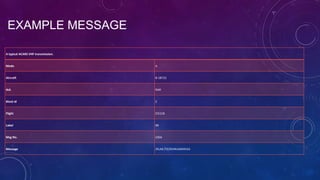
The document discusses ACARS, an aircraft communications system introduced in 1978 that uses VHF and satellite datalinks to transmit messages between aircraft and ground stations. It allows transmission of operational data like flight plans, maintenance issues, and position reports. While ACARS was a major improvement over prior voice-only systems, its 2400 baud rate is now too slow as data needs grow. Congestion is increasing on the VHF frequencies it uses. The solution is a transition over the next 20 years to newer protocols like ATN and the Internet Protocol that can better handle rising traffic demands.