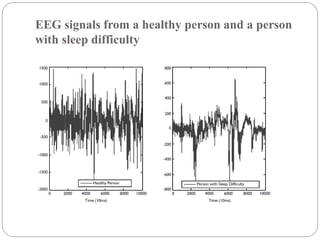
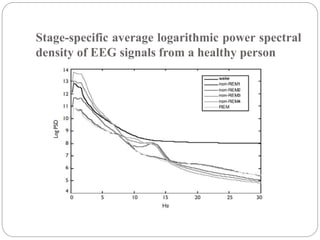
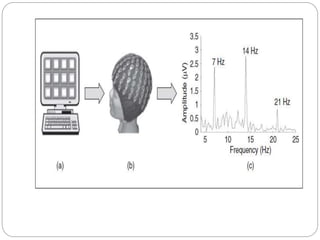
This document discusses two main applications of EEG waves: diagnosis of sleep disorders and brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). For sleep disorder diagnosis, EEG signals are analyzed to stage sleep and identify abnormalities. Statistical methods classify sleep stages over time. BCIs translate brain signals into commands, using visual evoked potentials from stimuli flickering at different frequencies to identify intended commands. Key issues discussed include reducing electrode numbers and optimizing frequency feature extraction from EEG signals to improve BCI accuracy and usability.