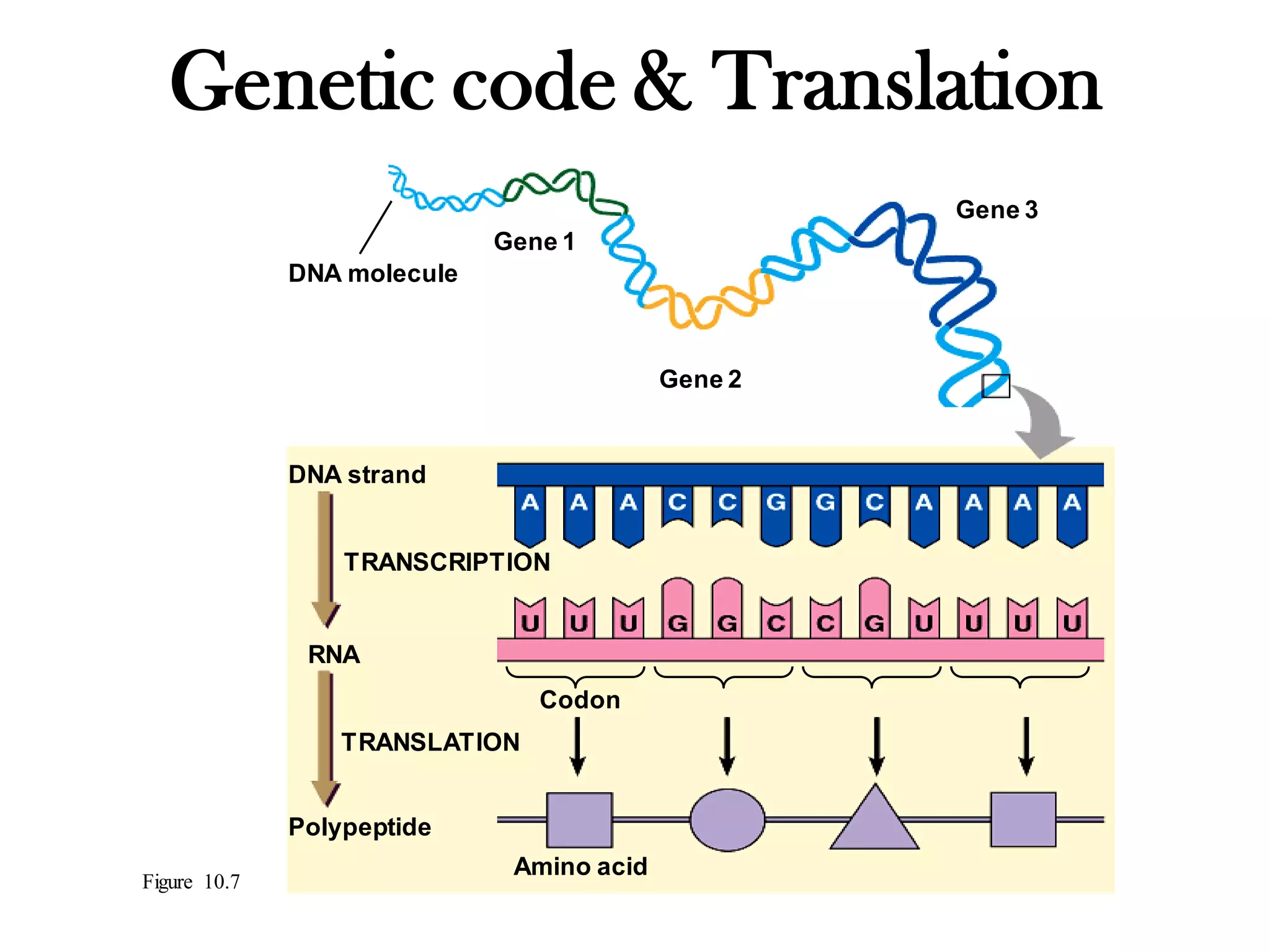
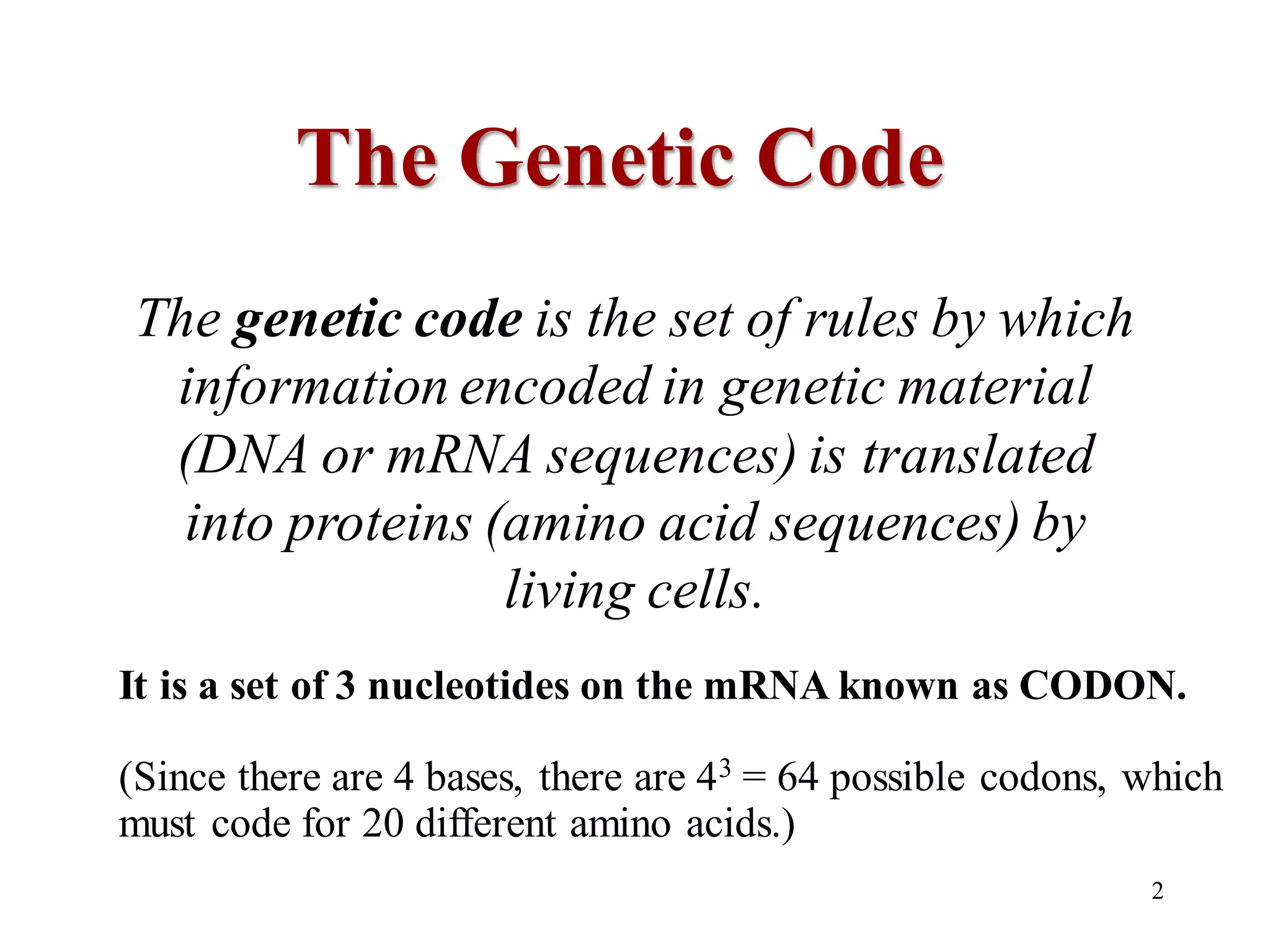
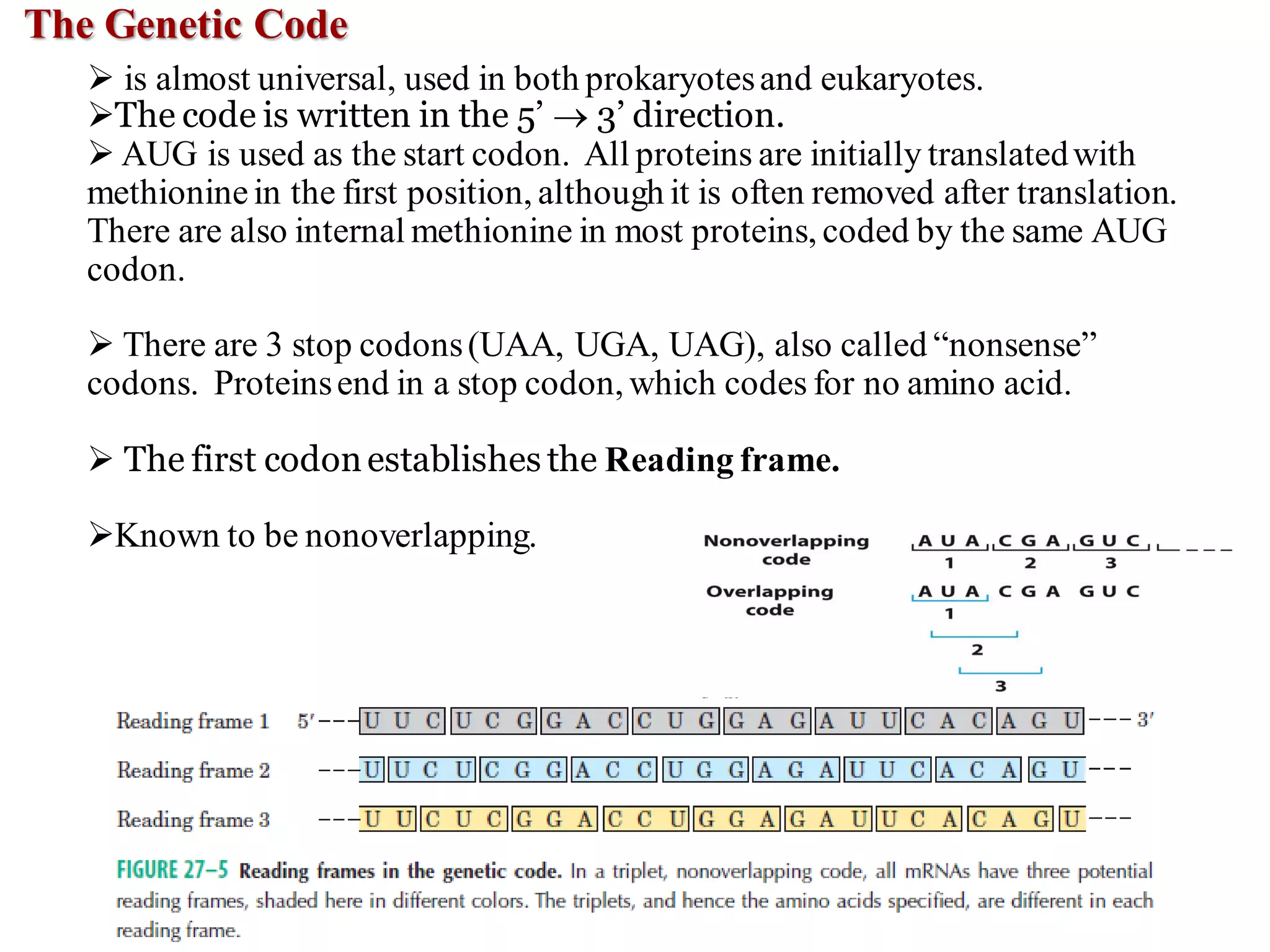
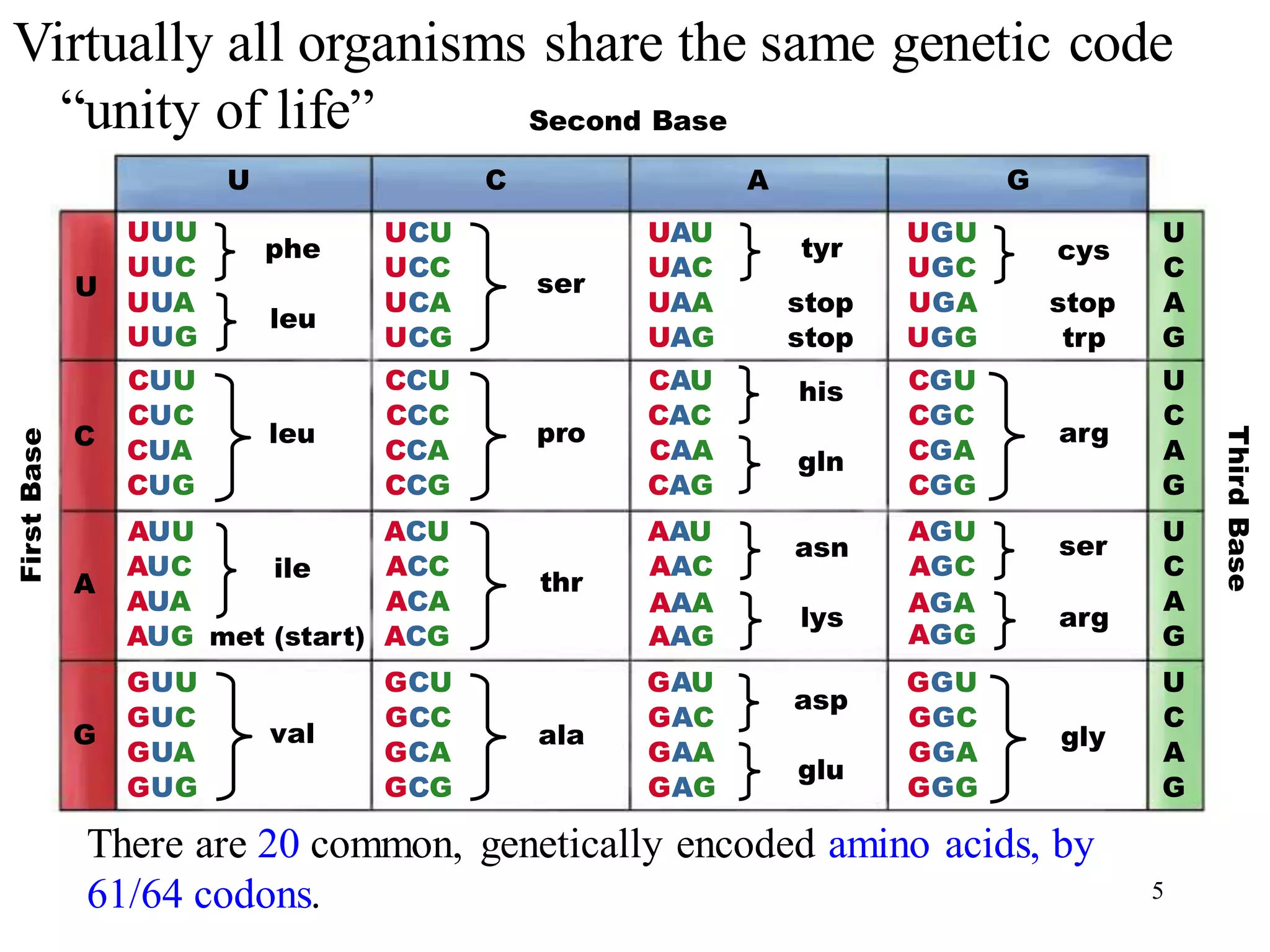
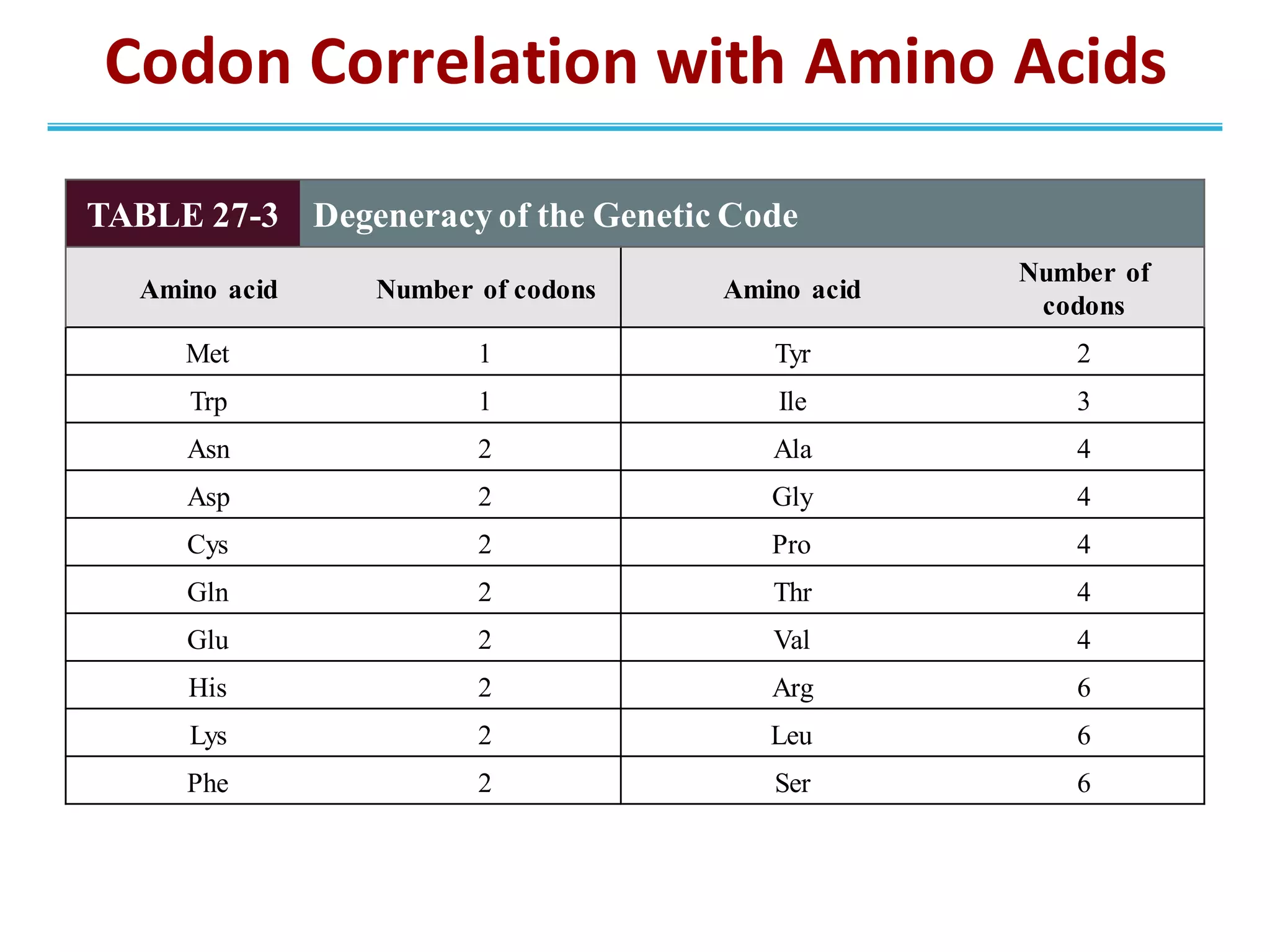
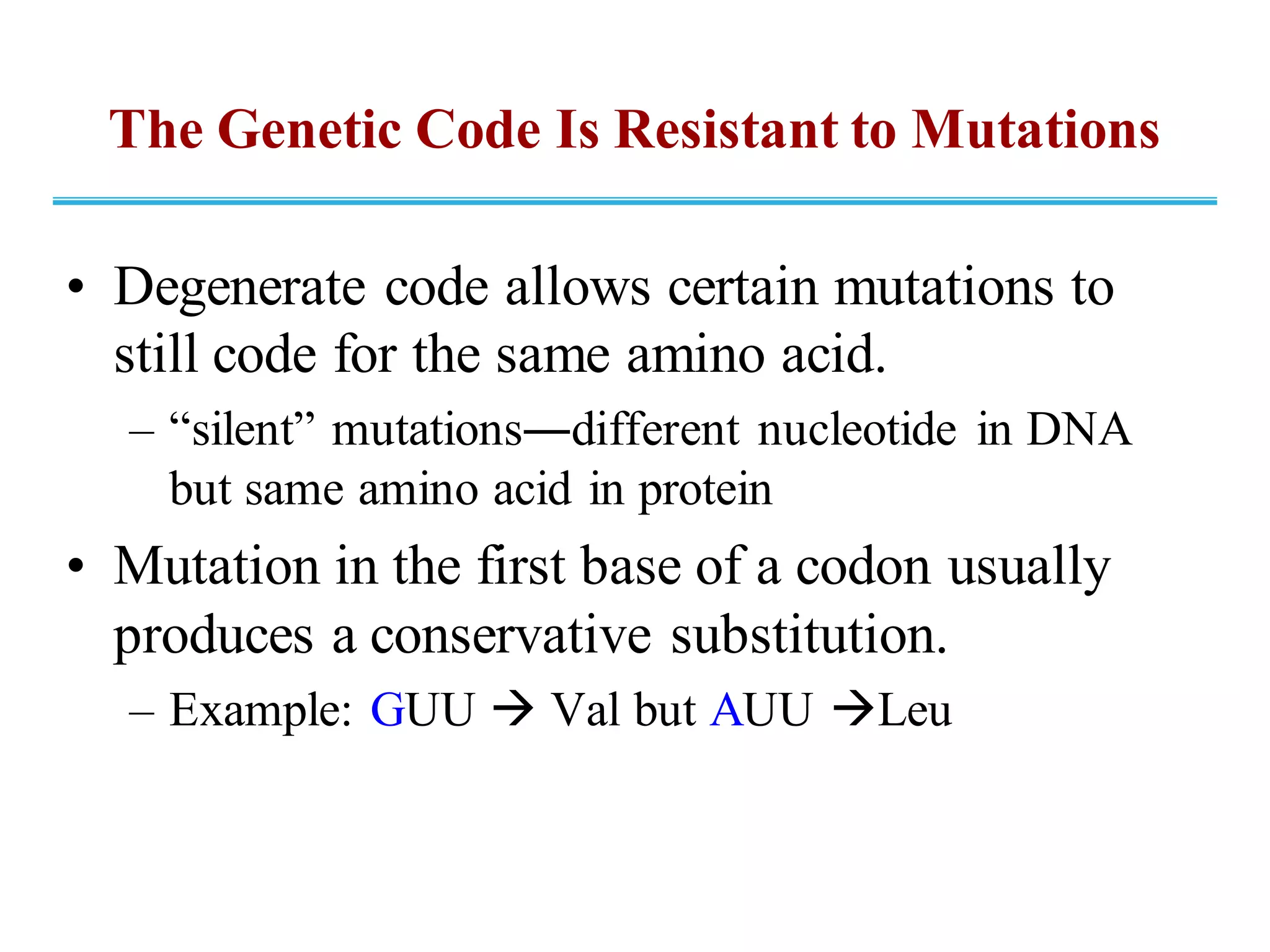
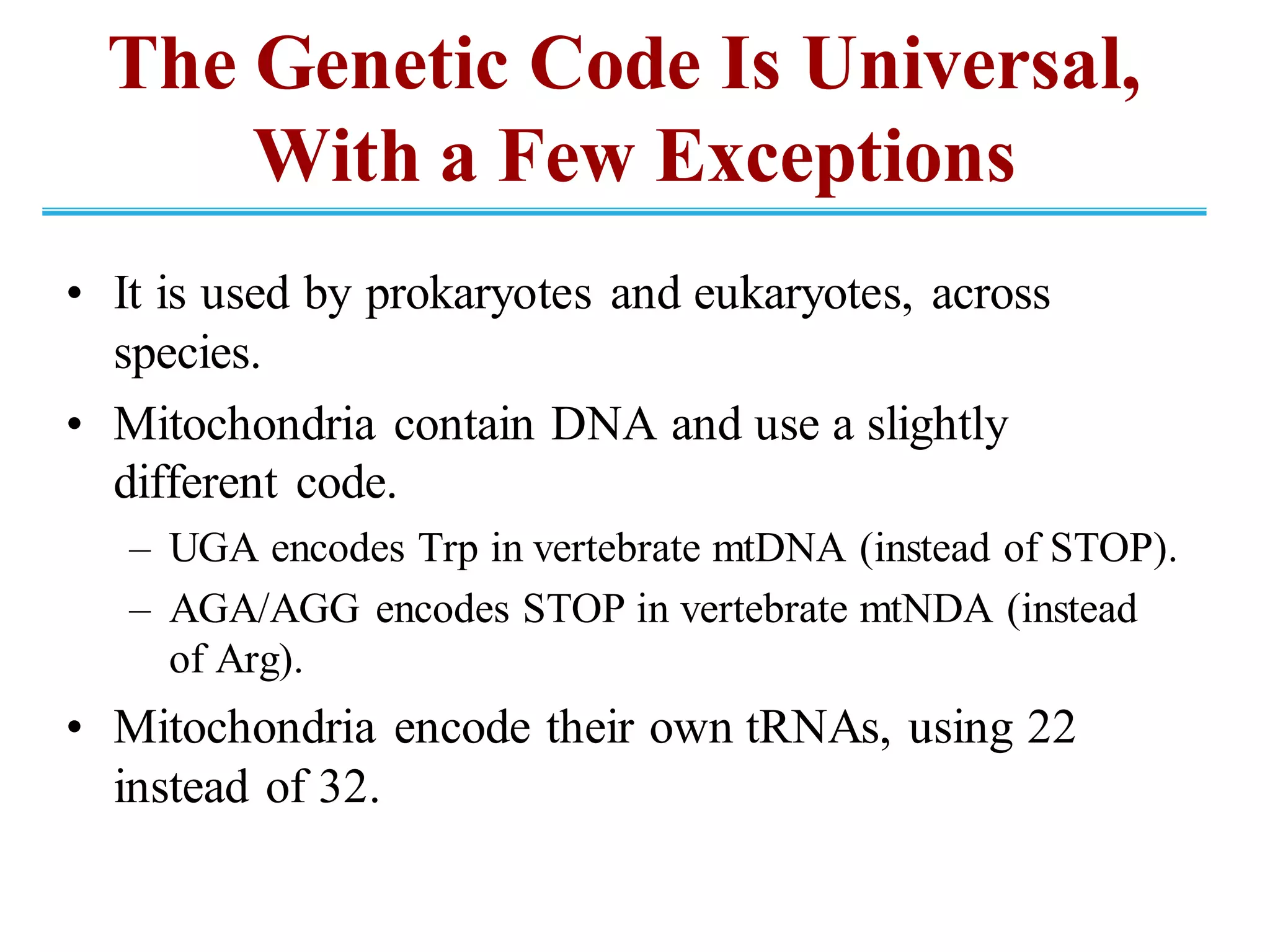
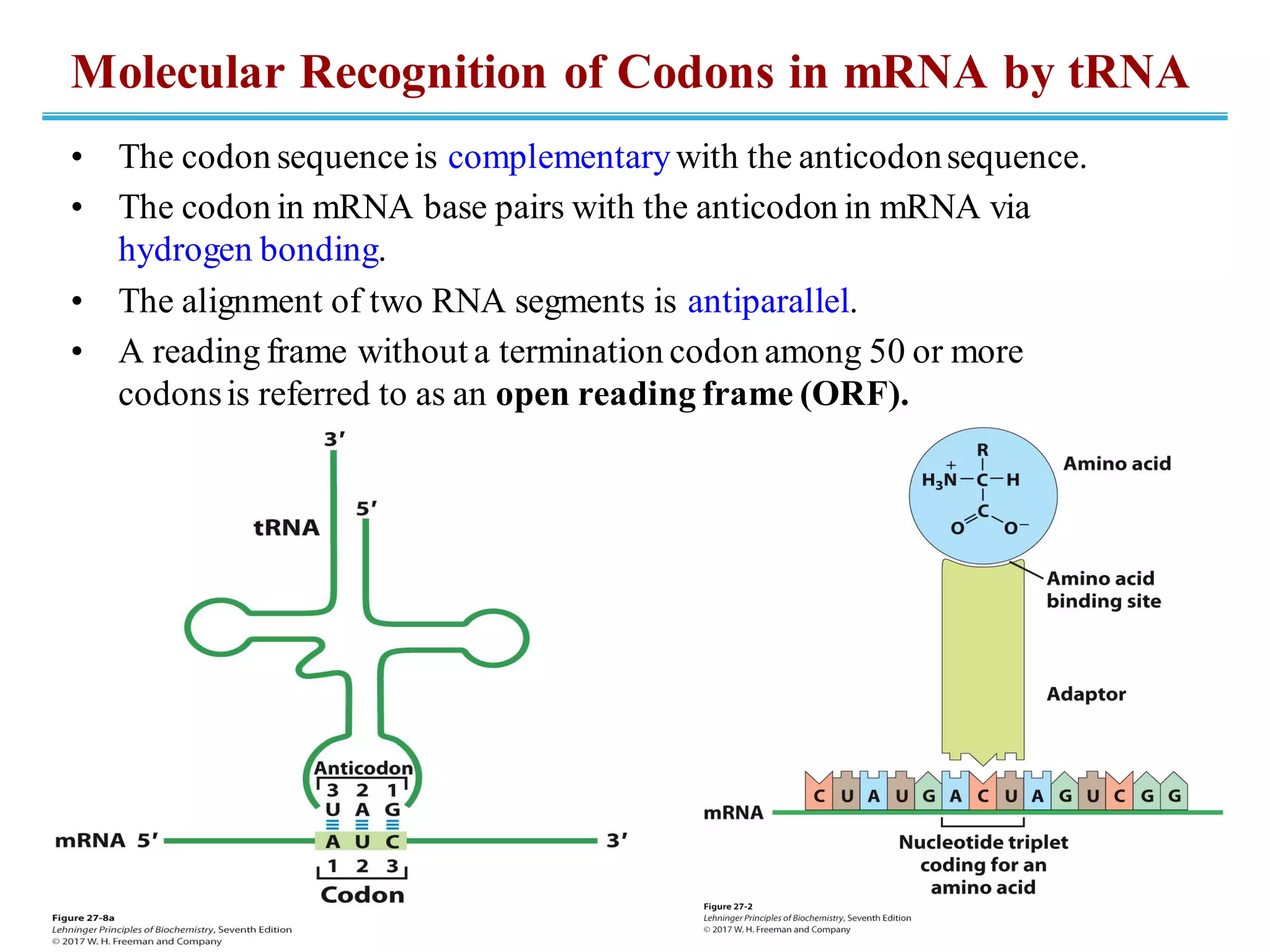
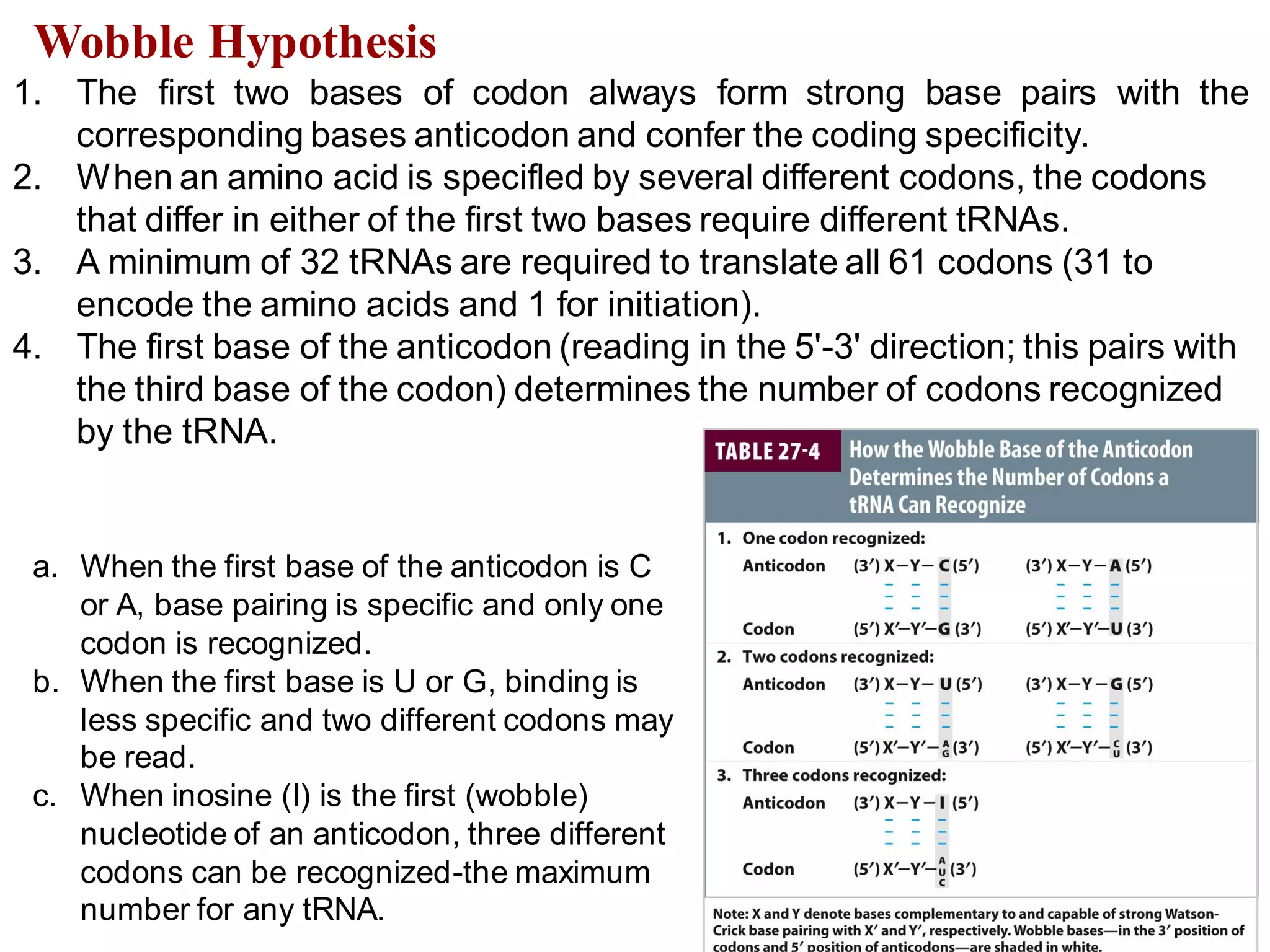
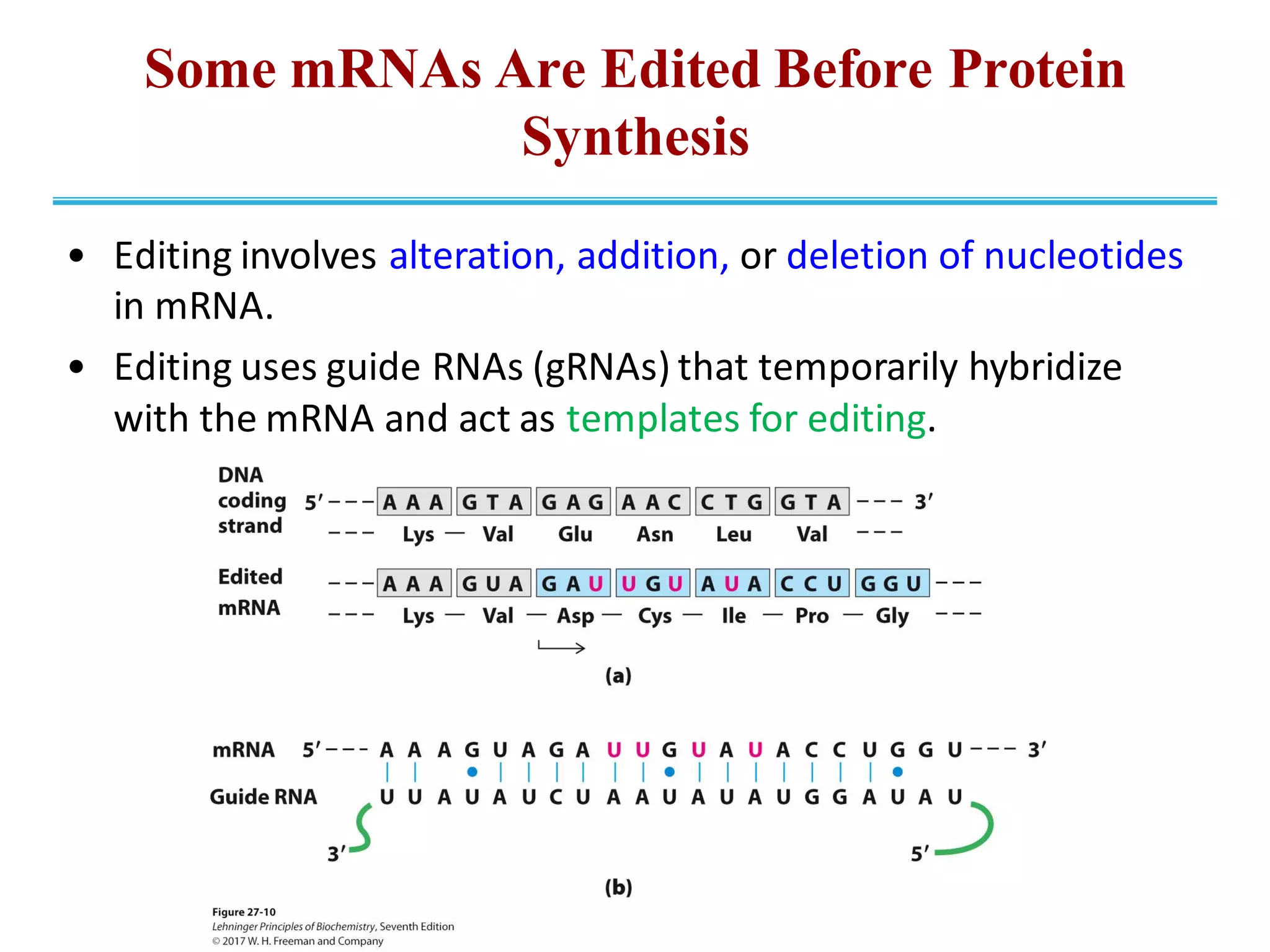
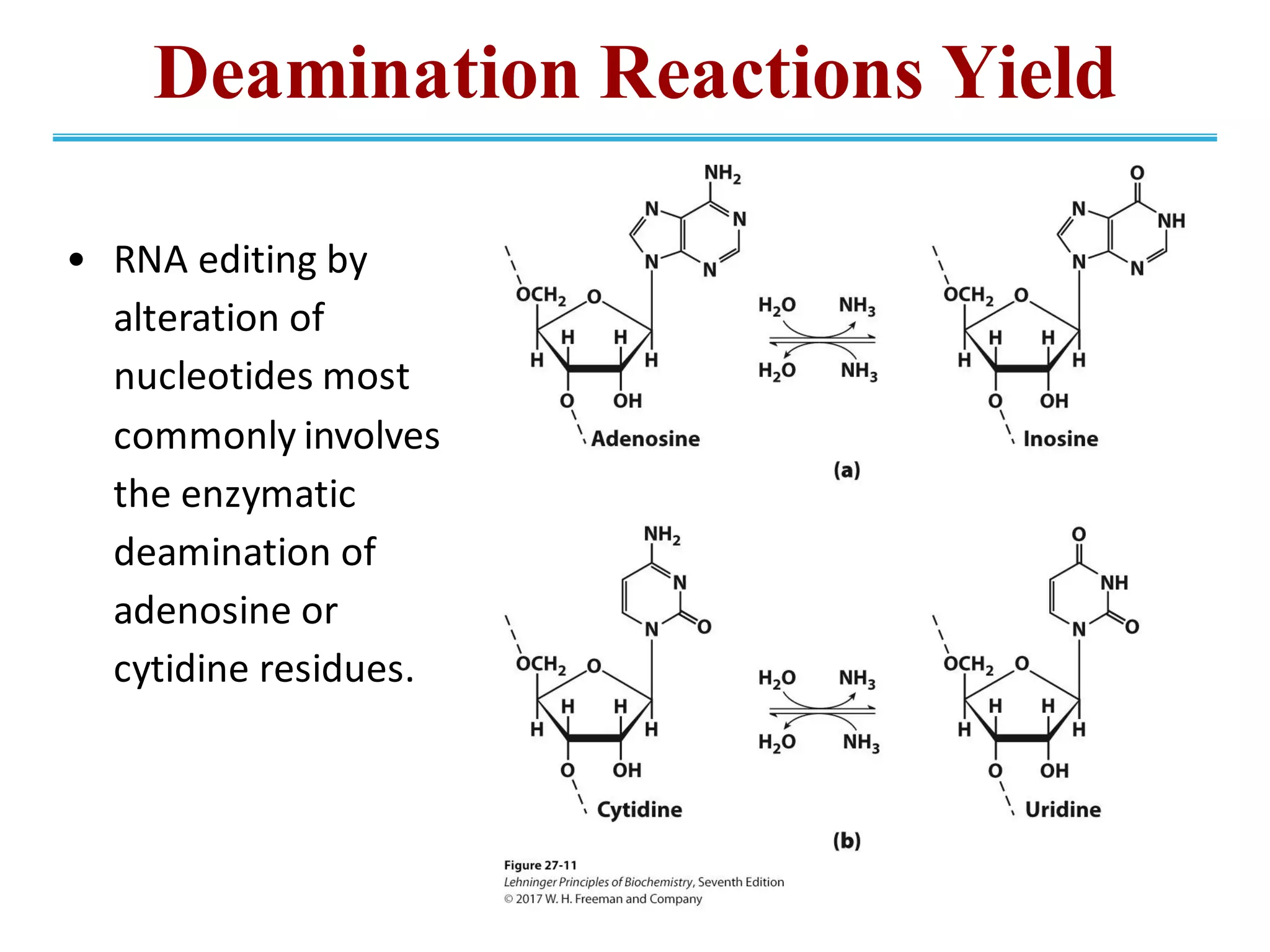
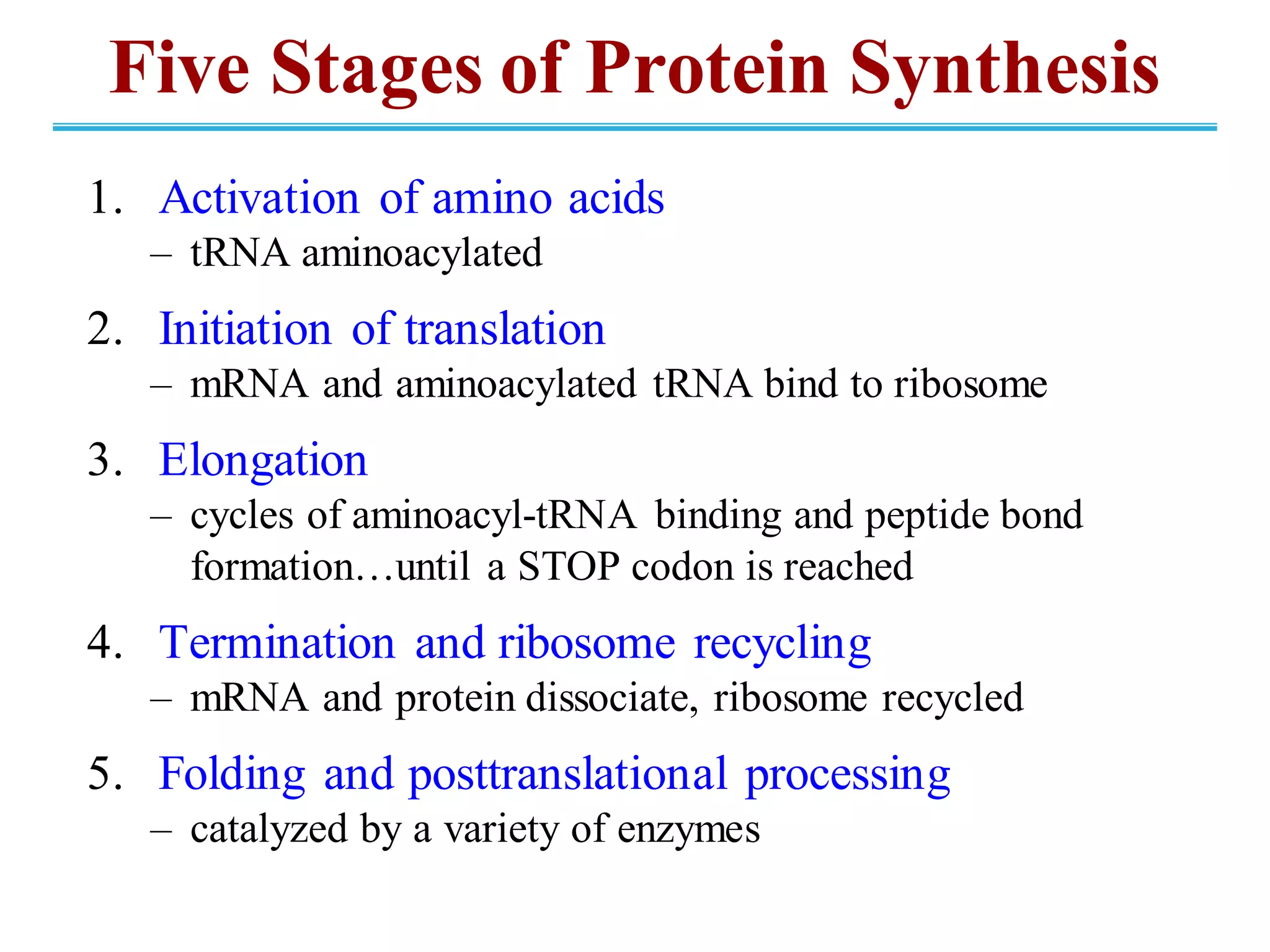
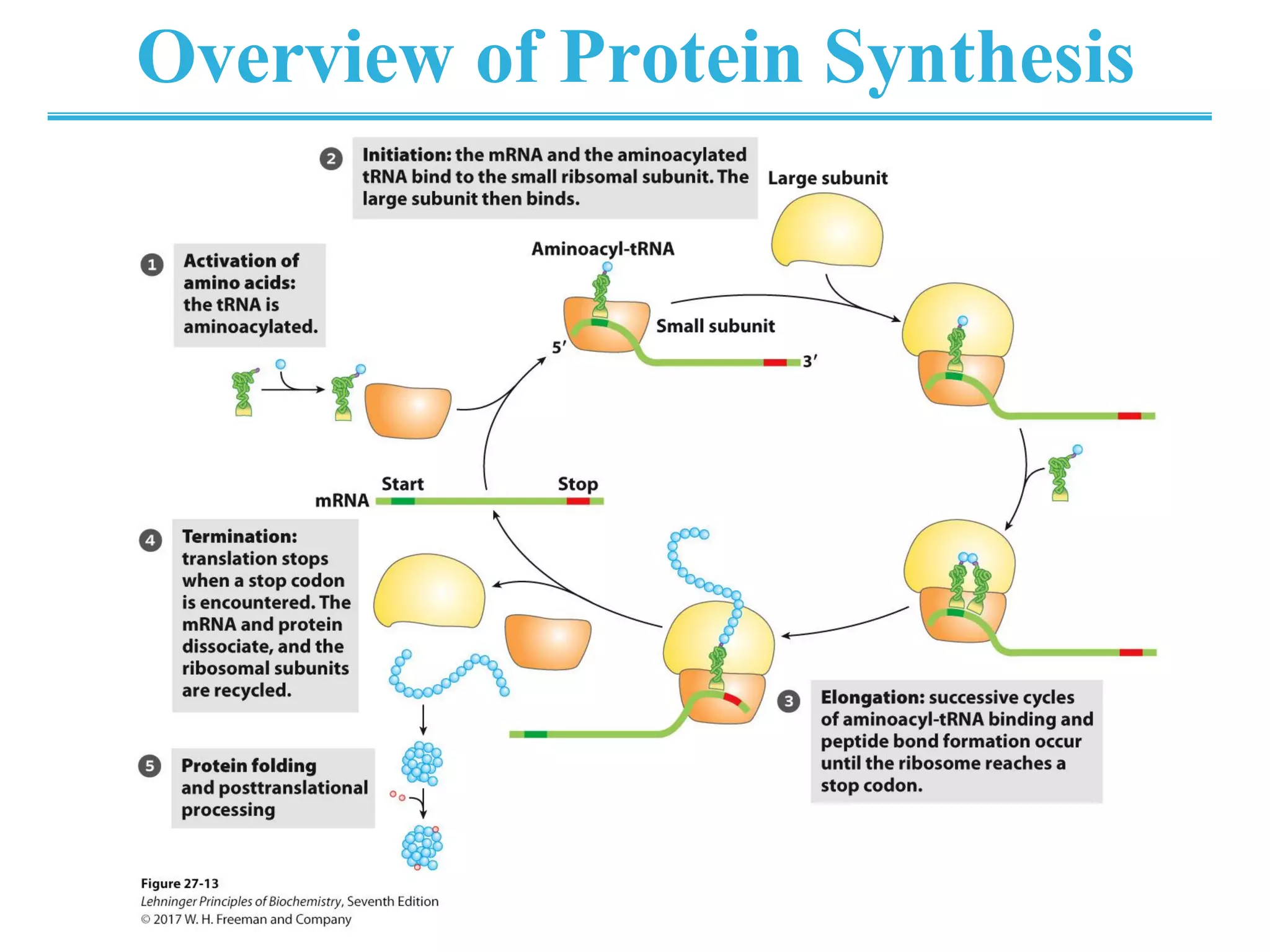
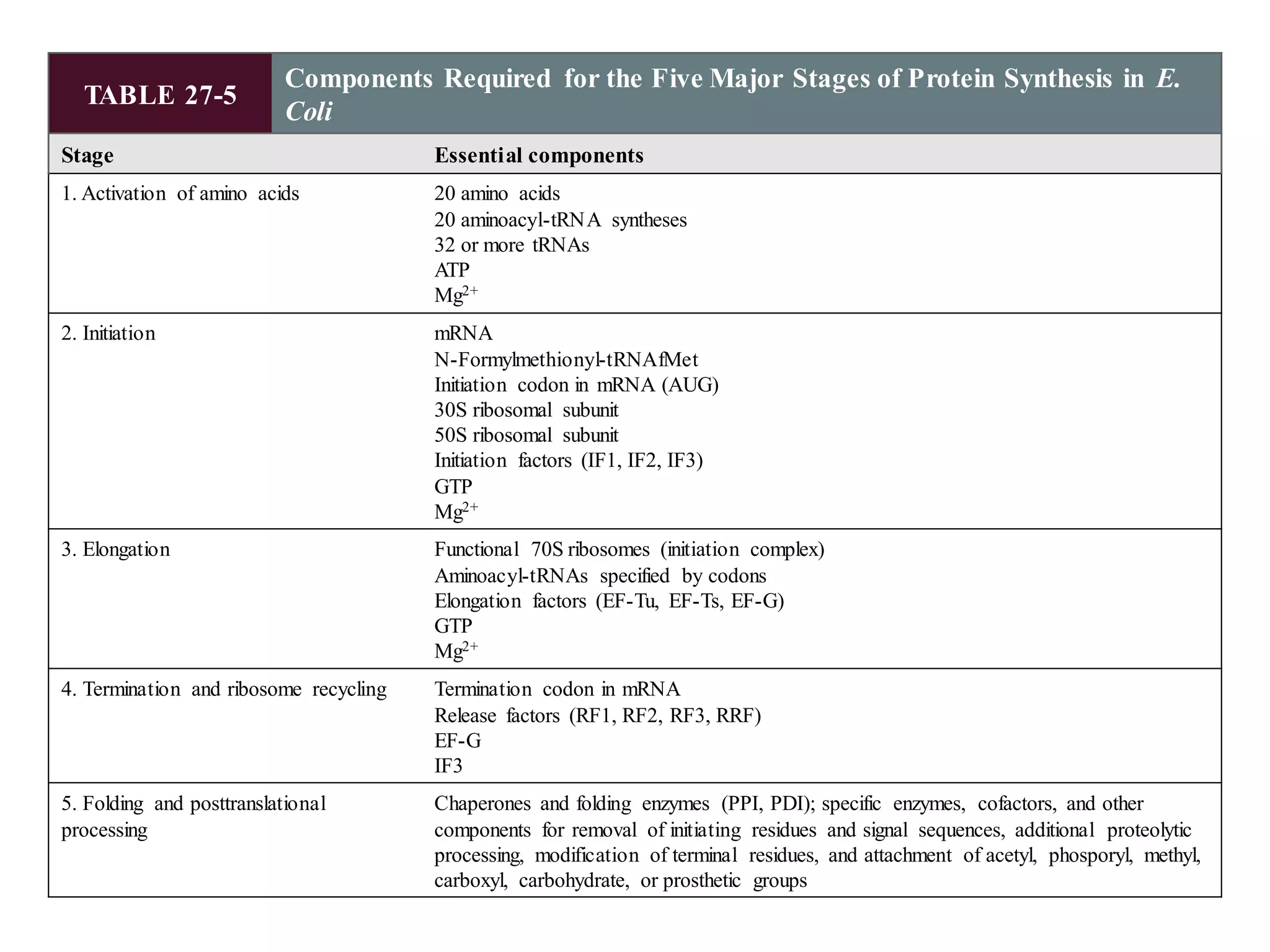
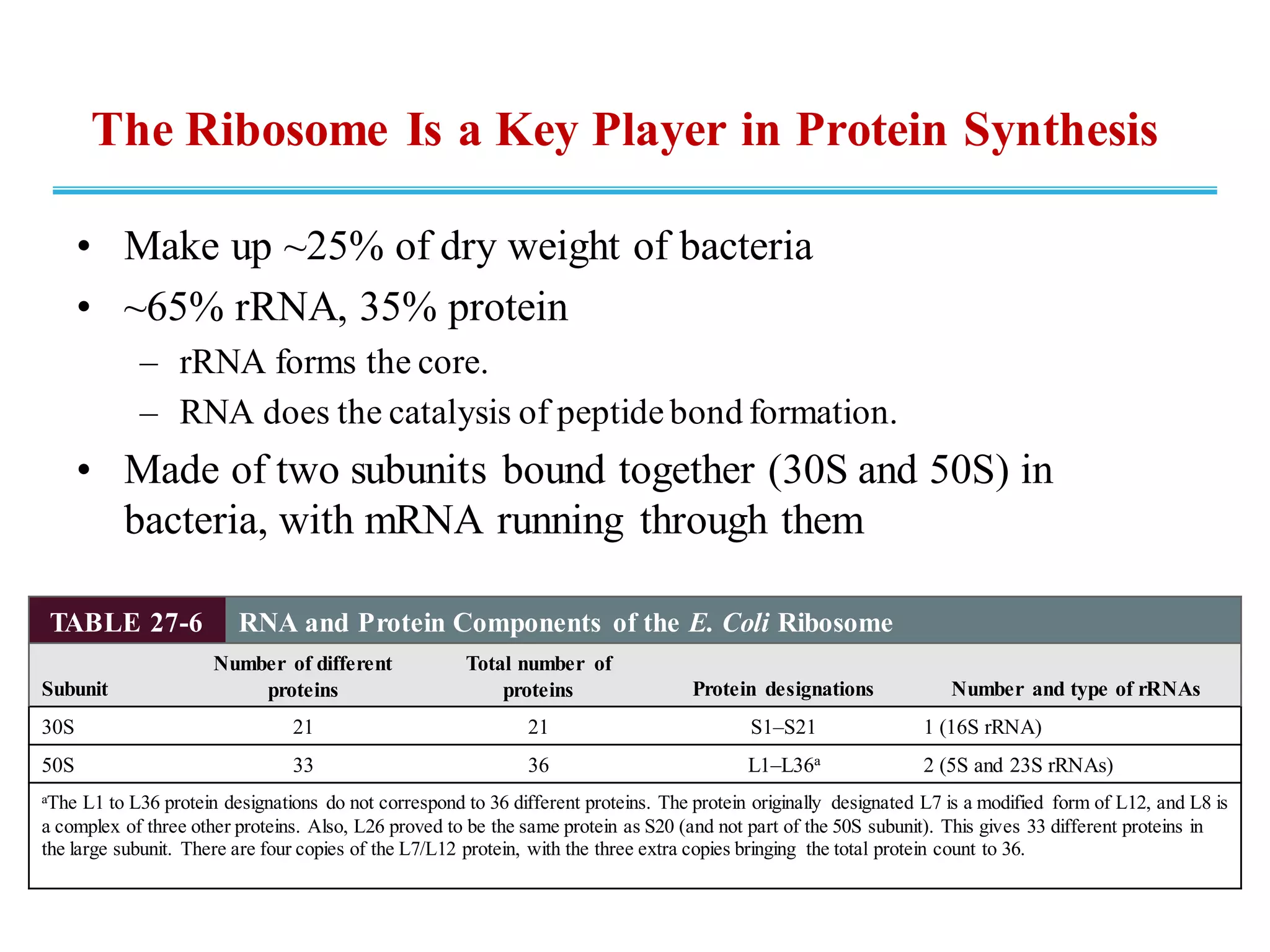
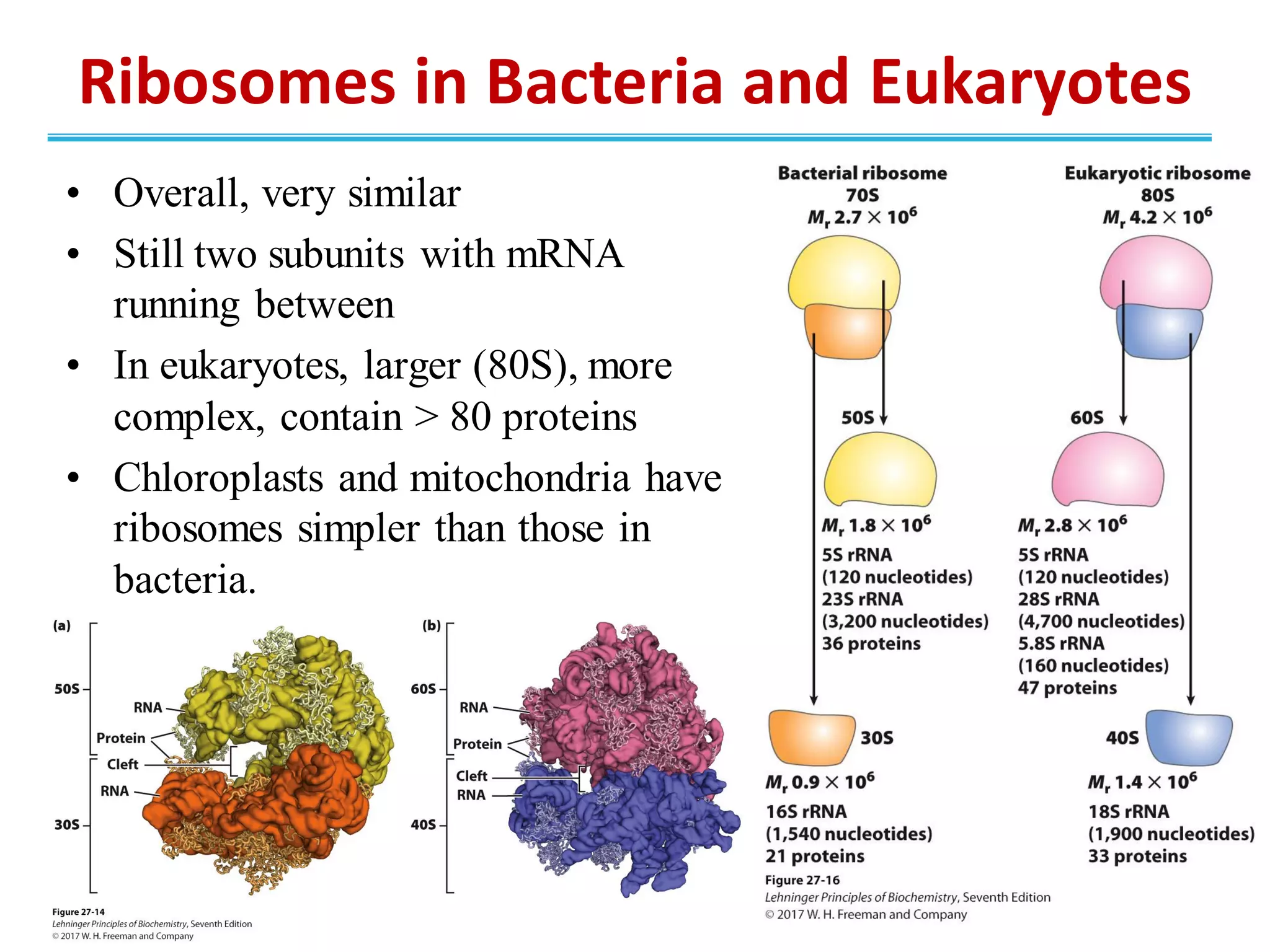
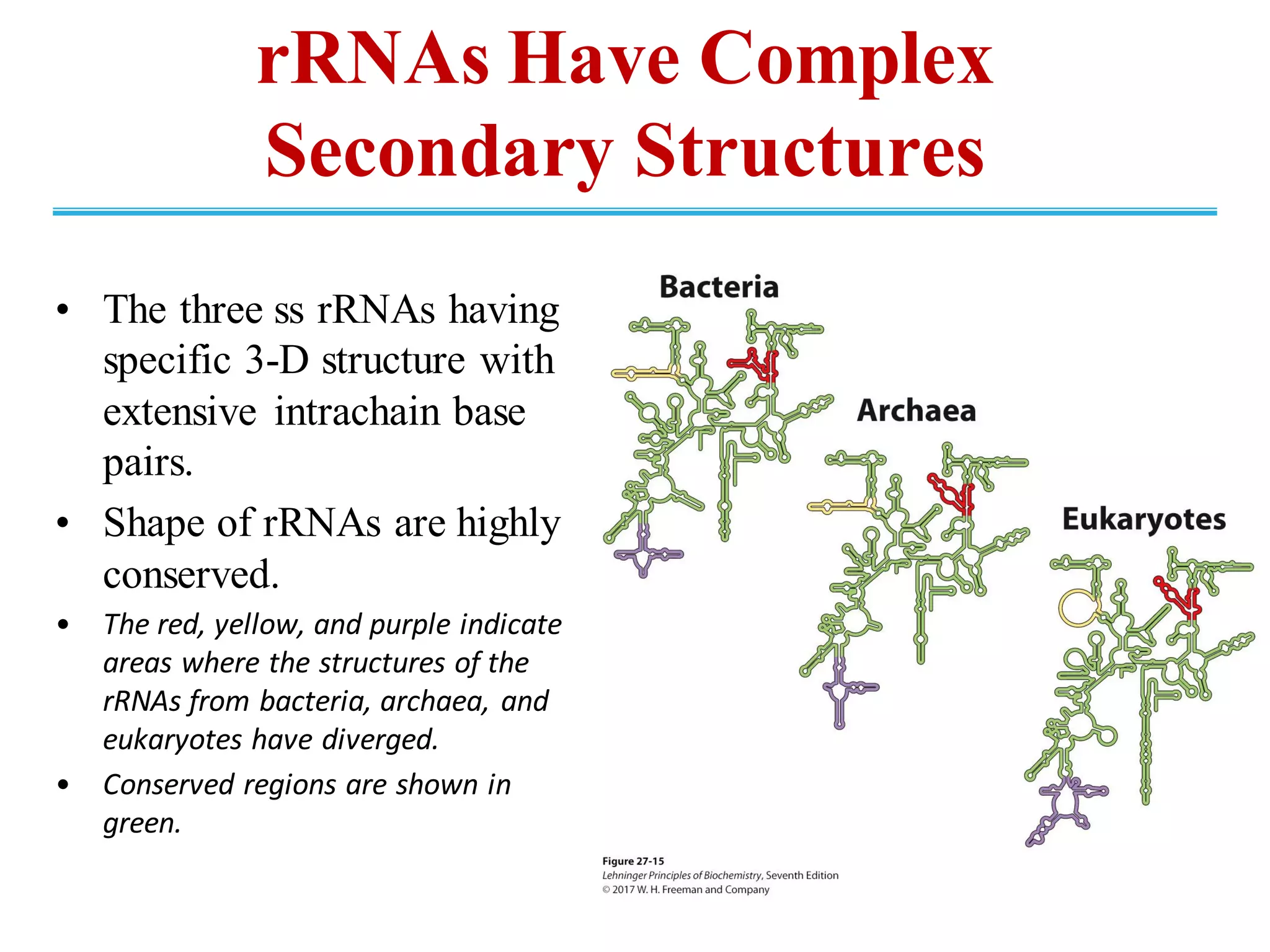
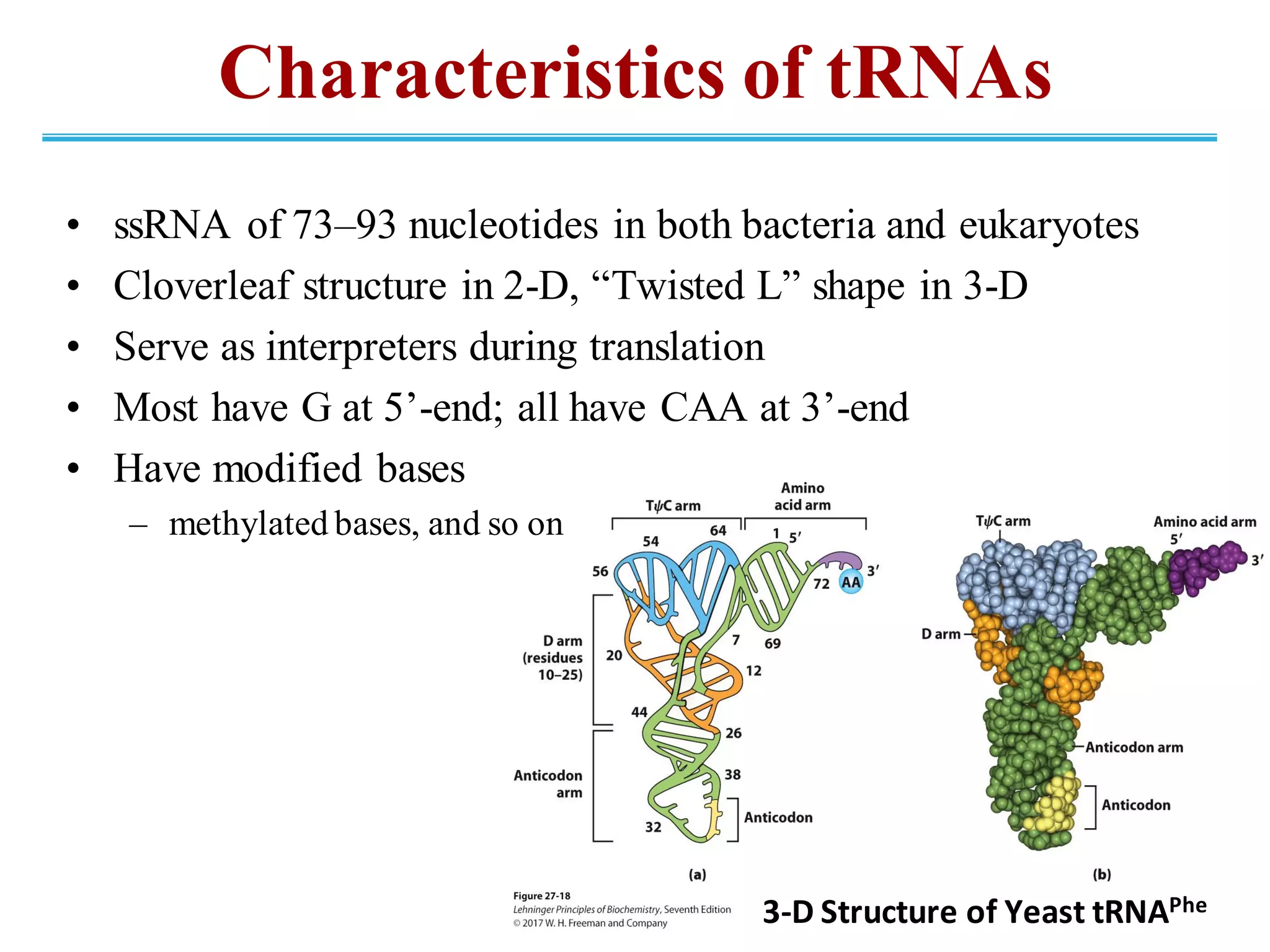
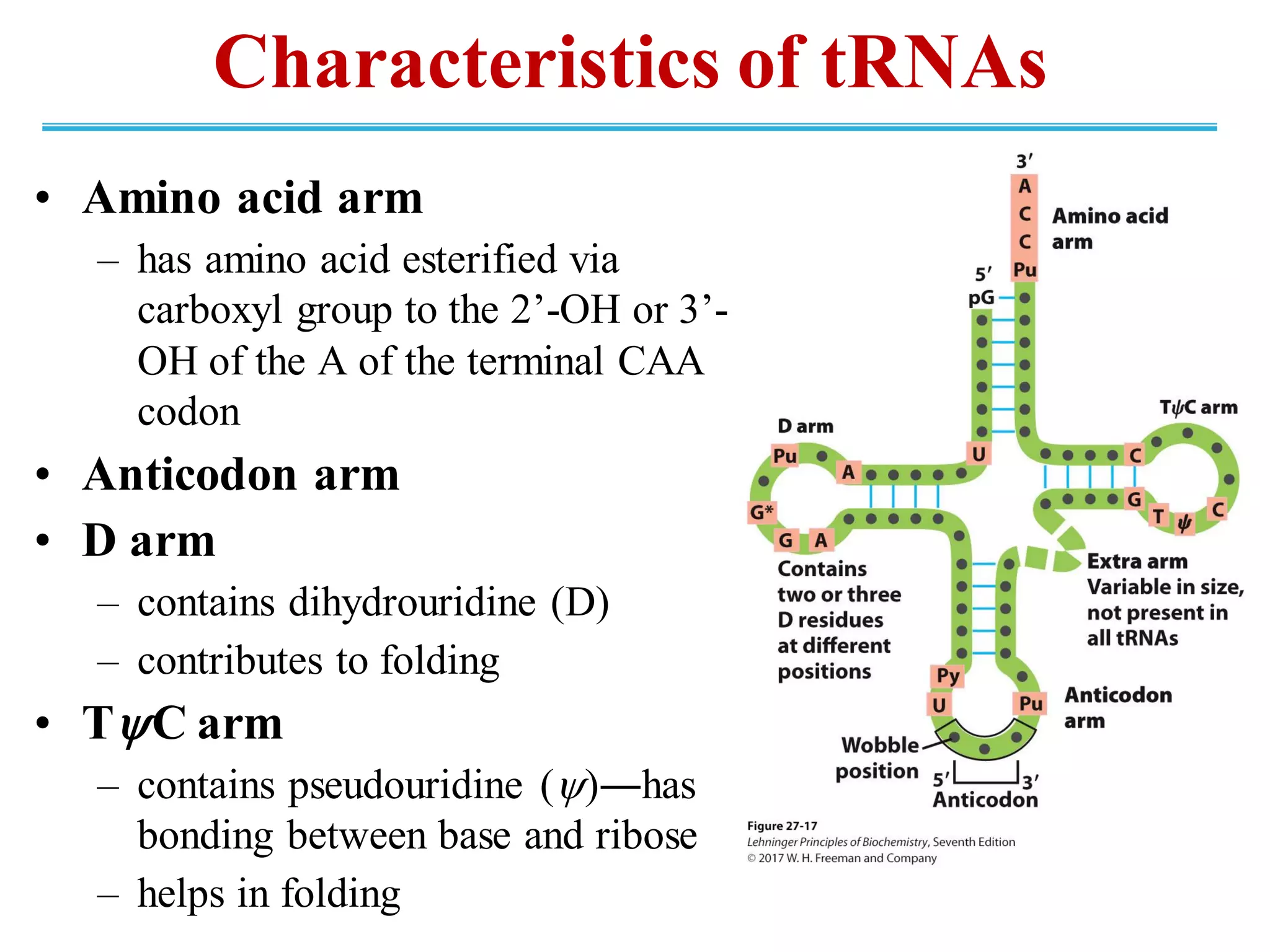
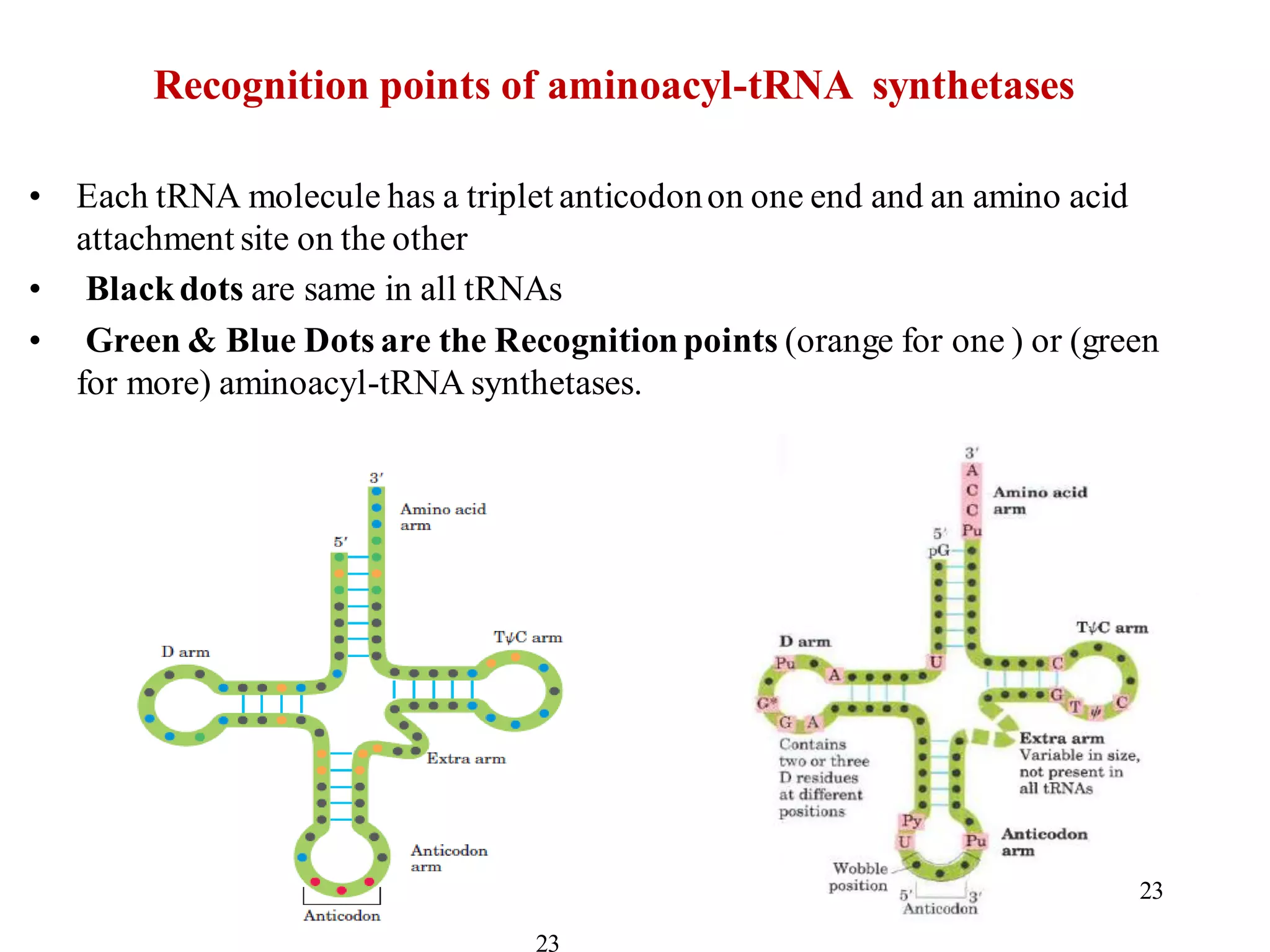
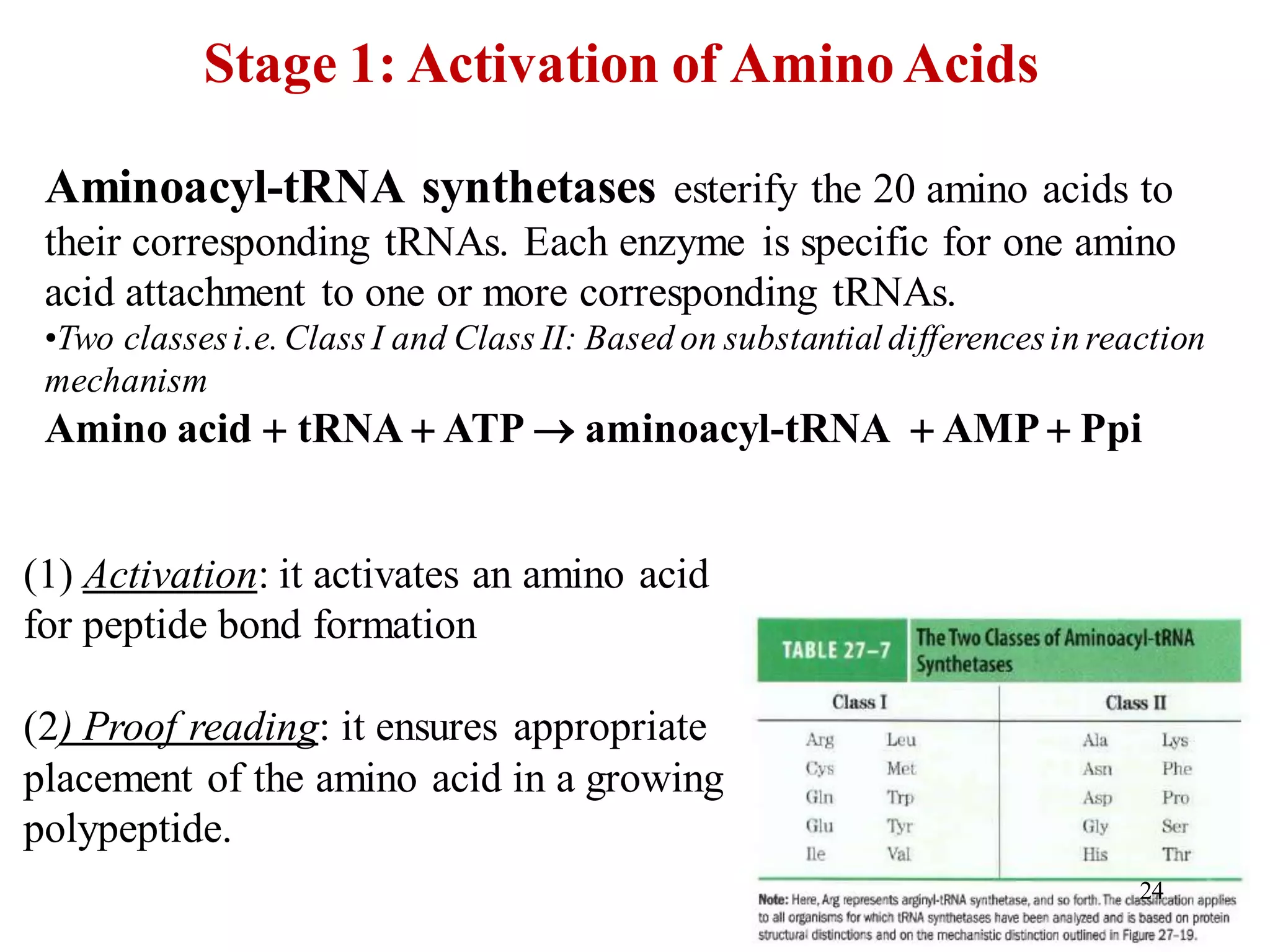
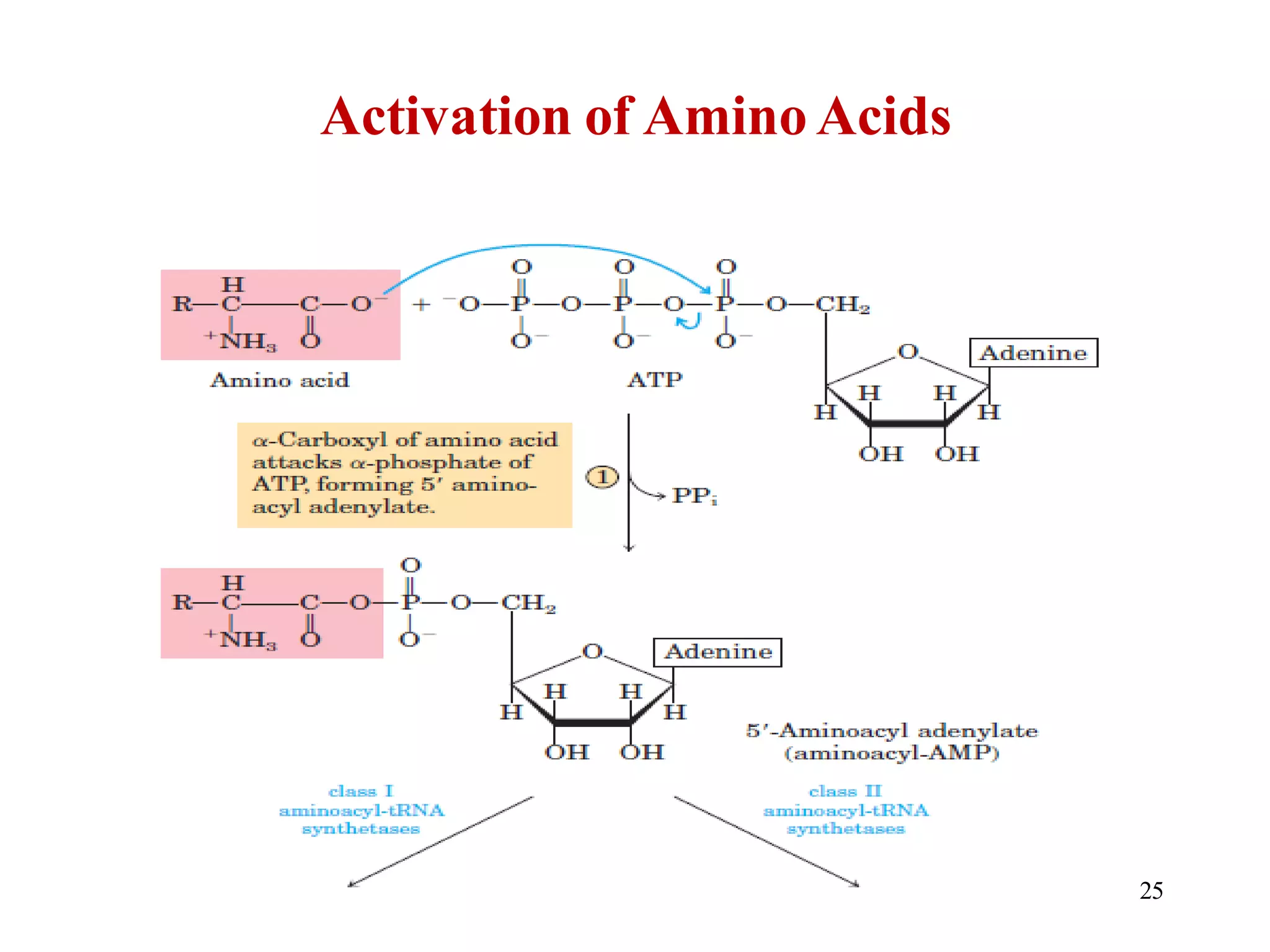
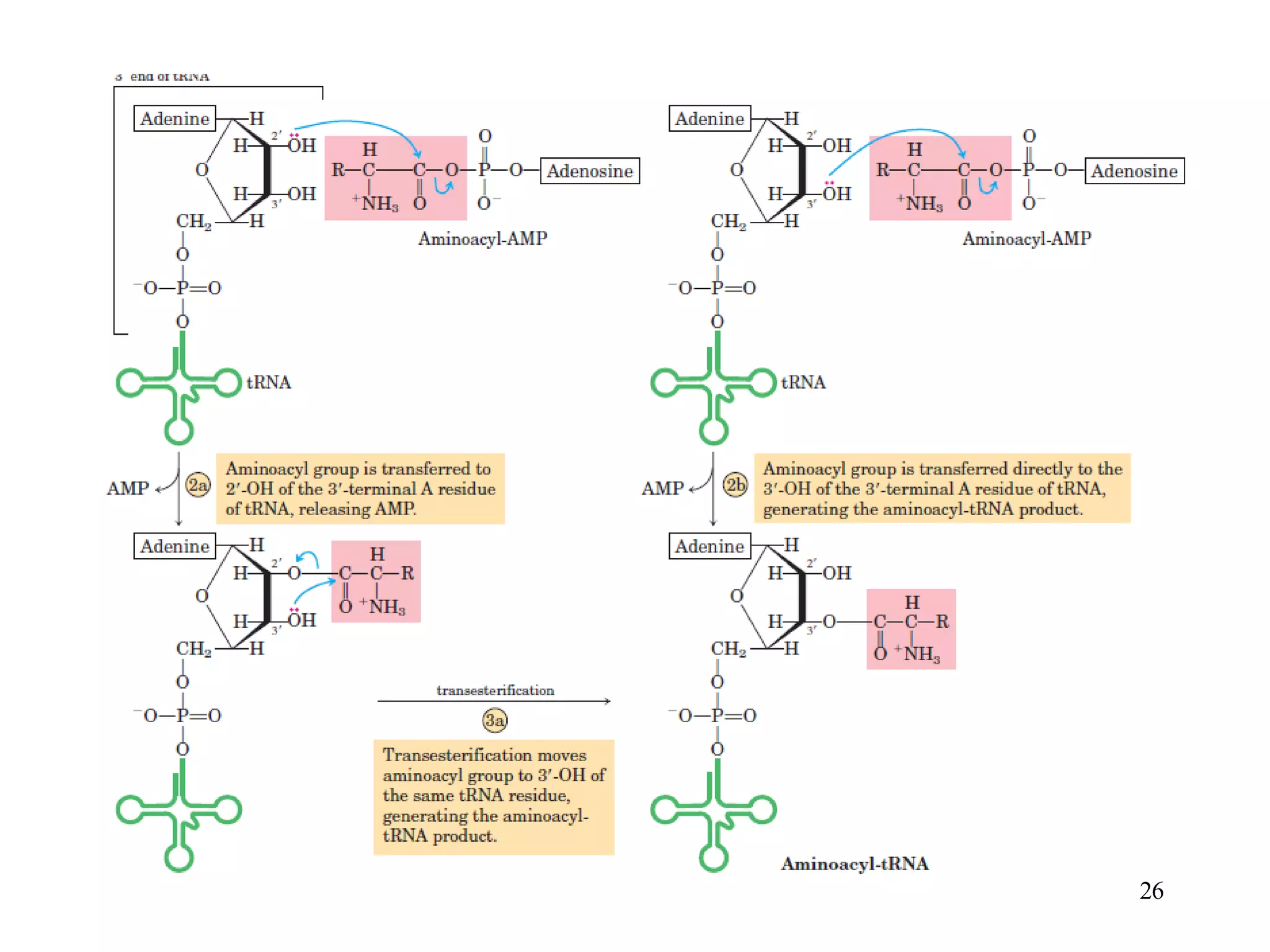
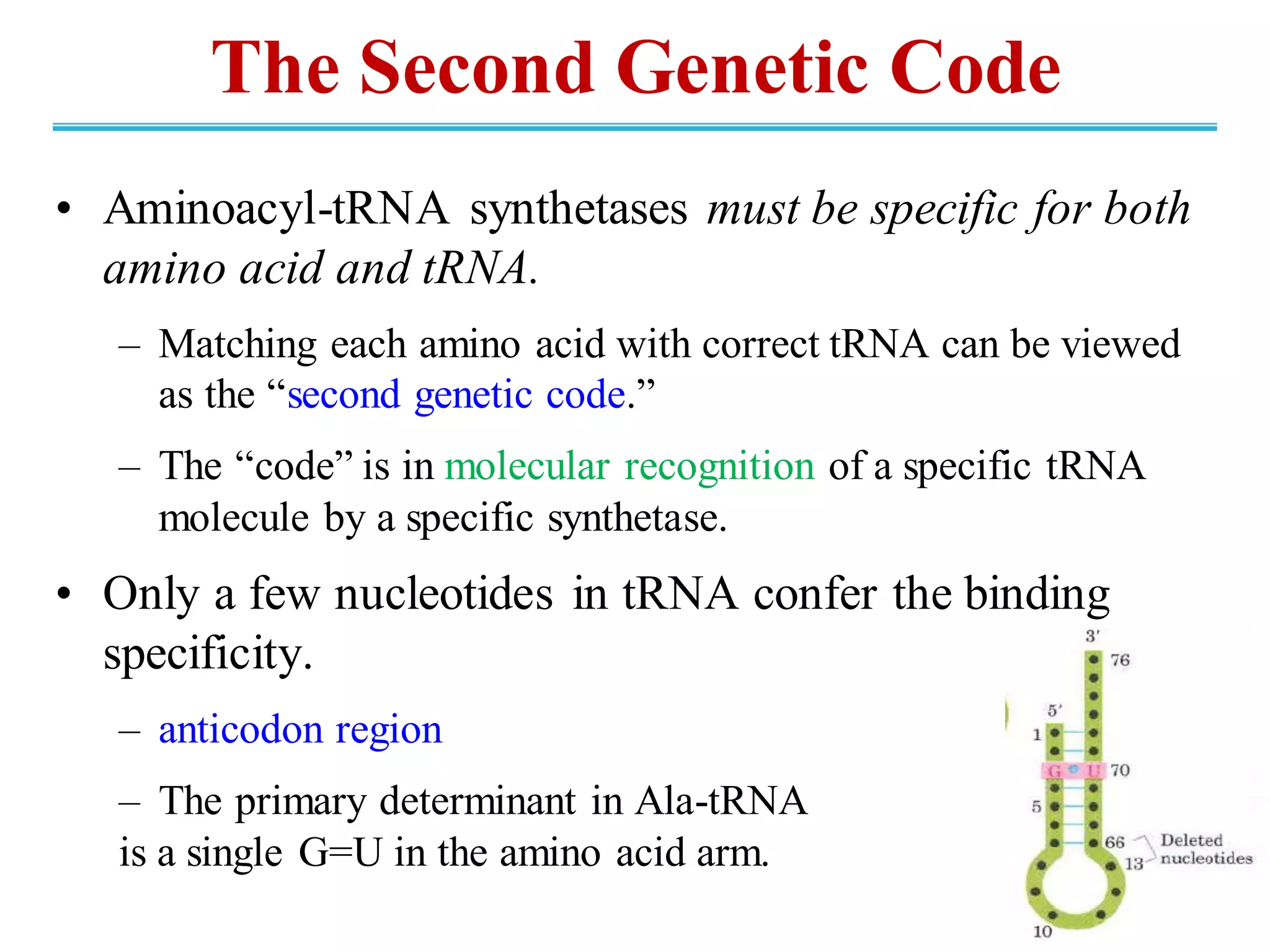
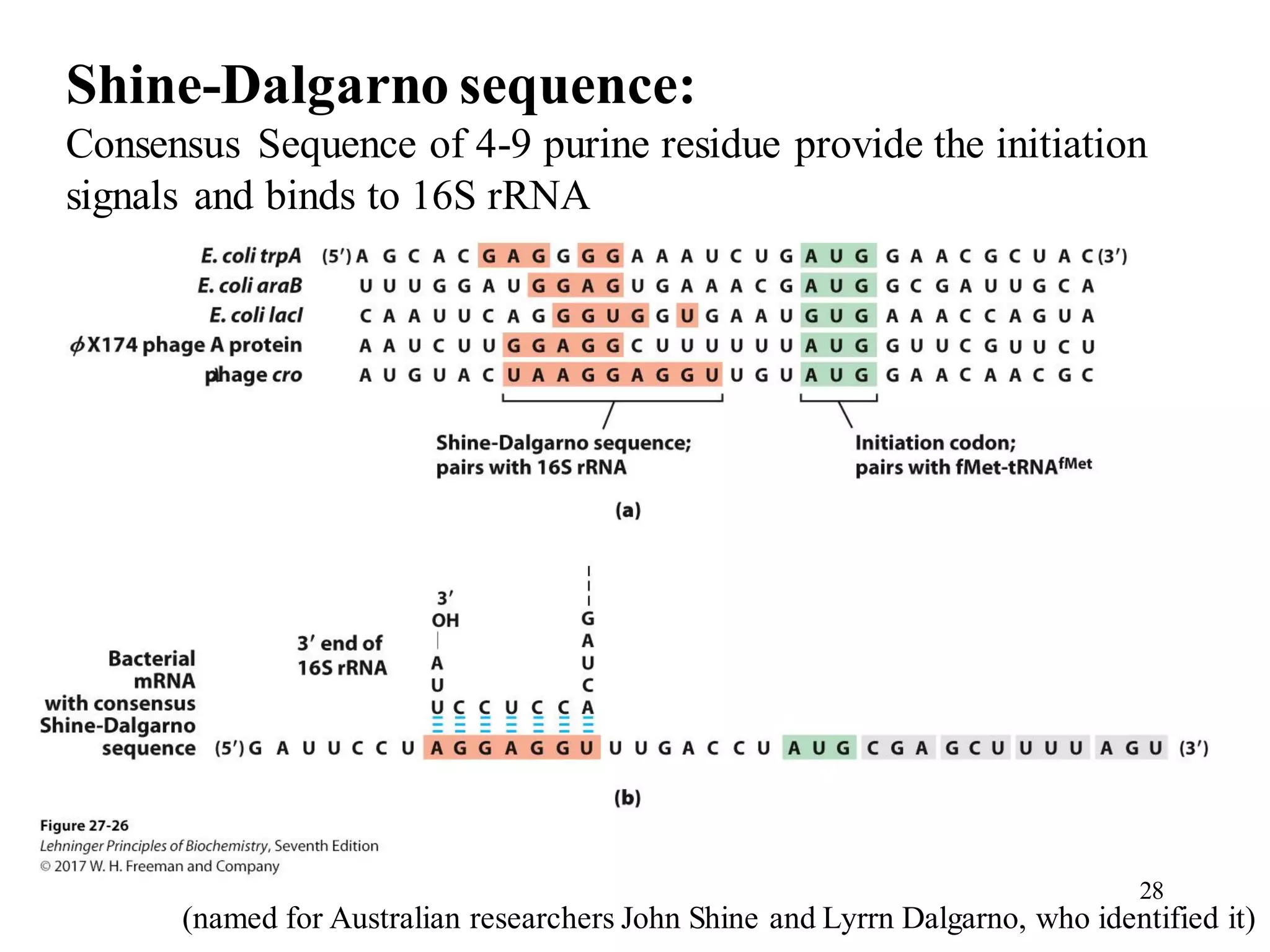
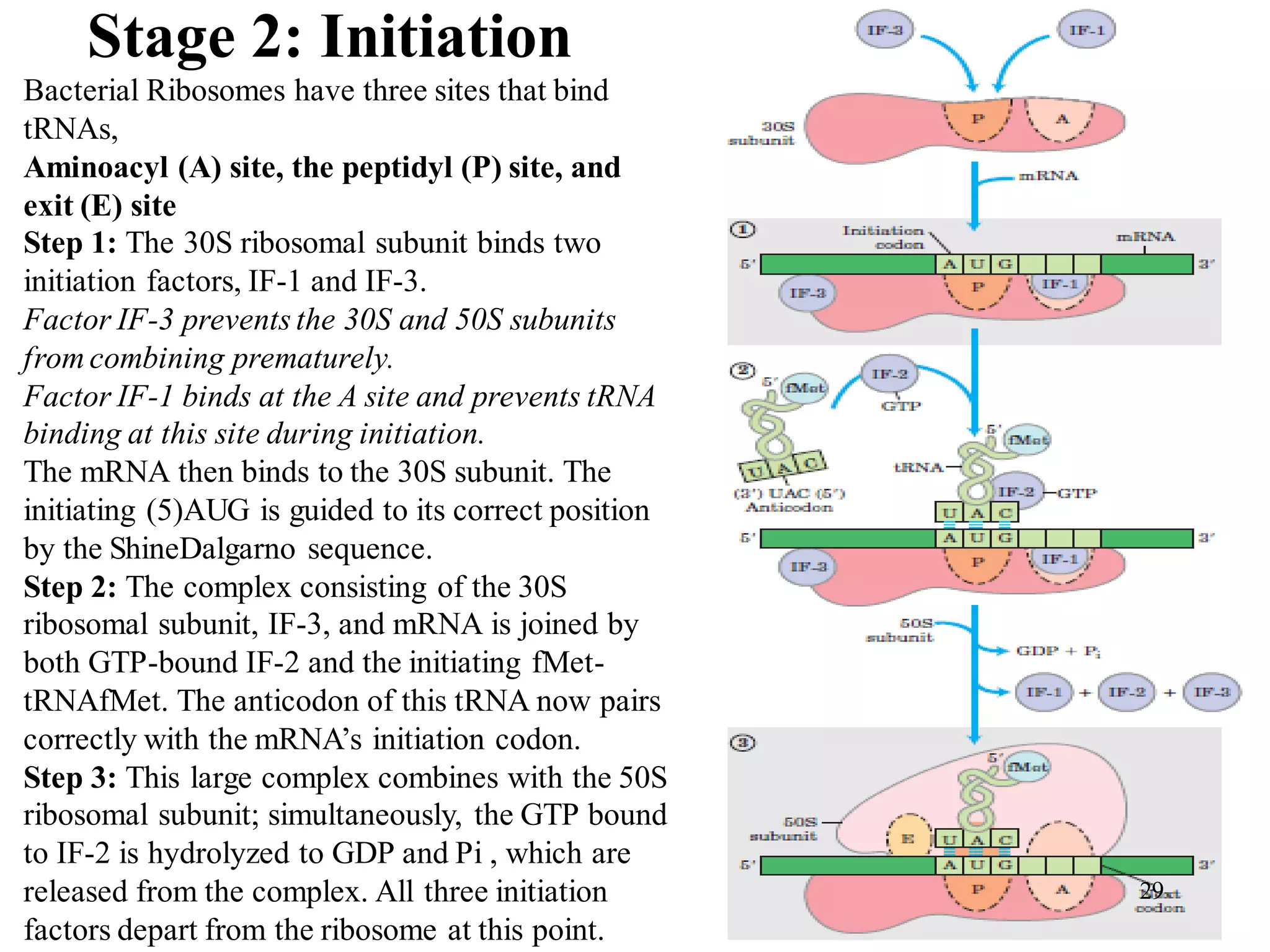
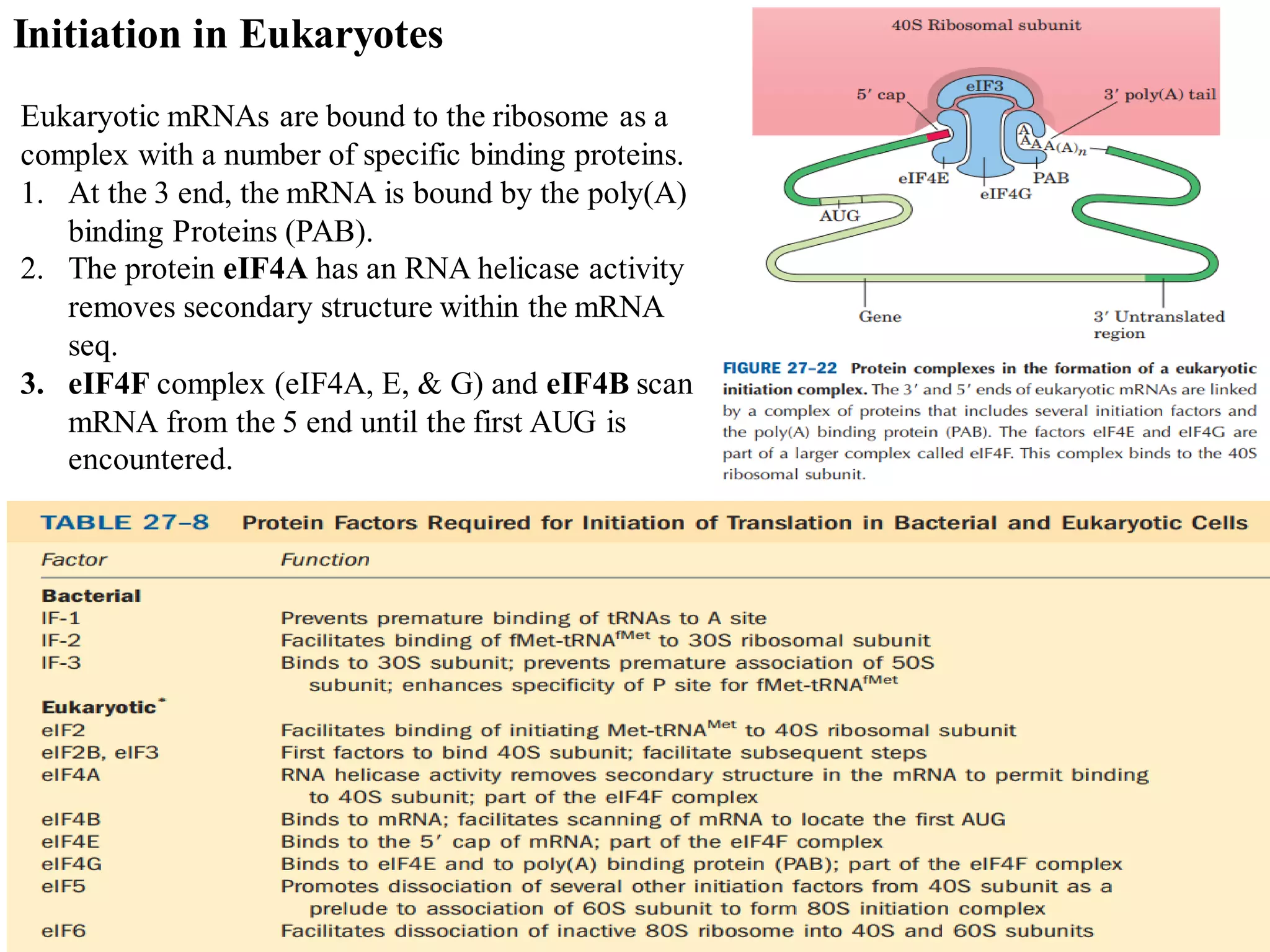
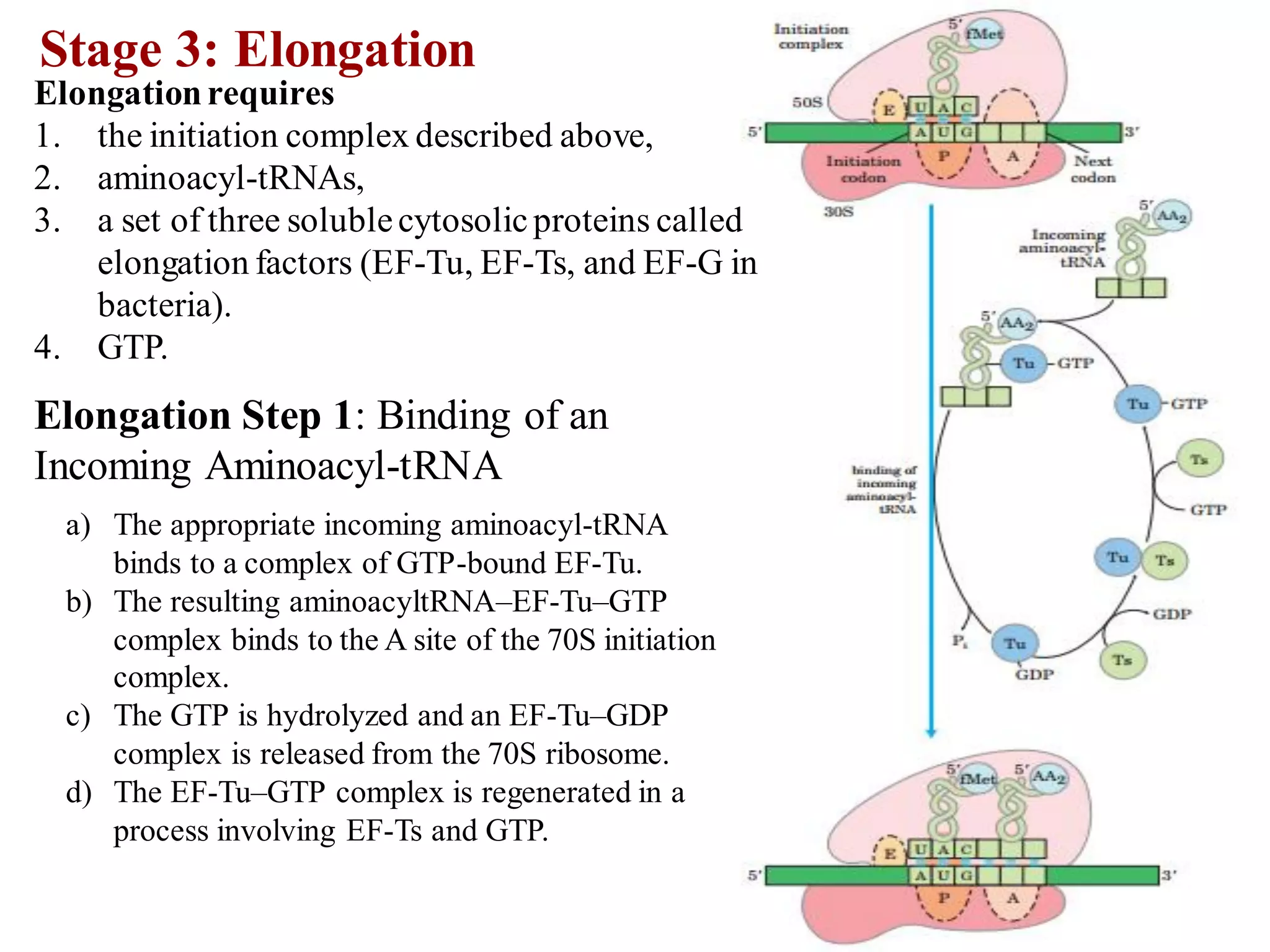
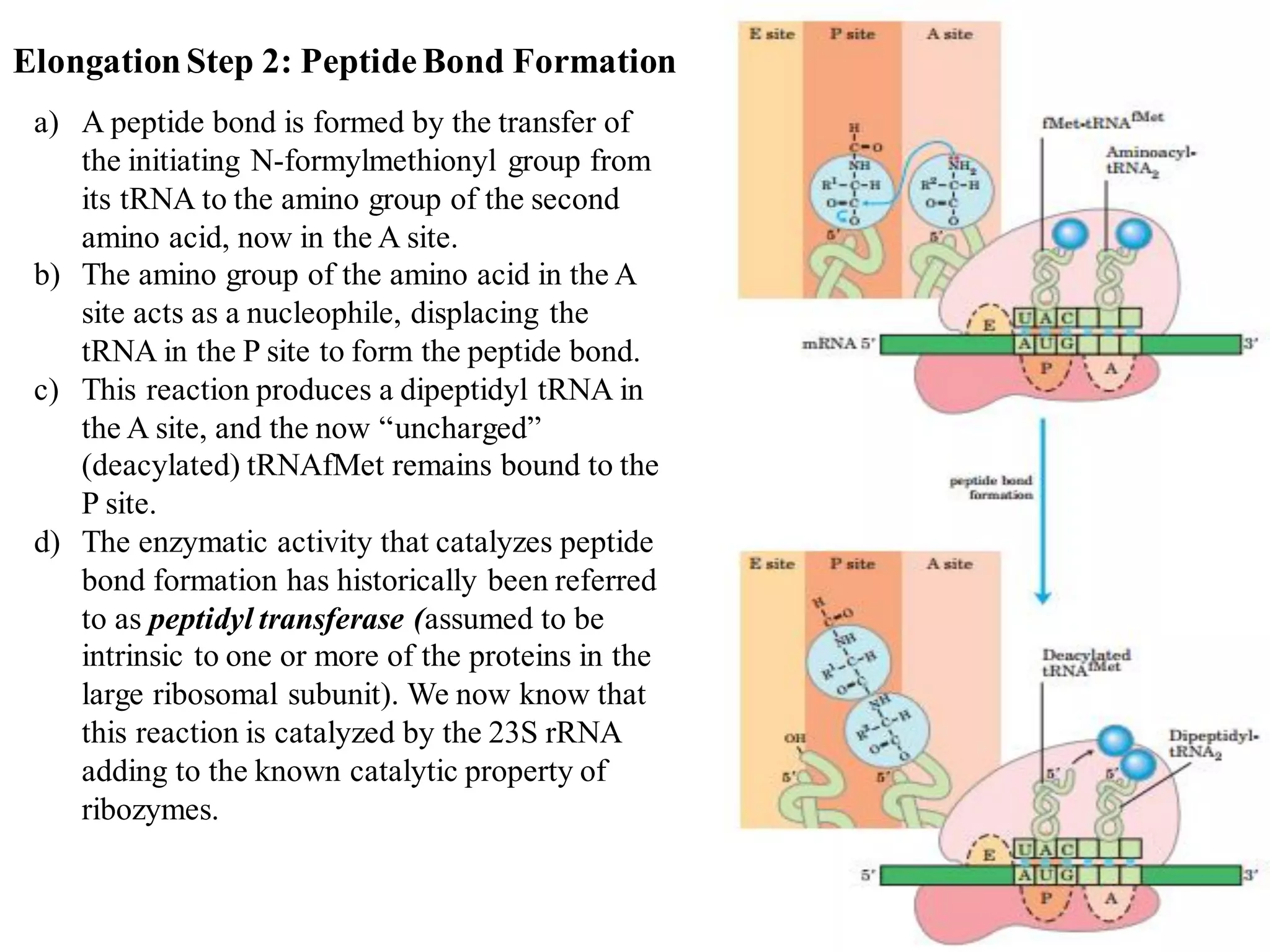
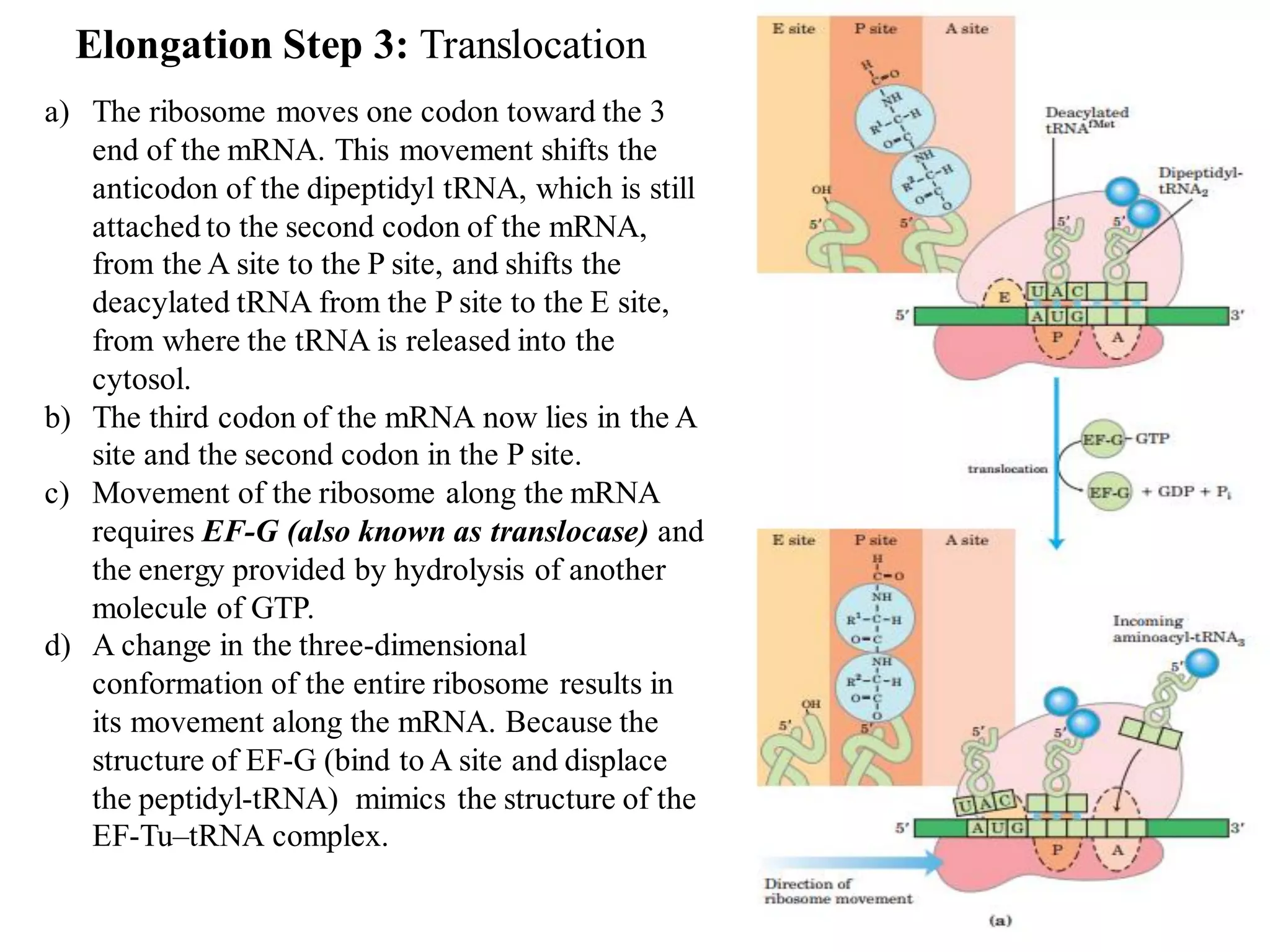
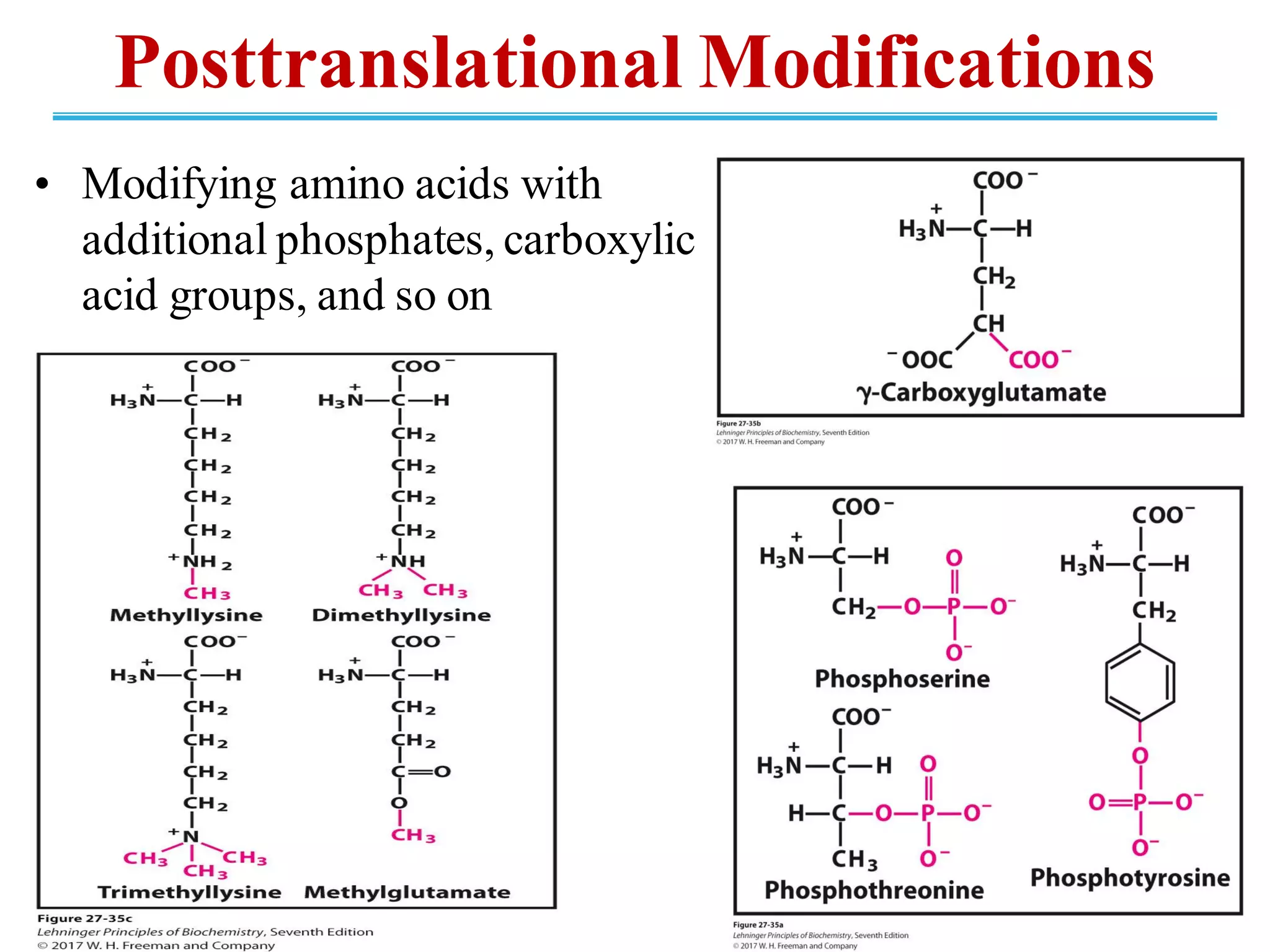
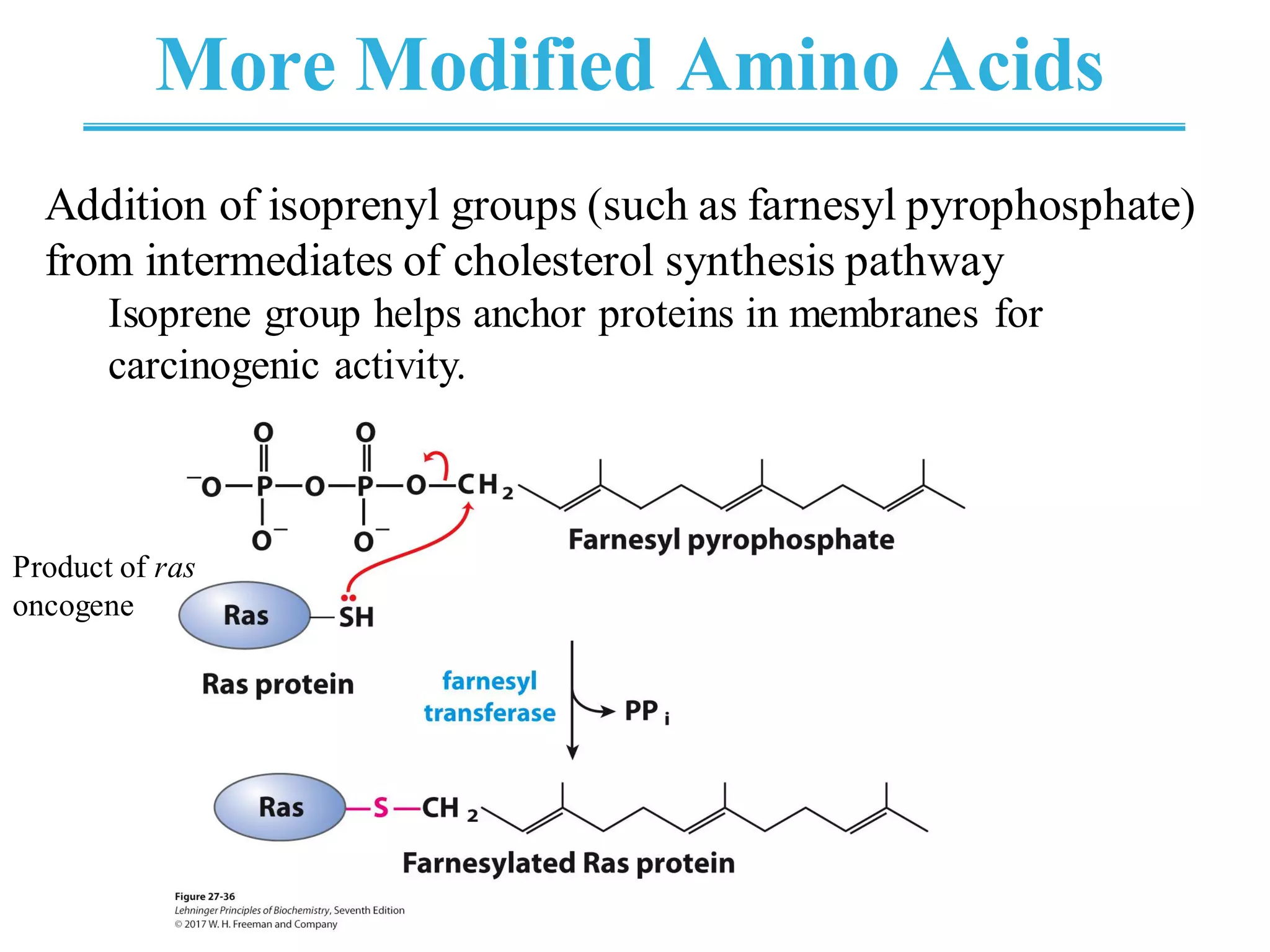
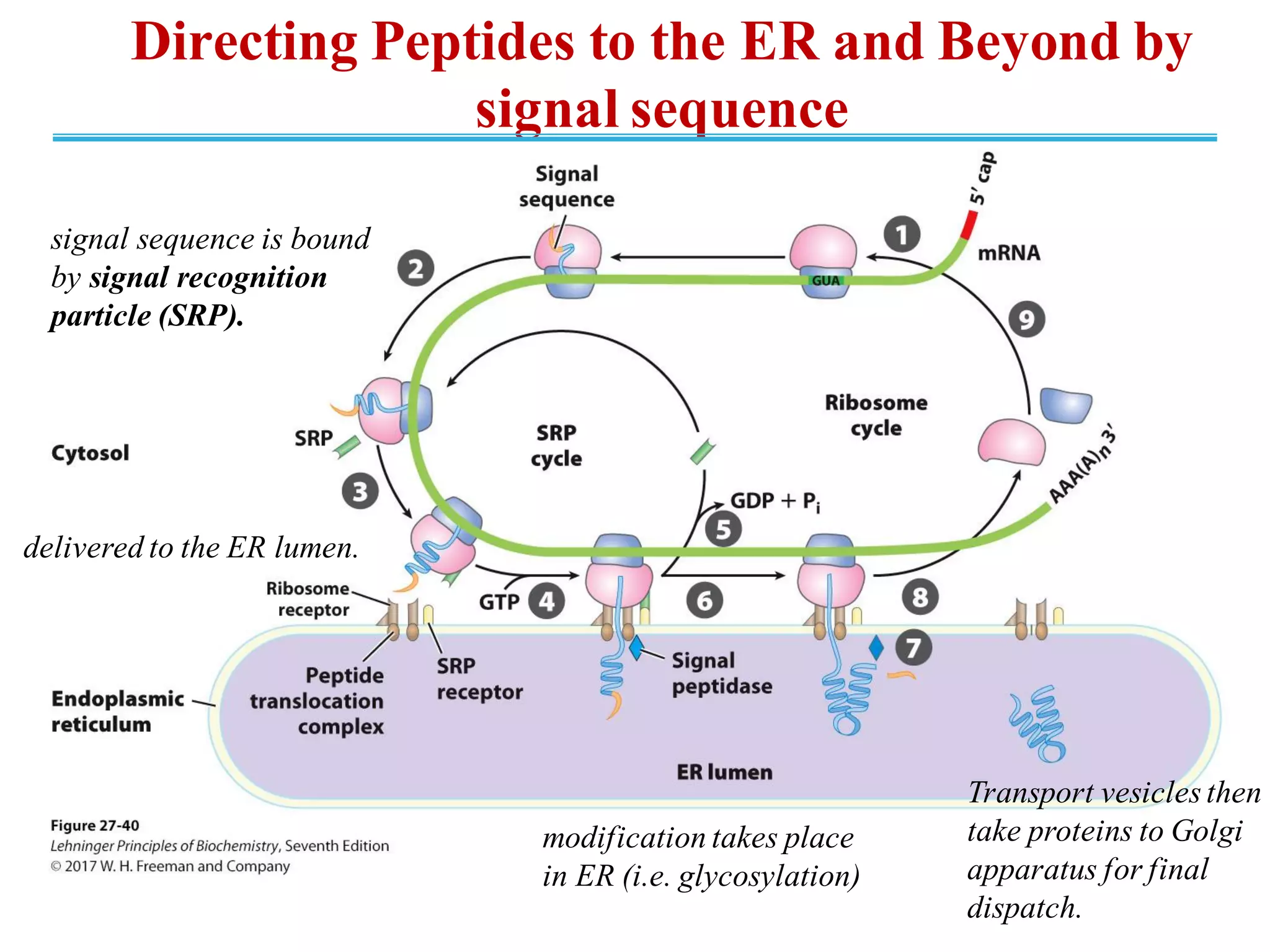
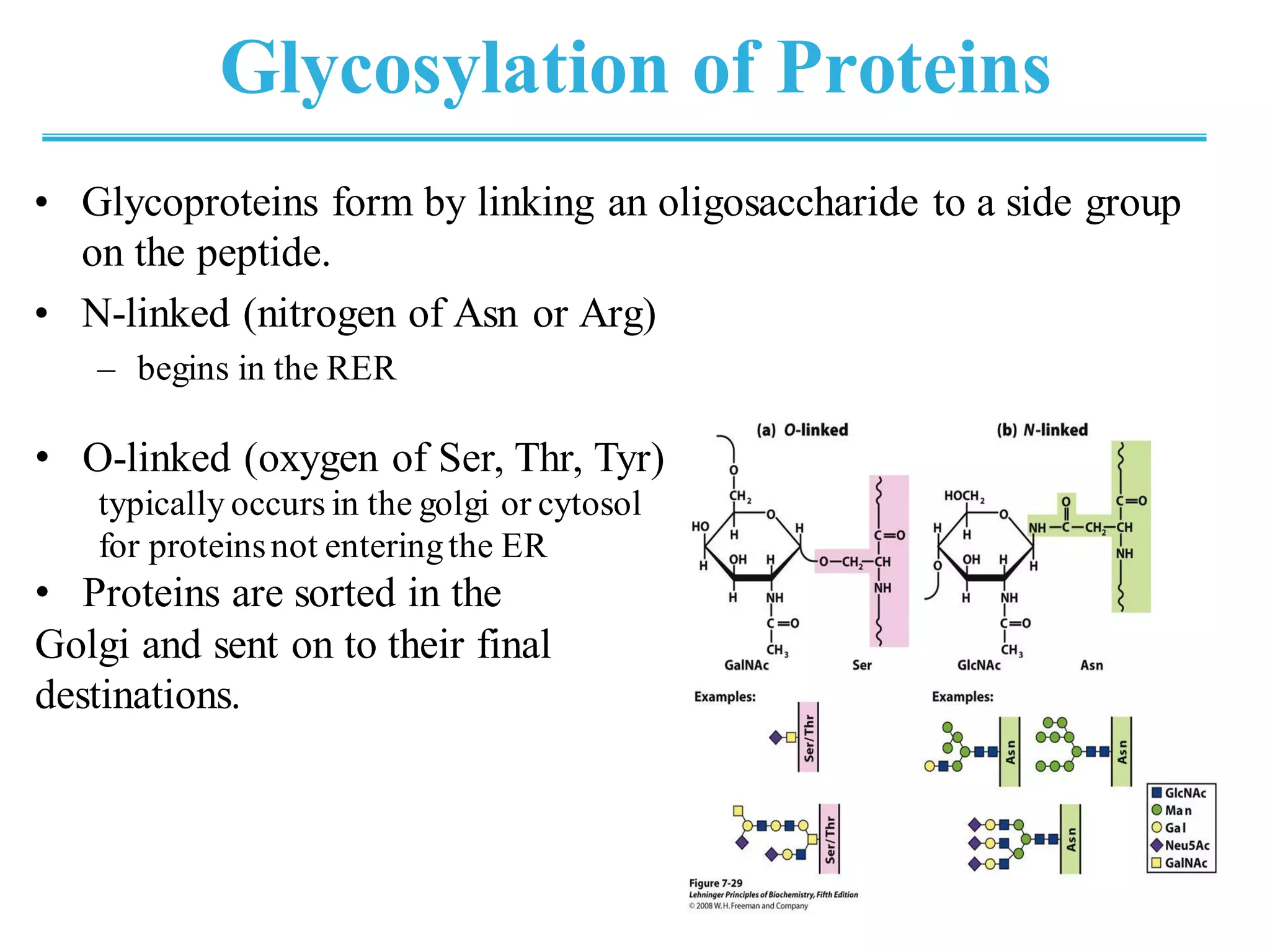
The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in DNA is translated into proteins by living cells. It specifies how sequences of nucleotides in mRNA are used to direct protein synthesis through codon-anticodon interactions between mRNA and tRNA. The genetic code is nearly universal, with some minor variations, and is written in the 5' to 3' direction on mRNA. It uses 64 possible codon combinations to specify 20 standard amino acids and 3 stop codons.