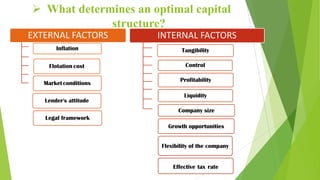
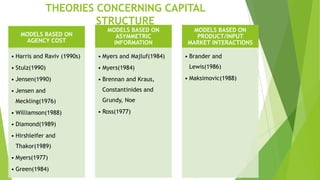
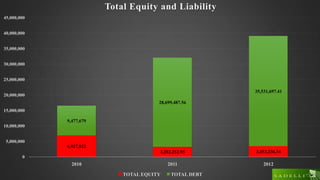
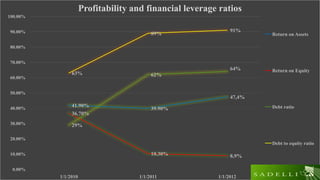
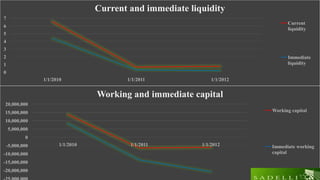
This document analyzes the capital structure of SC SADELLI PRODCOM SRL, an agricultural company in Romania. It discusses theories of optimal capital structure and the costs and benefits of debt versus equity. It also provides a case study of SC SADELLI PRODCOM SRL, including its financial statements from 2010-2012, ratios analyzing profitability and leverage, and working capital over time. It concludes that the company has generally performed well but should reduce its high leverage ratios to avoid liquidity issues that could lead to bankruptcy.