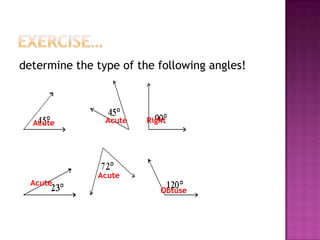
Here are the questions rewritten in hexadecimal system:
1. Find the angle formed by the hour and minute hands of a clock at 10:45.
2. Find the angle formed by the hour and minute hands of a clock at 5:15.
3. Find the angle formed by the hour and minute hands of a clock at 2:30.
4. Find the angle formed by the hour and minute hands of a clock at 11:30.
5. Find the angle formed by the hour and minute hands of a clock at 7:00.
Back