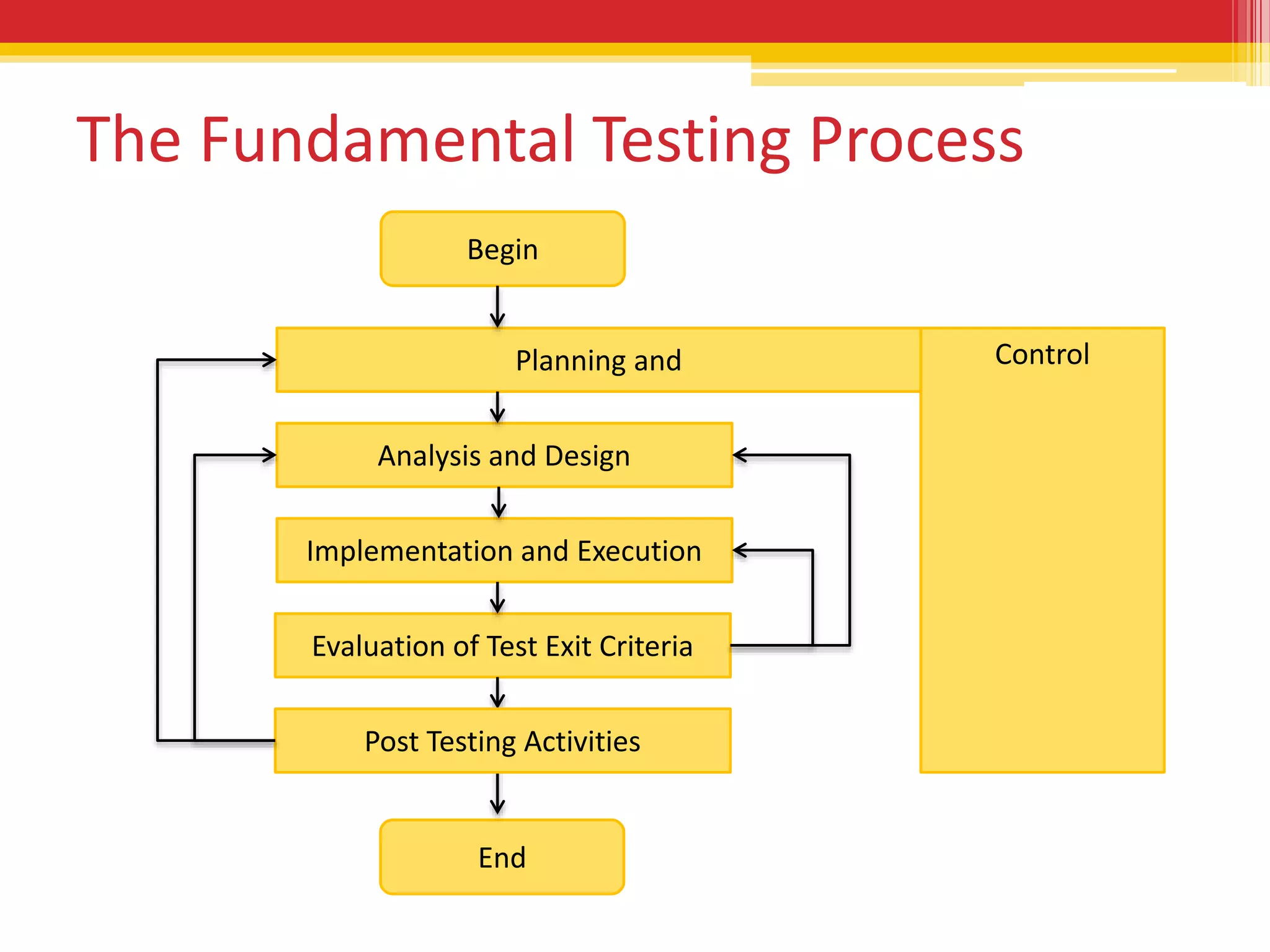
The fundamental software testing process involves 6 steps: 1) Planning and control to define the test strategy and plan, 2) Analysis and design to create logical test cases, 3) Implementation and execution to implement concrete test cases and execute testing according to priorities, 4) Evaluation of test exit criteria to determine when to stop testing based on metrics like defect detection percentage, 5) Reporting to communicate results to stakeholders, and 6) Post testing activities to analyze lessons learned and improve future testing. The process is iterative with several test cycles planned to fully test the software.