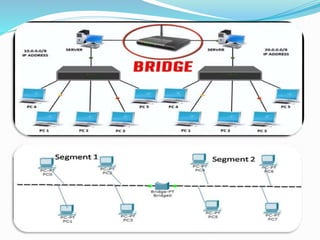
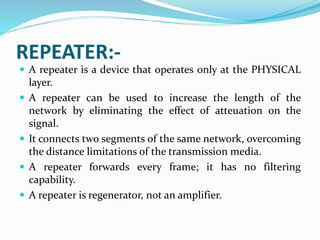
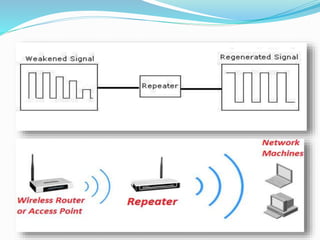
The document discusses communication devices presented in a seminar by Sanchit Sharma. It provides background on the history of communication, beginning with human voice and early writing systems. Various communication devices are defined, including modems, routers, hubs, switches, mobile phones, and bridges. For each device type, a brief description of its function is given. The seminar covered advantages and disadvantages of communication devices as well as the roles of different networking components in digital communication.