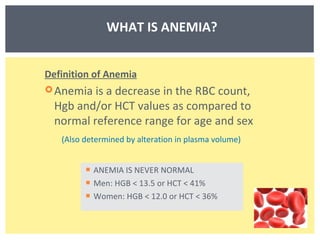
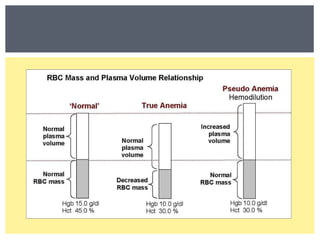
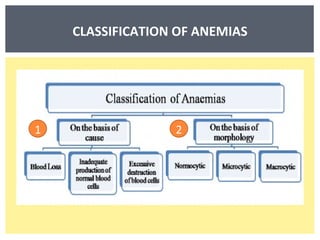
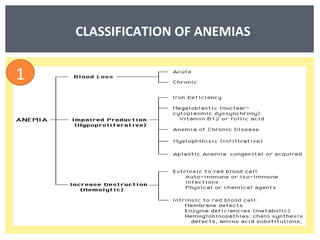
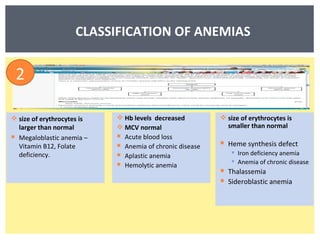
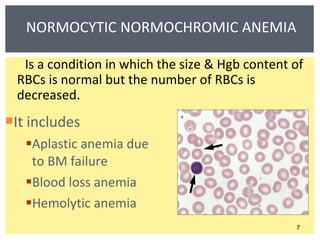
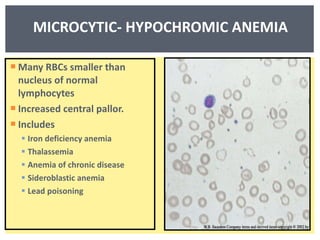
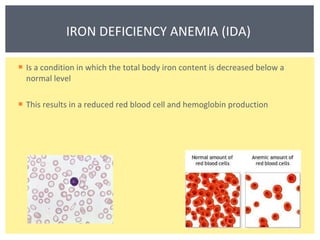
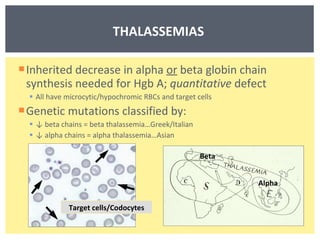
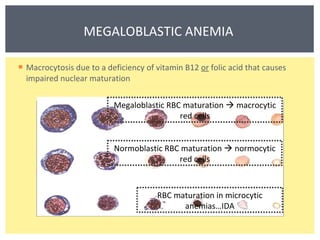
Anemia is a decrease in red blood cells (RBCs), hemoglobin (Hgb), or hematocrit (HCT) levels compared to normal levels for age and sex. Anemias can be classified based on RBC size and hemoglobin content as normocytic normochromic, microcytic hypochromic, or macrocytic normocytic. Common causes of anemia include iron deficiency, anemia of chronic disease, thalassemia, vitamin B12 or folate deficiency, blood loss, and aplastic anemia.