Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Grade 9 chemistry, ions and writing chemical formulae

Grade 9 chemistry, ions and writing chemical formulae
IB Chemistry on Crystal Field Theory and Splitting of 3d orbital

IB Chemistry on Crystal Field Theory and Splitting of 3d orbital
IB Chemistry on Crystal Field Theory and Splitting of 3d orbital

IB Chemistry on Crystal Field Theory and Splitting of 3d orbital
Oxidation reduction reactions BY Muhammad Fahad Ansari 12IEEM14

Oxidation reduction reactions BY Muhammad Fahad Ansari 12IEEM14
IB Chemistry on Periodic Trends, Effective Nuclear Charge and Physical proper...

IB Chemistry on Periodic Trends, Effective Nuclear Charge and Physical proper...
IB Chemistry on Standard Reduction Potential, Standard Hydrogen Electrode and...

IB Chemistry on Standard Reduction Potential, Standard Hydrogen Electrode and...
IB Chemistry on Redox, Oxidation states, oxidation number

IB Chemistry on Redox, Oxidation states, oxidation number
IB Chemistry on Reactivity Series vs Electrochemical Series

IB Chemistry on Reactivity Series vs Electrochemical Series
IB Chemistry on Redox, Oxidation states and Oxidation number

IB Chemistry on Redox, Oxidation states and Oxidation number
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (18)
More from shaunoff
More from shaunoff (19)
IGCSE 11.3.1
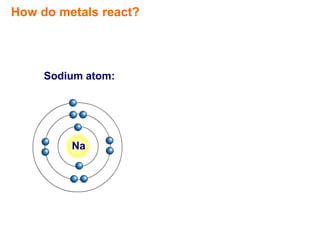
- 1. How do metals react? Sodium atom: Na
- 2. How do metals react? Sodium atom: loses Na 1 electron
- 3. How do metals react? Sodium atom: loses Na 1 electron Na
- 4. How do metals react? Sodium atom: + loses Na 1 electron Na
- 5. How do metals react? Sodium atom: Sodium ion: + loses Na 1 electron Na [2.8] (full outer shell)