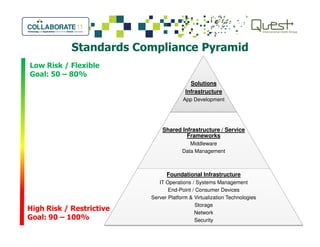
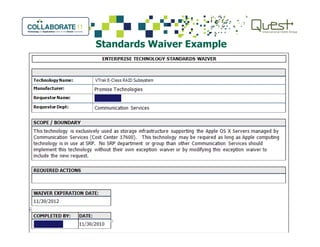
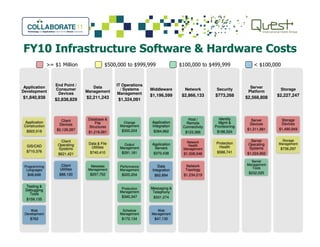
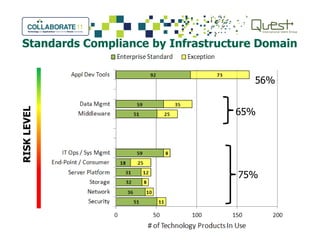
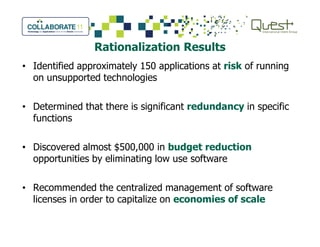
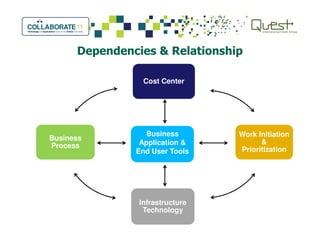
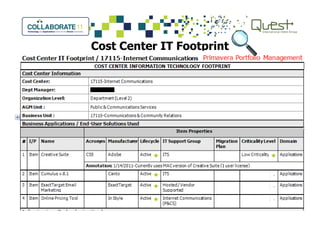
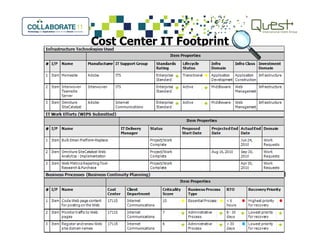
This document summarizes Salt River Project's use of Oracle's Primavera Portfolio Management software to help simplify their IT portfolio. SRP used the software to create an enterprise IT asset portfolio that provided transparency into their inventory of applications and infrastructure technologies. This allowed them to identify redundant functionality, assess asset value, and rationalize their portfolio. Their first rationalization process identified opportunities to reduce costs through consolidation and eliminating unsupported technologies.