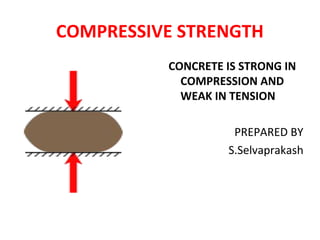
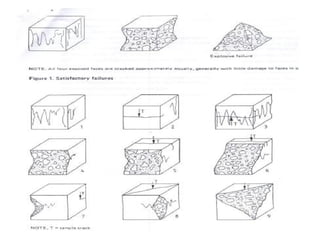
This document discusses the compressive strength of concrete. It defines compressive strength as the ability of a material to withstand pushing forces. Concrete is strong in compression but weak in tension. The document describes how to test the compressive strength of concrete cube and cylinder specimens. It provides details on specimen size, curing, loading rate, and calculating compressive strength based on applied load divided by cross-sectional area.