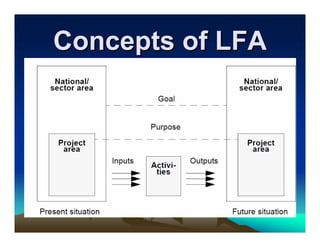
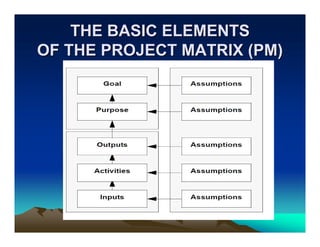
The document provides details about a workshop on introducing the Logical Framework Approach (LFA) as a project planning tool. It includes an agenda with sections on introducing participants, an overview of LFA including its history and benefits, components of project planning, and an example of applying LFA to modernize settlement services. The workshop aims to help participants understand LFA and use it as an analytic framework for participatory project planning, assessment, and evaluation.