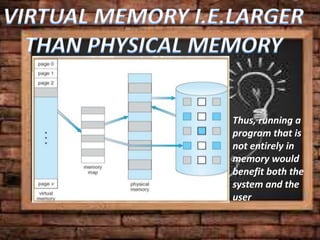
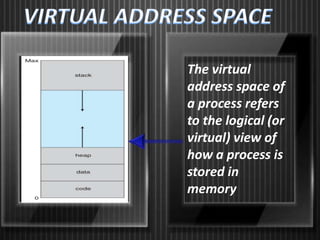
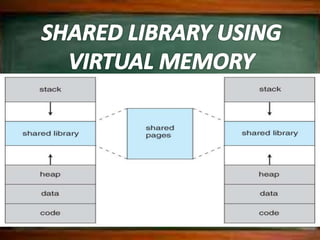
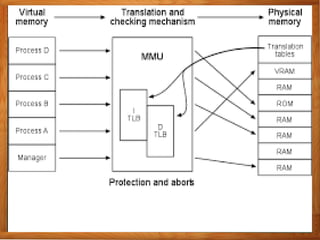
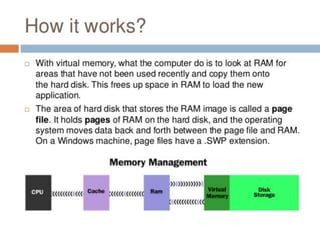
Virtual memory allows a computer to use secondary storage like a hard disk as if it were part of main memory. It allows programs to access more memory than the physical RAM capacity by swapping memory pages between RAM and secondary storage as needed. This provides benefits like running programs larger than available RAM, sharing memory between processes, and not needing programs to be loaded contiguously or completely into RAM. However, virtual memory can slow a computer down by increasing hard disk access.