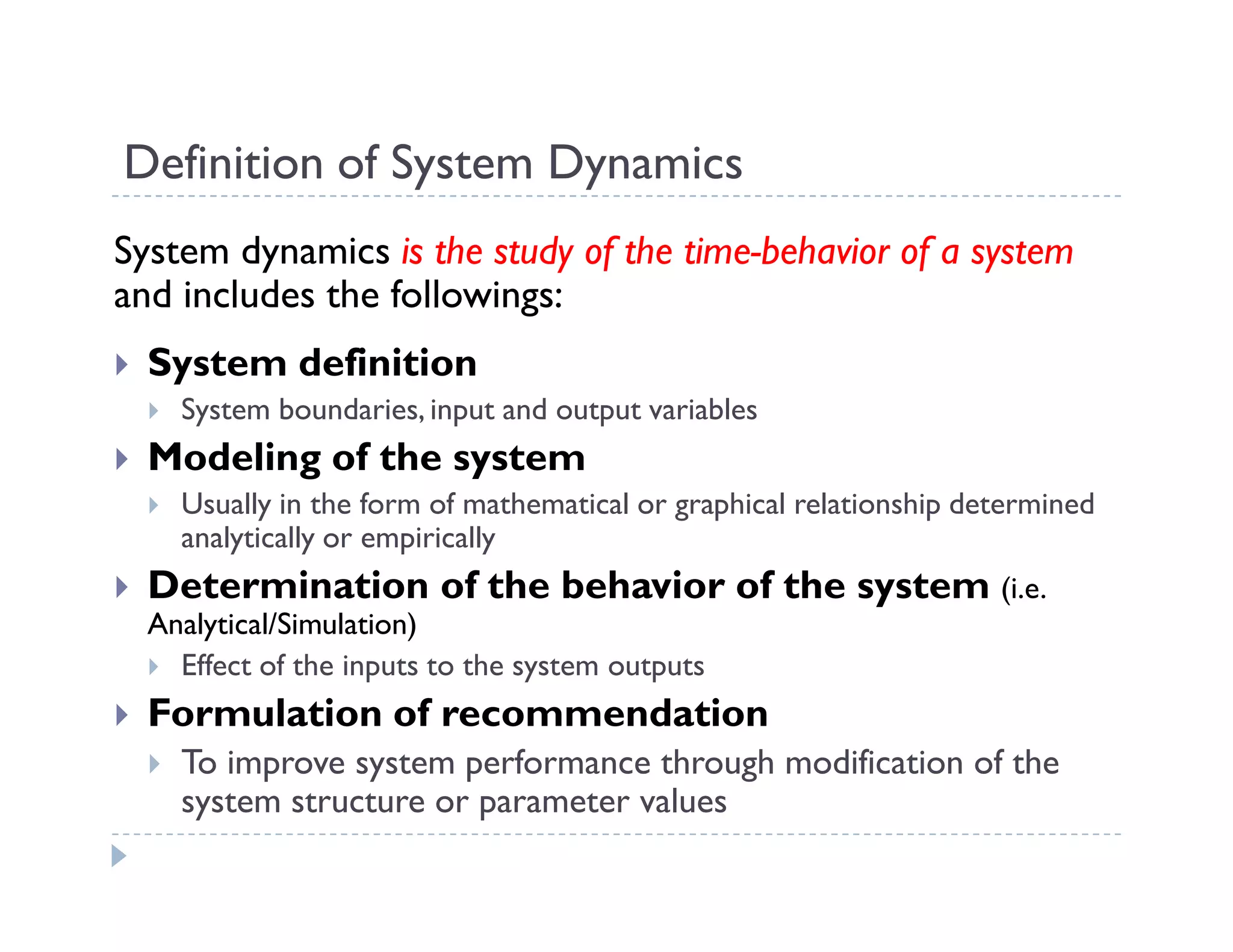
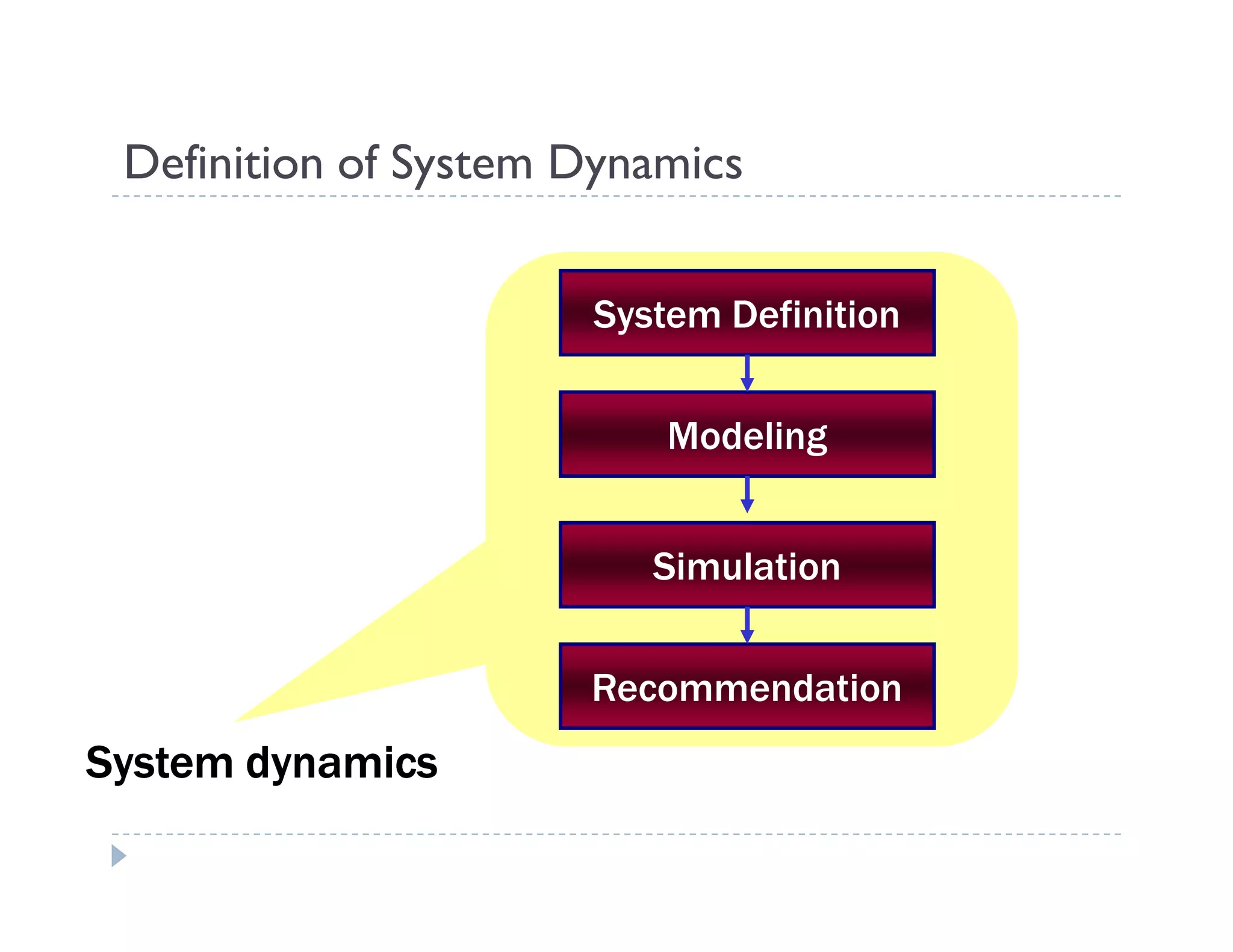
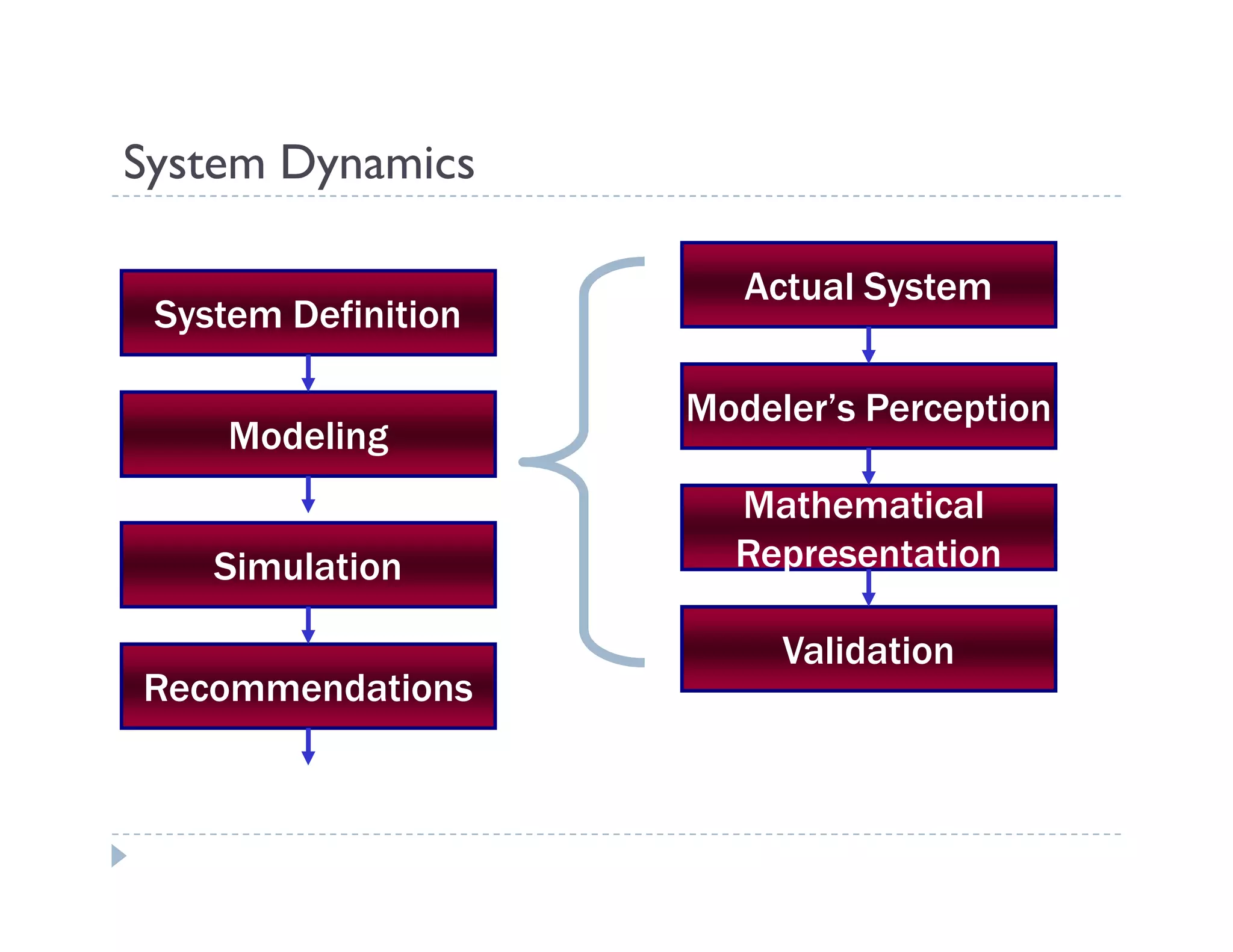
This document provides an introduction to system dynamics. It defines a system as a collection of interacting components with defined boundaries and inputs/outputs. Dynamic systems change over time even if inputs are constant, while static systems only depend on current inputs. Common dynamic systems include mechanical, electrical, thermal, and fluid systems. System dynamics involves defining a system, creating a mathematical model, simulating the model's behavior, and making recommendations. Models allow studying systems without experimenting on real systems. Simulation uses models to compute how systems react to inputs over time.