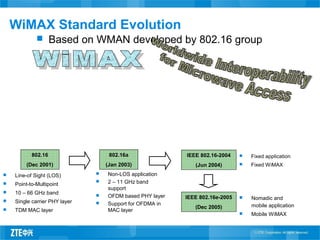
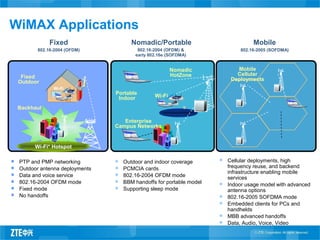
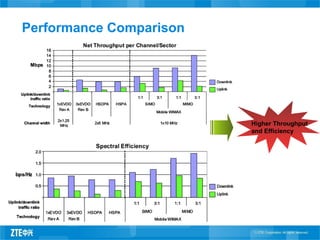
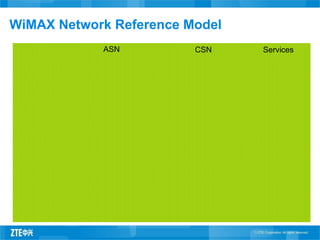
This document provides an overview of WiMAX standards and technology. It discusses the evolution of WiMAX standards, the role of the WiMAX Forum in promoting compatibility, and the growth forecast for the industry. It describes key aspects of WiMAX including available spectrum, features and advantages compared to other technologies, network architecture and profiles. The document provides details on WiMAX certification testing and requirements.