Projectile motion
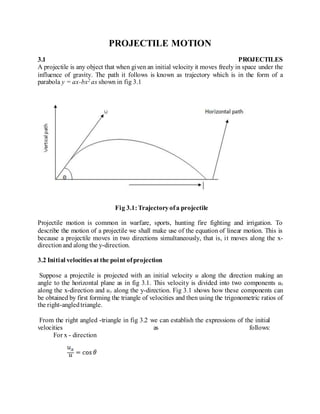
- 1. PROJECTILE MOTION 3.1 PROJECTILES A projectile is any object that when given an initial velocity it moves freely in space under the influence of gravity. The path it follows is known as trajectory which is in the form of a parabola y = ax-bx2 as shown in fig 3.1 Fig 3.1:Trajectoryofa projectile Projectile motion is common in warfare, sports, hunting fire fighting and irrigation. To describe the motion of a projectile we shall make use of the equation of linear motion. This is because a projectile moves in two directions simultaneously, that is, it moves along the x- directionand along the y-direction. 3.2 Initial velocitiesat the point ofprojection Suppose a projectile is projected with an initial velocity u along the direction making an angle to the horizontal plane as in fig 3.1. This velocity is divided into two components ux along the x-direction and uy along the y-direction. Fig 3.1 shows how these components can be obtained by first forming the triangle of velocities and then using the trigonometric ratios of the right-angledtriangle. From the right angled -triangle in fig 3.2 we can establish the expressions of the initial velocities as follows: For x - direction
- 2. For y-direction After a time t, the velocities of the projectile can be obtained from the first equation of linear motion Along the x-direction Where This means that at any time t when the projectile is in flight the horizontal component of the initial velocityremains constant. Along the y-direction Where At the same time the horizontal and vertical displacements can be obtained from the secondequationlinear motion For horizontal displacement
- 3. Since For vertical displacement Given that (Showsthatthe accelerationisagainstthe gravity) 3.3 Equation of a trajectory The mathematical relationship between horizontal and vertical displacements that defines the path followed by the projectile. This canbe obtainedbycombining-equations(3.5)and(3.6)as follows: From equation,(3.5)t = . Substitutefort in(3.6) Onsimplificationwehave From the above equations it is now possible to getotherexpressions for the maximum height, time of flight,rangeandmaximumrange. 3.4 Maximum height The maximum height istheverticaldistanceabove thehorizontalplaneaprojectilecan possible attain for given initial velocity and angle of projection. This is the position where a projectile ceases to move upwards in This case vy = 0 as shown in the figure 3.3.
- 4. Figure 3.3: Maximum height and range ofa projectile From equation (3.4) when This is the time taken by the projectile to attain the maximum height γ. Substituting for t in equation(3.6)we get Whensimplifiedthisexpression become 3.5 Time of flight The time taken by the projectile to move from the point of projection to the target' horizontally is known as time of flight. In other words it is the time a projectile remains in air. When the projectile lands on the target, the vertical displacement becomes zero which means y - 0. Usingthis conditioninequation(3.6) we cansolve fort as follows. Either
- 5. Thus the time offlightistwicethe timetakenbyprojectileto reachthemaximum height. 3.6 The Range (R) The range of a projectile is the horizontal displacement between the point of projection and the target. Since the horizontal component of the initial velocity of the projectile remains constant, the range is obtainedfrom equation(3.5) When R = u2 sin2θ/g ... ... ... ... ... ... ... (3.9). 3.7 The Maximum Range When a projectile is projected at different angles with the horizontal, the ranges covered differ. However there is a single angle for which the range is greatest of all. We can get this angle from the range expressioninequation(3.9). Write therange expressionas Rearrange the expression R = U2 (2cosθsinθ)/g From the trigonometric identities ∴ R = U2 sin2 θ)/g For maximum range
- 6. Example 3.1: A projectile is launched from a point on a level ground with a velocity of in the directionmakinganangle of 60° to thehorizontal. (a) Sketch the trajectoryof the projectile (b) What are the initial velocitiesof the projectile alongthe x- and y-directions? (c) Find the velocities of the projectile along the horizontal and vertical planes 3seconds after launch (d) Determine the greatest height attainedbythe projectile (e) What is the time of flight? (f) What is the range? Solution The main assumptions to consider in a projectile motion are such as the effect of air resistance is reflectedthe effect of earth curvature and it is rotationare neglected. Figure 3.2
- 7. (b) The initial velocities (i) (ii) (c) The velocities (d) The greatestheight Y
- 8. (e) The time offlight (f) The range R 3.8 Projectile firedfrom raisedground Let us consider the projectile fired from the top of a cliff. Here the projectile may be launched horizontally or at an angle with the horizontal. The equations used to describe the motion in this case are the same as what have been derived so far but with some modifications. Figure 3.4 projectilefiredhorizontally
- 9. Projectile fired horizontallyfrom the top ofa cliff Consider a projectile launched horizontally with velocity u from the top of a cliff as shown in fig 3.4. The gravity causes the projectile to follow the trajectory as it advances the nature of which is identical to that in fig 3.1. The following are the factors to observe: The horizontal velocity remains constant throughout the motion The initial velocity along the horizontal direction u = ux and that along the vertical direction Uy = 0 The vertical distance projectile fall through is always assigned negative sign. The time the projectile takes to move along the trajectory equal to the time it takes to fall through the vertical distances h The resultant velocity v is obtained by Pythagoras's theorem Example 3.2: A bullet is fired horizontally from the gun with muzzle velocity of 200 ms1from the top of a cliff 120m high. Find. (a) The velocities of the bullet after it has fallen of the vertical distance (b) The time it takes to land on a level ground (c) The distance from the foot of a cliff to where it lands
- 10. Figure. 3.4 A bullet firedfrom topof the cliff. (a) To find and Let t = time taken From (b) By the moment it lands on the ground, the vertical distance coveredis From
- 11. -It takes the bullet 4.948 seconds to land on its target (c) Since the horizontal velocity is constant through out the motion Example 3.3: A shell is launched from the top of a hill 90m above the plane ground with a velocityof150ms-1 inthedirectionmakinganangle 30° tothehorizontal. Find (a) The velocities along the x- and y-directions when it is half-way between the top and ground (b) The horizontal distancecoveredbythe momentit landsontheground The velocity and direction as the shell hits the ground. (Useg= 9.8m/s2 Solution (a) Lett =time fortheshelltodescend45m From
- 12. This isaquadratic equation intthat canbe solved bythe formula (i) (ii) (b) Whenitlands ontheplane the distance coveredisnow -90mand thereforefrom
- 13. The shell takes 16.4s to the land on the target and by then the horizontal distance is (c) Let By formingthe triangle of vector we can use Pythagoras theorem The velocityof the shell is 153 m The directionof the shell at this moment is given by
- 14. Exercise 3.0 3.1. A projectile is launched from a point on a horizontal ground with an initial velocity of 100ms "1 along the direction making an angle of 60° with the horizontal. a) (a)Sketchalabeleddiagram showing how the projectile moves. (b) What are the initial velocities at the point of projection (c) Determine the velocities of the projectile 4 seconds after projection. what is the highest point does theprojectilereachwhile inmotion? d) (d) Calculate the range of the projectile. 3.2 (a) Show that the equation of the trajectory of a projectile is, Where angle of projection, u= initial velocity, x =horizontal distance, y = vertical distance and g = accelerationdue to gravity. (b) State the condition for a projectile to attain the maximum range and show that the maximum range is 3.3 Find the two possible angles of projection for a projectile to just clear the wall 10m high if the point of projection is 40m from the wall and the initial velocity of a projectile is 50ms-1. 3.4 A man standing on a cliff 50m high sees a dog running away 20m from the footnote cliff. He throws astone horizontallywithvelocityof 30ms-1, if thestone hits thedog, find (a) The distance of the dogfrom the cliff (b) The speed of the dog by the time it is hit by the stone.(Take g = 9.8ms-2) 3.5 A projectile is fired with an initial velocityof u at an angle to the horizontal as in figure 3.3. When it reaches its peak, it has, coordinates given by and when it strikes the ground, its coordinates are , where R is the horizontal range, (a) Show that it reaches the maximum height, Y, given by (b) Show that its horizontal range is given by 3.6 In fig 3.6, a projectile is fired at a falling target. The target begins falling at the same time as projectile leaves the gun. Assuming that the gun is initially aimed at the target, show that the target will be hit.
- 15. 3.7 An object slides from rest along a frictionless roof 8m long, inclined 37°to the horizontal. While sliding, the object accelerates at towards the edge of the roof which is 6m above the 'ground. Find (a) the velocity components when it reaches the edge of the roof (b) the total time it remains in motion (c) the distance from the wall of the house to where the object hits the ground. Figure 3.6 3.8. A particle is projected at point on a level ground in such a way that its horizontal and vertical components of the initial velocity are 30m/s and 30m/s respectively. From this information;find. (a) The highest point above the ground reached, by the particle (b) The horizontal distance coveredafter landingonthe ground (c) The magnitude and directionofthe initialvelocity. 3.9 A warplane flying horizontally at l000kmh-1 releases a bomb at a height of 1000m.| The bomb hits the intended target, what was the distance of the plane from the target when the bomb was released? 3.14 A basketball player 1.8m tall throws a ball at a velocity of 10m/s in the direction 40º with the horizontal. The ball passes through the basket fixed at a height of 3m above the ground level. Find the horizontal distance of the basket from the point where the ball was thrown.