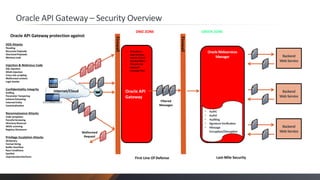
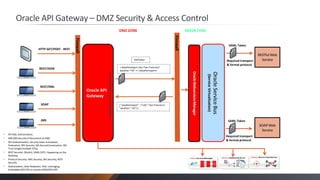
Oracle API Gateway integrates, accelerates, governs, and secures Web API and SOA-based systems. It serves REST APIs and SOAP Web Services to clients, converting between REST and SOAP and XML and JSON. It applies security rules like authentication and content filtering. It also provides monitoring of API and service usage, caching, and traffic management.