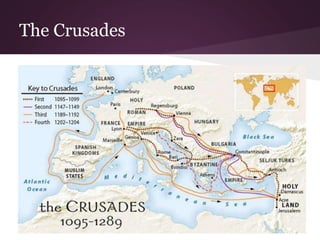
1) Medieval Christianity had a strong influence on all aspects of life, including rituals, prayer, fasting, and tithing. The Crusades aimed to retake Jerusalem from Muslim control.
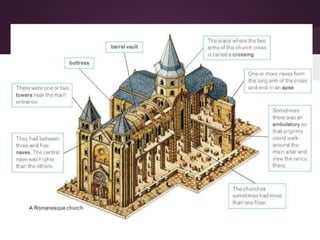
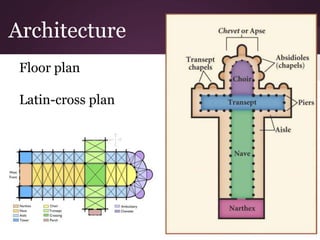
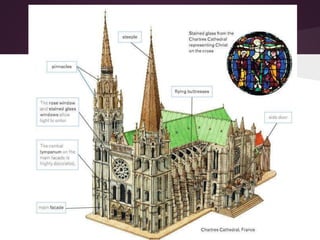
2) Romanesque art from the 11th-12th centuries aimed to spread religion through symbolic sculptures and paintings in churches. Architecture used stone and thick walls with small windows.
3) In the 13th century, urban culture grew as cities commissioned art, universities were founded, and new mendicant orders emerged to serve in cities instead of monasteries.