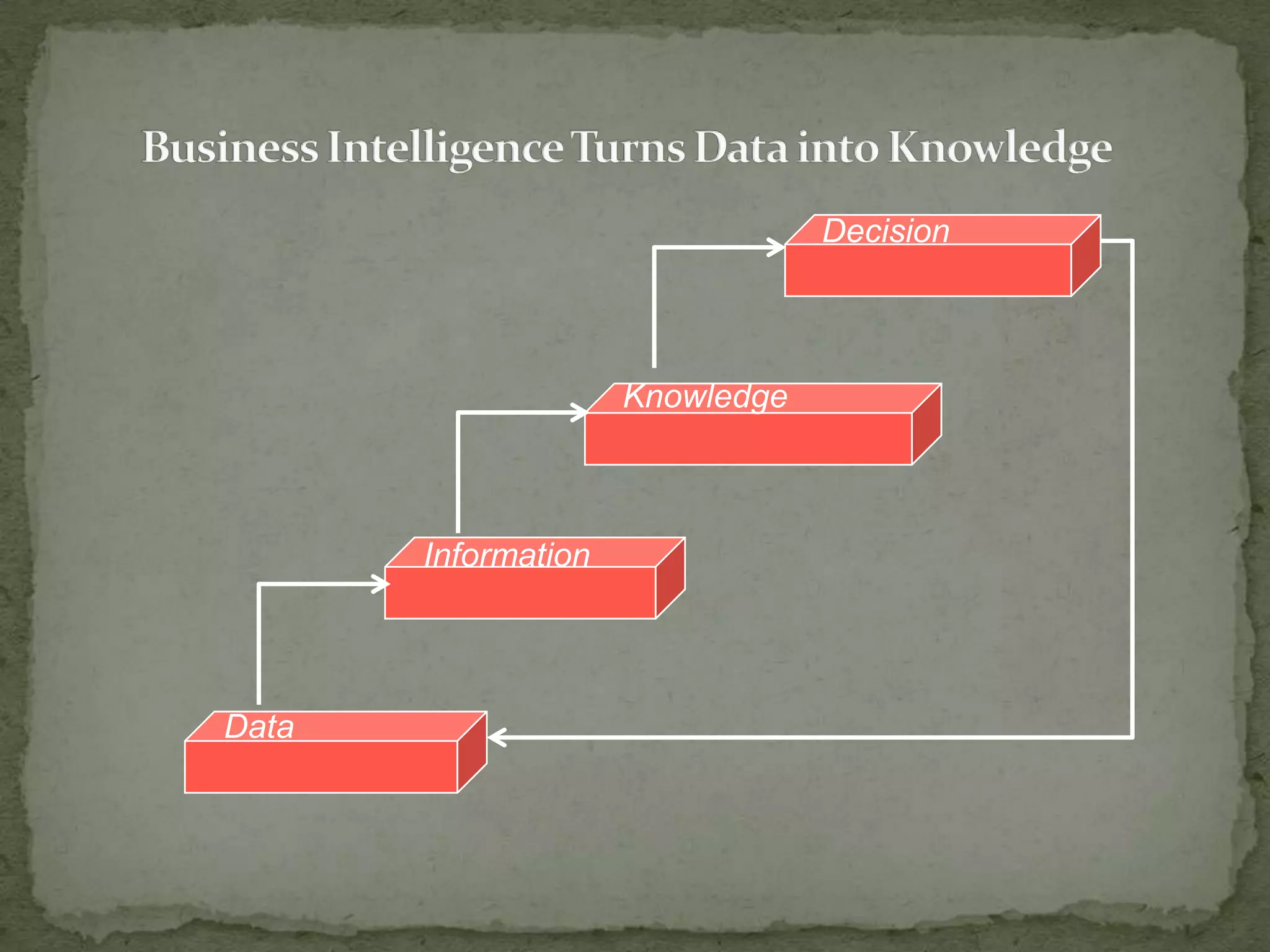
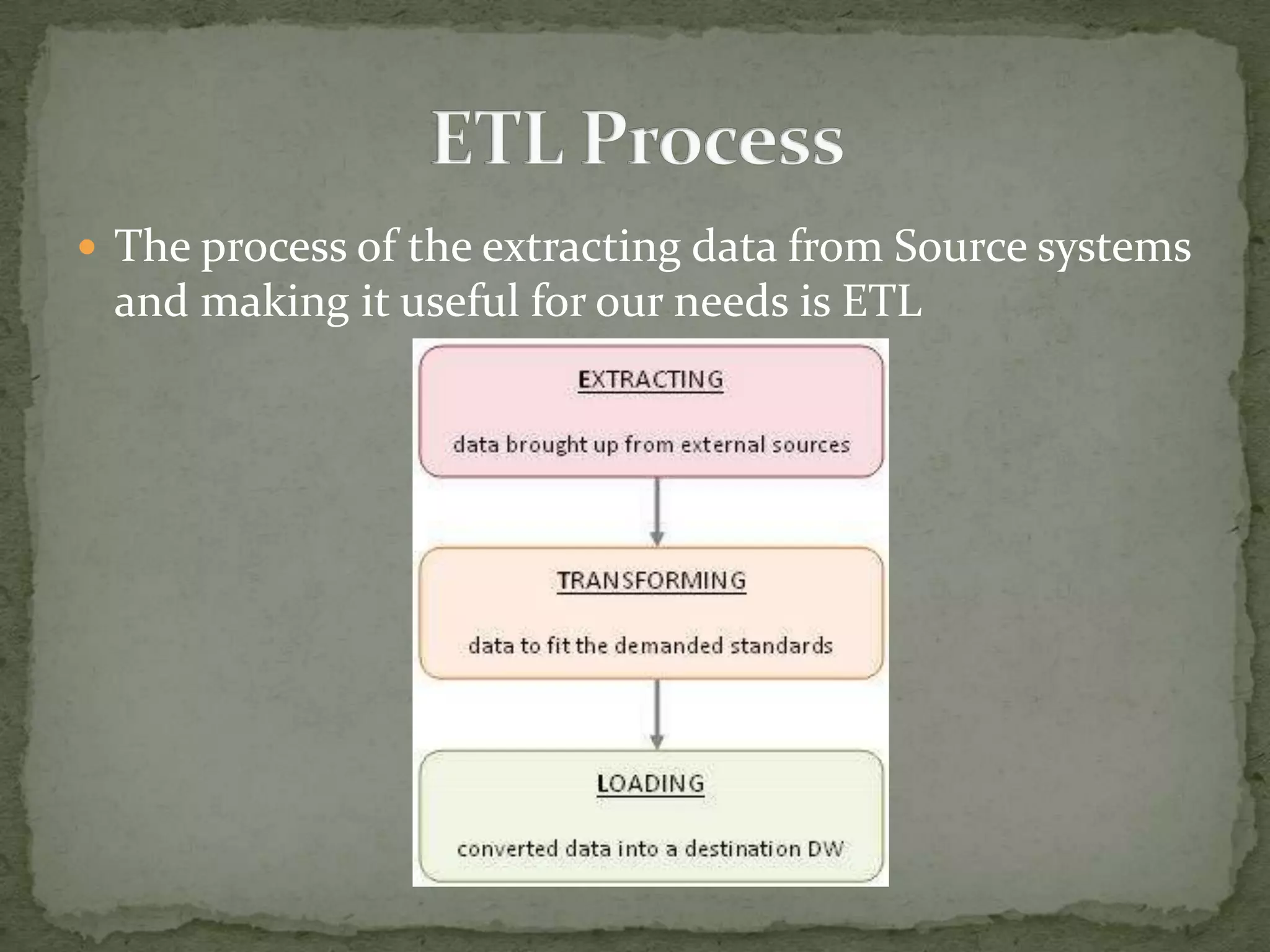
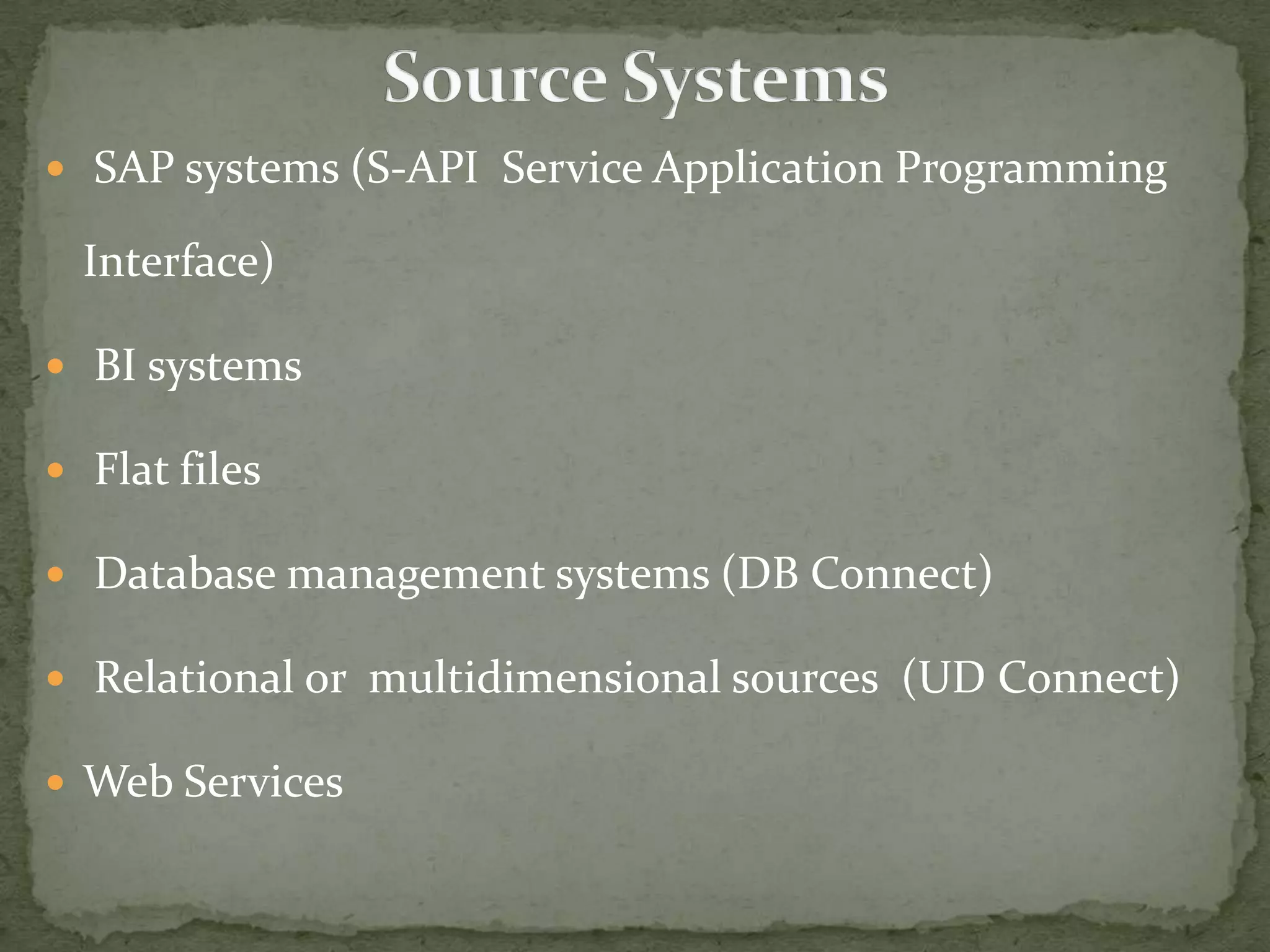
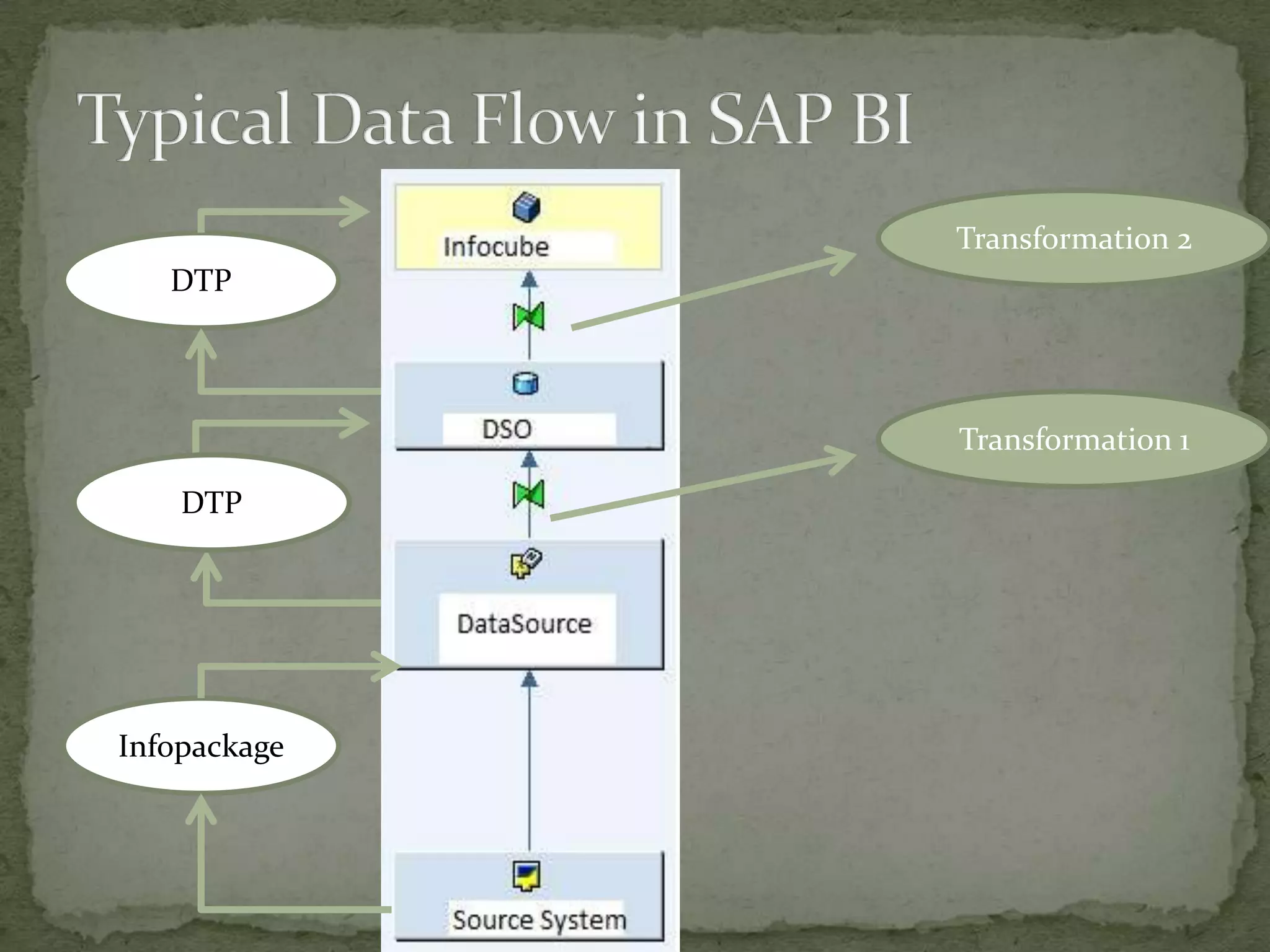
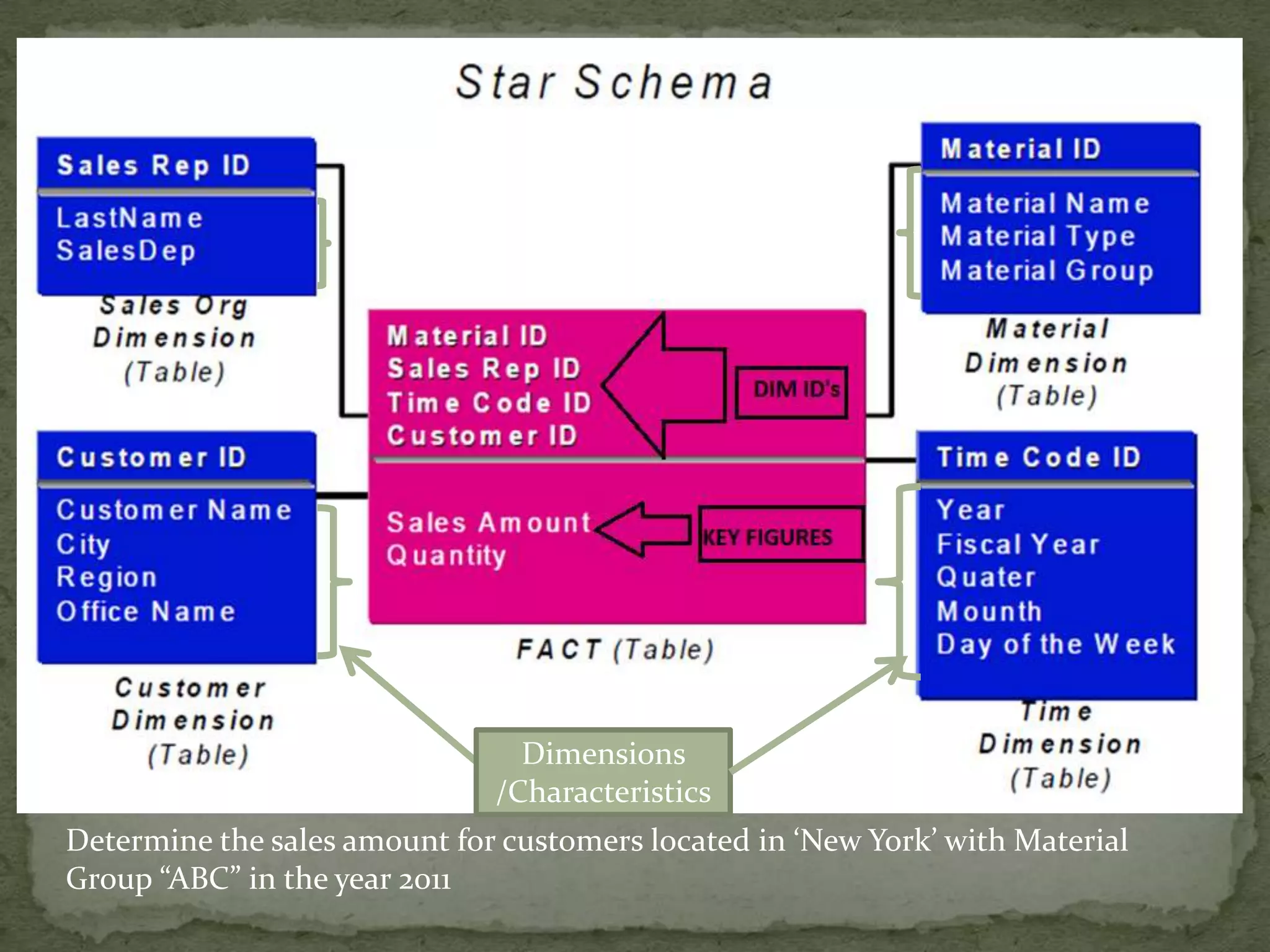
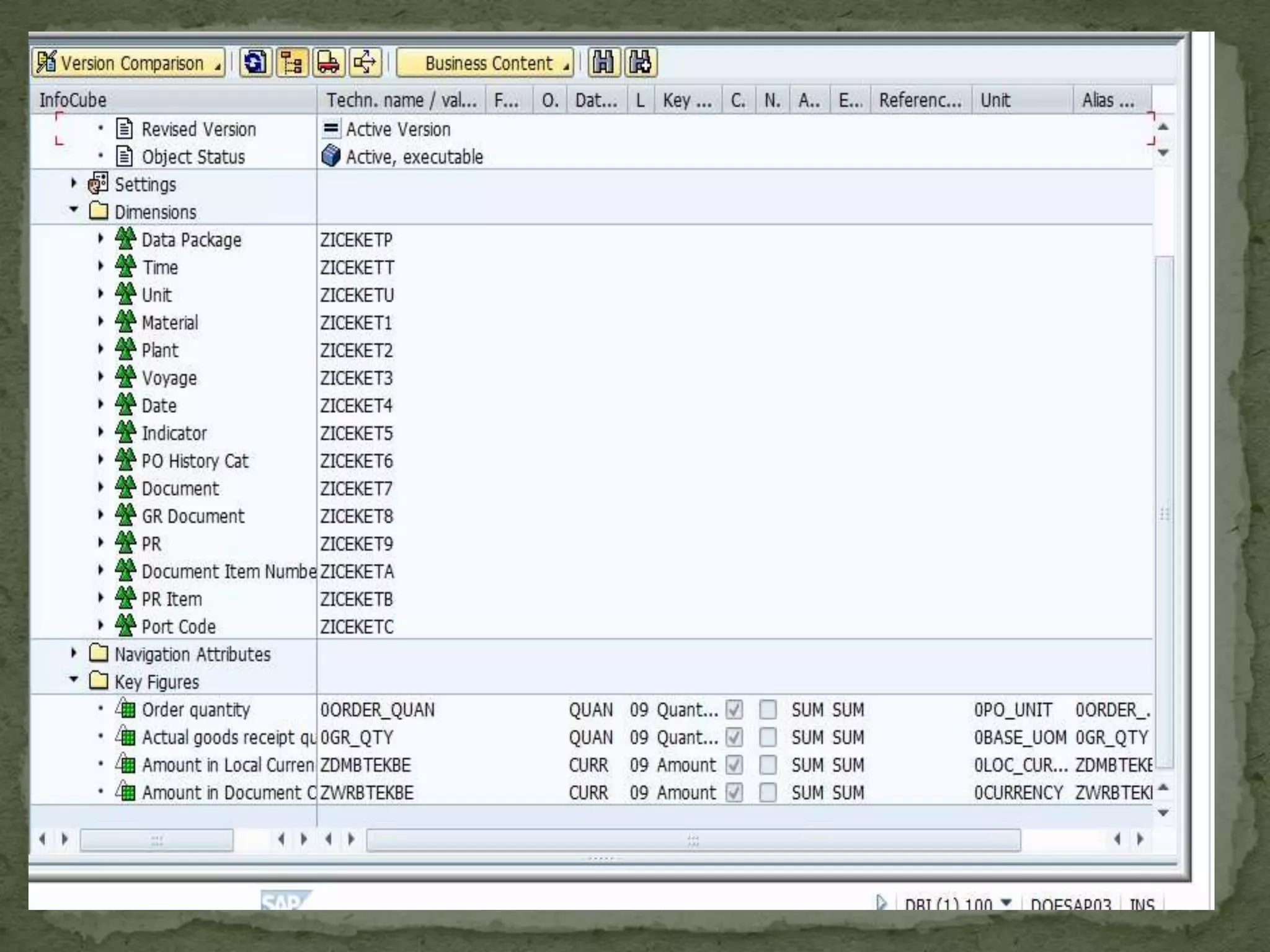
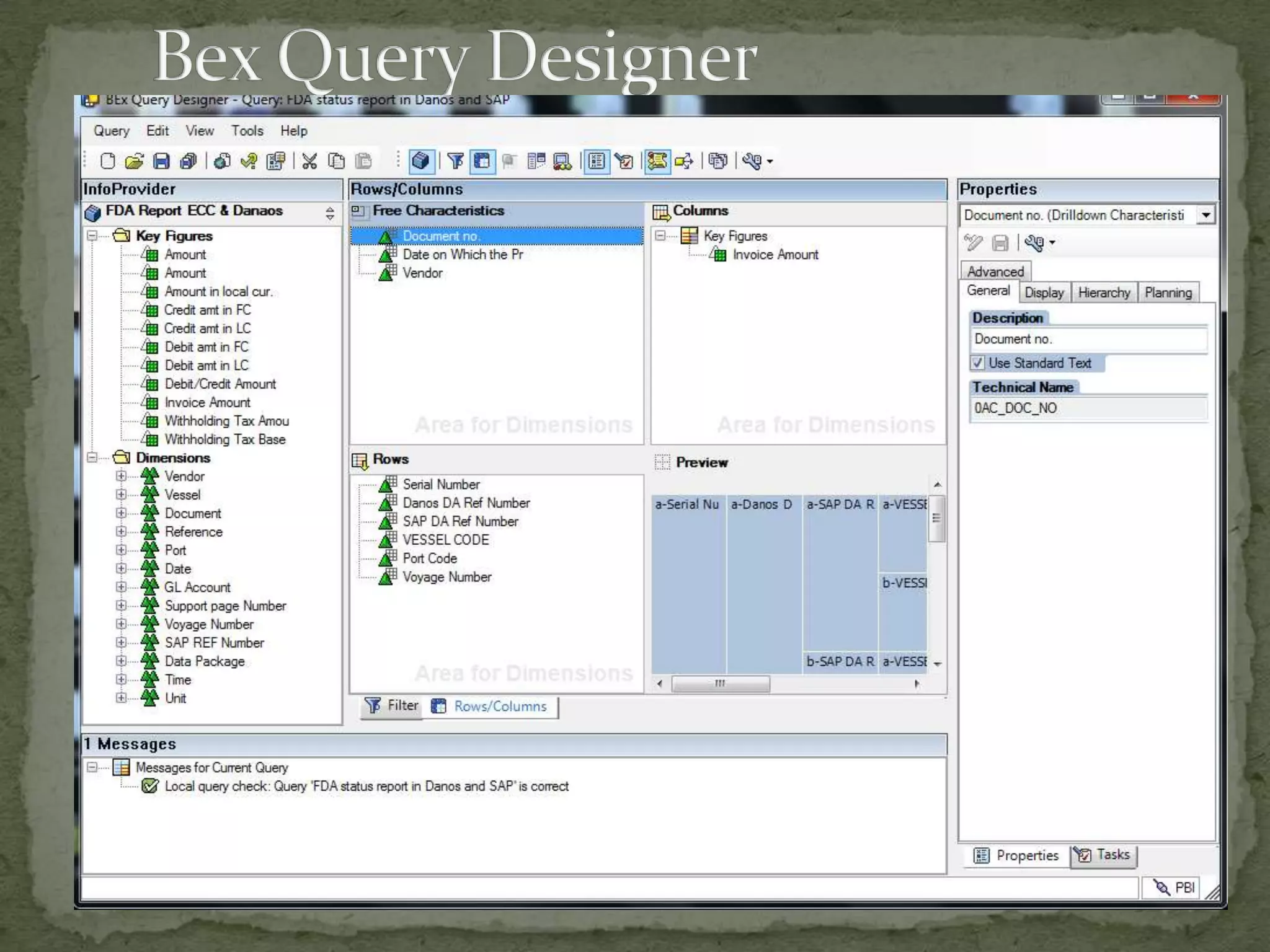
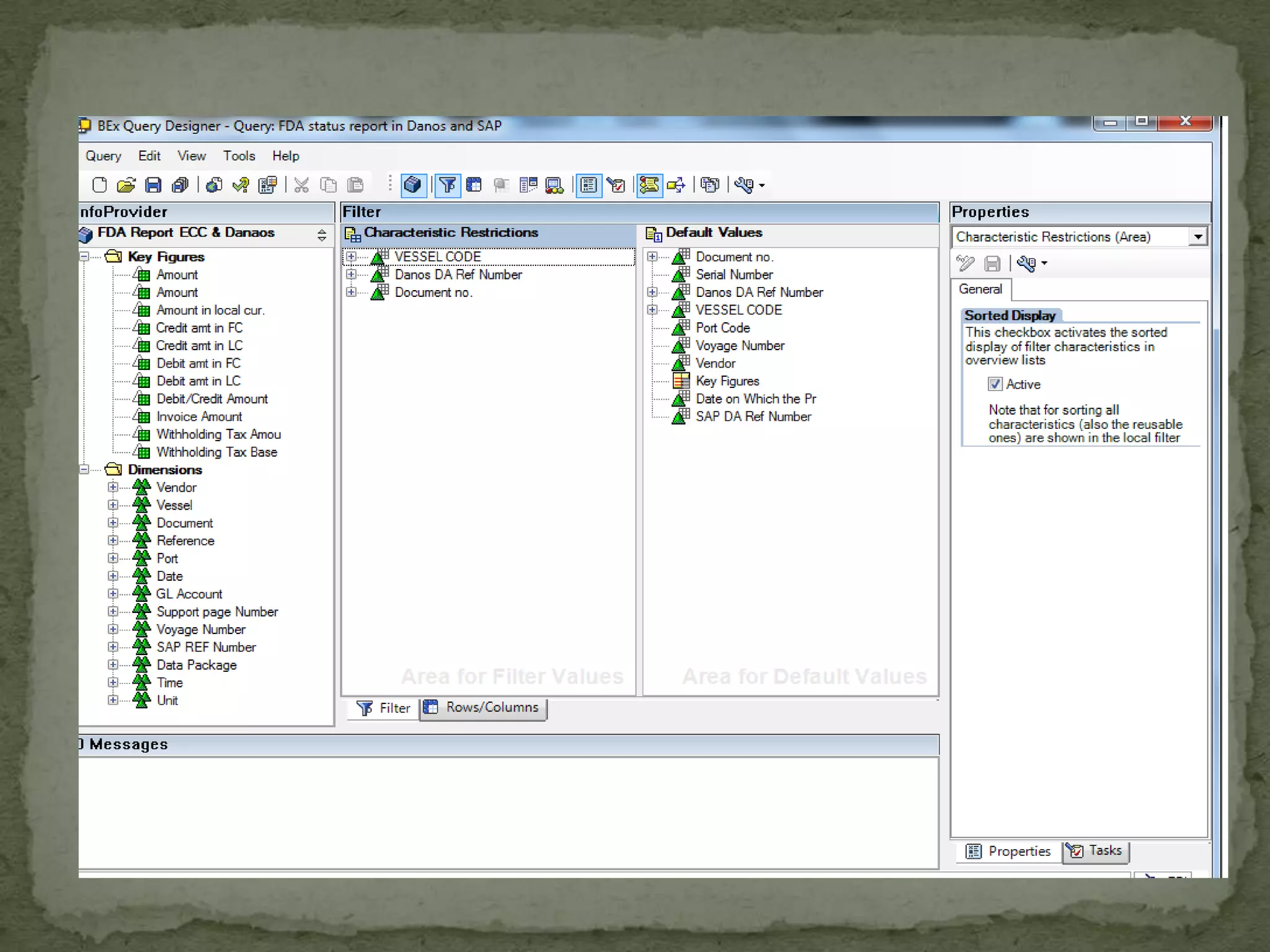
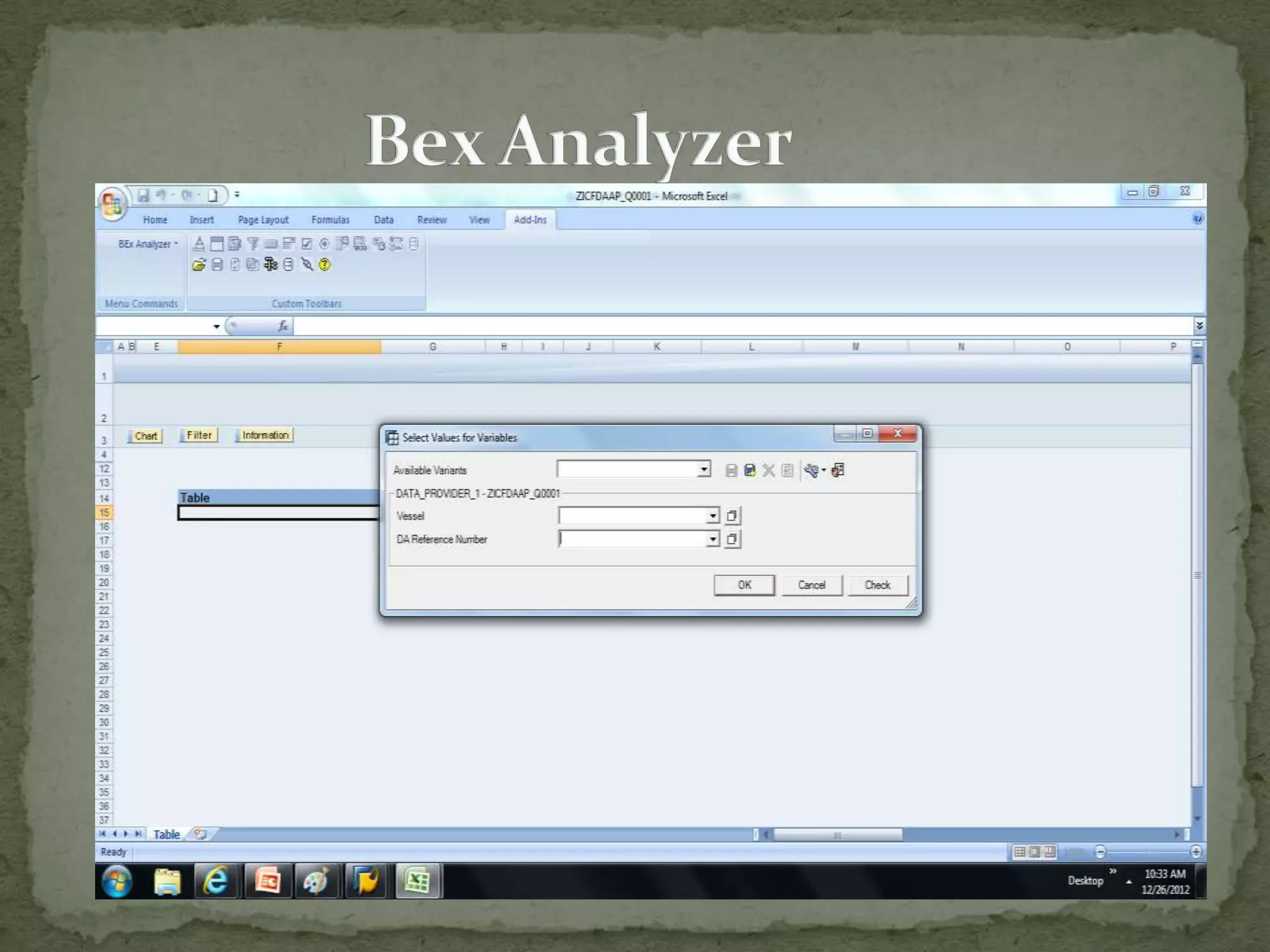
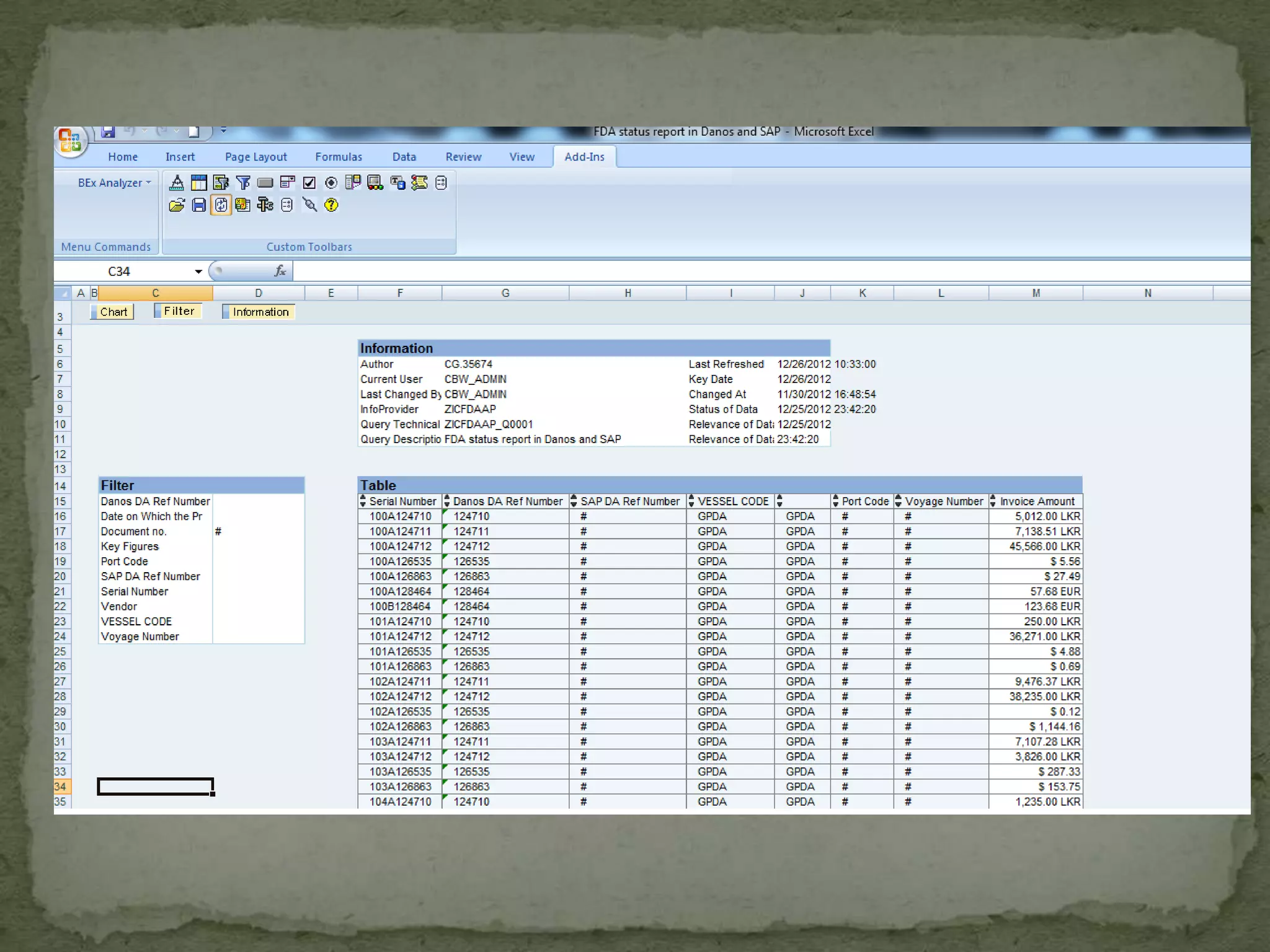
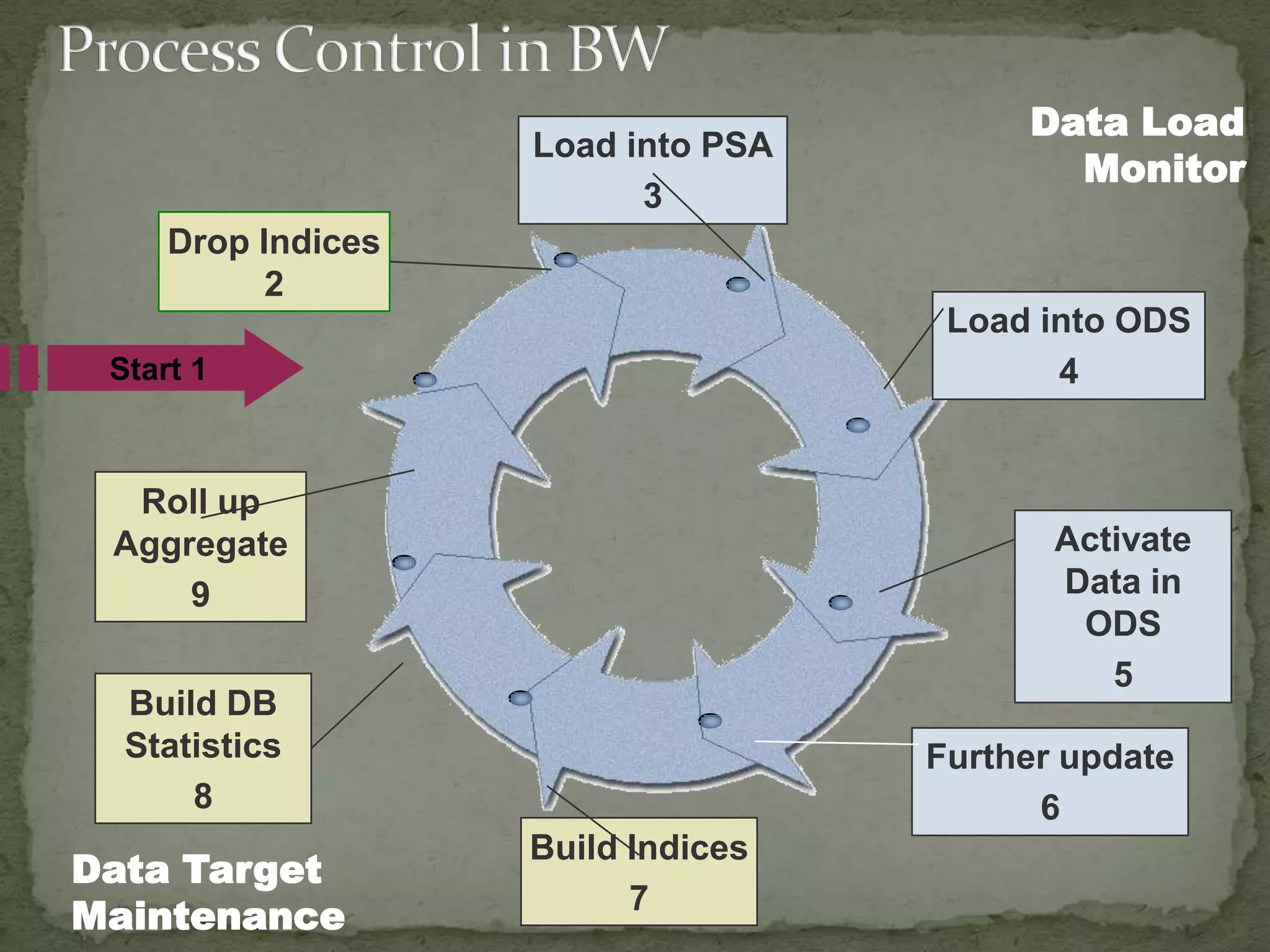
This document provides an overview of Business Intelligence (BI) and SAP BI. It defines BI as gathering, storing, analyzing, and providing access to data to help organizations make better decisions. The document then discusses SAP BI specifically, describing it as a data warehousing solution that integrates, transforms, and consolidates business data for flexible reporting and analysis. It provides historical details on the evolution of SAP BI and describes the typical data flow and architecture within SAP BI including extraction, transformation, loading, data storage, and analysis tools.