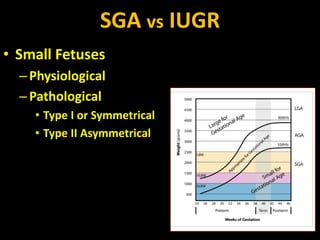
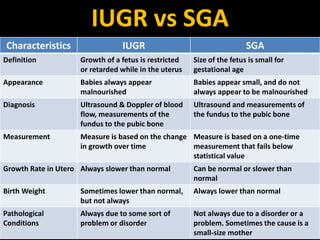
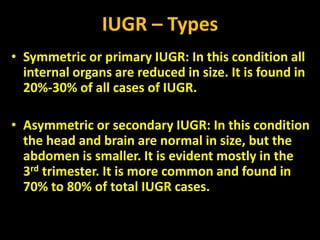
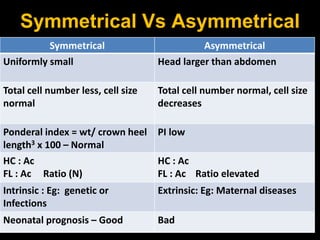
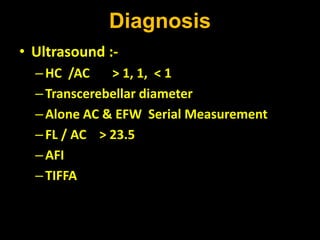
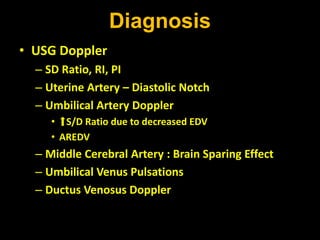
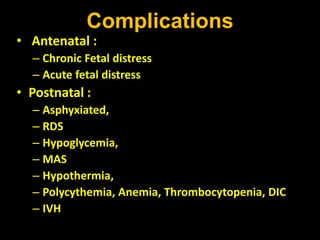
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) refers to reduced growth of the fetus while in the uterus. It increases risks of perinatal mortality and morbidity. IUGR is defined as birth weight below the 10th percentile for gestational age. It affects 5% of term and 15% of post-term babies. IUGR can be symmetric, affecting all organs uniformly, or asymmetric, where the head is normal size but abdomen is smaller. Causes include maternal health issues, fetal abnormalities, placental dysfunction, and unknown factors. Diagnosis involves ultrasound measurements and Doppler studies. Management focuses on monitoring, timely delivery, and newborn care. Prevention emphasizes preconception health, antenatal care, nutrition, lifestyle habits