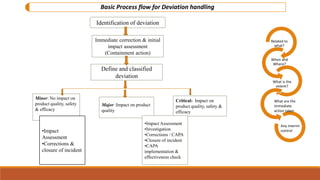
This document discusses deviation handling and root cause analysis. It defines deviations as departures from standard procedures and outlines regulatory expectations to investigate deviations and prevent reoccurrence. The basic process flow for handling deviations includes identification, assessment, classification, investigation and corrective actions. Root cause analysis is presented as a method to systematically identify underlying causes of problems using techniques like brainstorming, 5 whys, and cause-and-effect diagrams. The goals of root cause analysis are failure identification, analysis, and resolution through an iterative process.


![Regulatory Expectation
• “Any unexplained discrepancy…shall be thoroughly investigated…The
investigation shall extend to other batches …that can have been associated with the
specific failure or discrepancy. A written record of the investigation shall be made
and shall include the conclusions and follow-up
21 CFR 211.192
•“Any deviations from instructions or procedures should be avoided as far as
possible. If a deviation occurs, it should be approved in writing by a competent
person…”
• Any significant deviations [from defined procedures and instructions] are fully
recorded and investigated
EC Guide to GMP, Chapter 5
(5.15)
• Any deviation from established procedures should be documented and explained.
Critical deviations should be investigated, and the investigation and its conclusions
should be documented.
ICHQ7A
• The organization should ensure process outputs, products, and services that do not conform to
requirements are identified and controlled to prevent unintended use or delivery. The
organization should take appropriate action based on nature of nonconformity and its impact on
conformity of products and services. This is applicable also to nonconforming products and
services detected after delivery of products during or after provision of service
ISO 9001:2015,Clause 8.7
When a deviation occurs the responsible firm must undertake and investigation to determine what went wrong
and what damage, if any , the product might have suffered.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deviationandrootcauseanalysis-170225131302/85/Deviation-and-root-cause-analysis-in-Pharma-3-320.jpg)