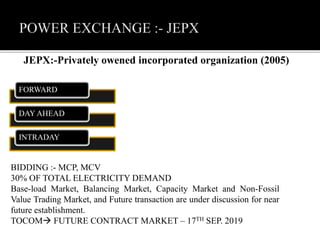
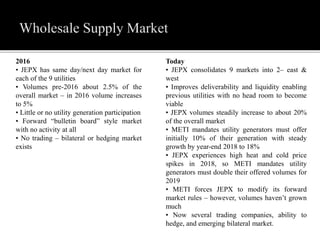
1. Japan has two interconnected power grids operating at different frequencies that are connected by a 1.2 GW HVDC link. It has the second highest pumped storage capacity and is the third largest producer of solar power.
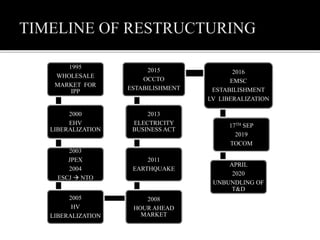
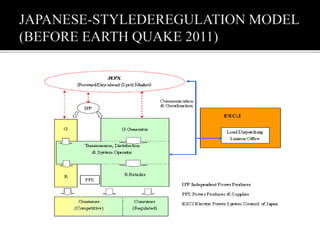
2. Following the 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster, Japan restructured its power sector to increase competition and diversify its energy mix away from nuclear and fossil fuels. This included establishing independent system operators and power exchanges to liberalize the market.
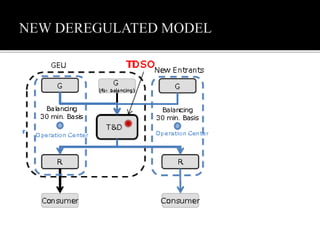
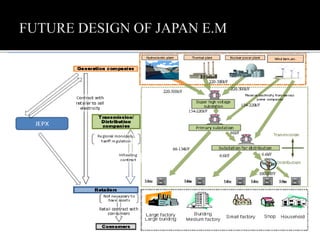
3. Reforms over the past decade have included establishing a capacity market, requiring utilities to divest generation assets, and mandating greater participation in wholesale markets. These changes aim to improve security of supply, reduce costs for consumers, and expand business opportunities in the power










![[1] A. Yanagisawa et al., “Economic and Energy Outlook of Japan through FY2019.
Decelerating growth and growing disquiets.,” no. July, pp. 1–30, 2018.
[2] T. Shinkawa, “Electricity System and Market in Japan,” IT World, no. March, 2018.
[3] I. Kurihara, “Deregulation of Electric Power Industry in Japan and the Present Practice,” pp.
143–146, 2000.
[4] H. Asano, “Restructuring the electricity industry and emerging issues in Japan,” 3rd Int.
Conf. Deregul. Restruct. Power Technol. DRPT 2008, no. April, pp. 162–166, 2008.
[5] International Atomic Energy Agency, “Country Nuclear Power Profiles – Germany,” 2018.
[6] I. Kurihara, “Restructuring of the electric power industry and the current state of the power
market in Japan,” 2006 IEEE Power Eng. Soc. Gen. Meet. PES, pp. 1–6, 2006.
[7] M. Marmiroli and Y. Tsukamoto, “Technical impact of deregulation in Japan [power
industry],” PowerCon 2002 - 2002 Int. Conf. Power Syst. Technol. Proc., vol. 1, pp. 178–181,
2002.
[8] “Classification of Businesses Specified in the Electricity Utilities Business Act ( extract from
the Act ),” p. 2019, 2019.
[9] T. C. Exchange, “Overview of TOCOM Electricity Market Electricity Market in Japan,” no.
September, 2019.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/japanpowersectorliberalizationrohitvijay-191119070439/85/Japan-power-sector-liberalization-17-320.jpg)