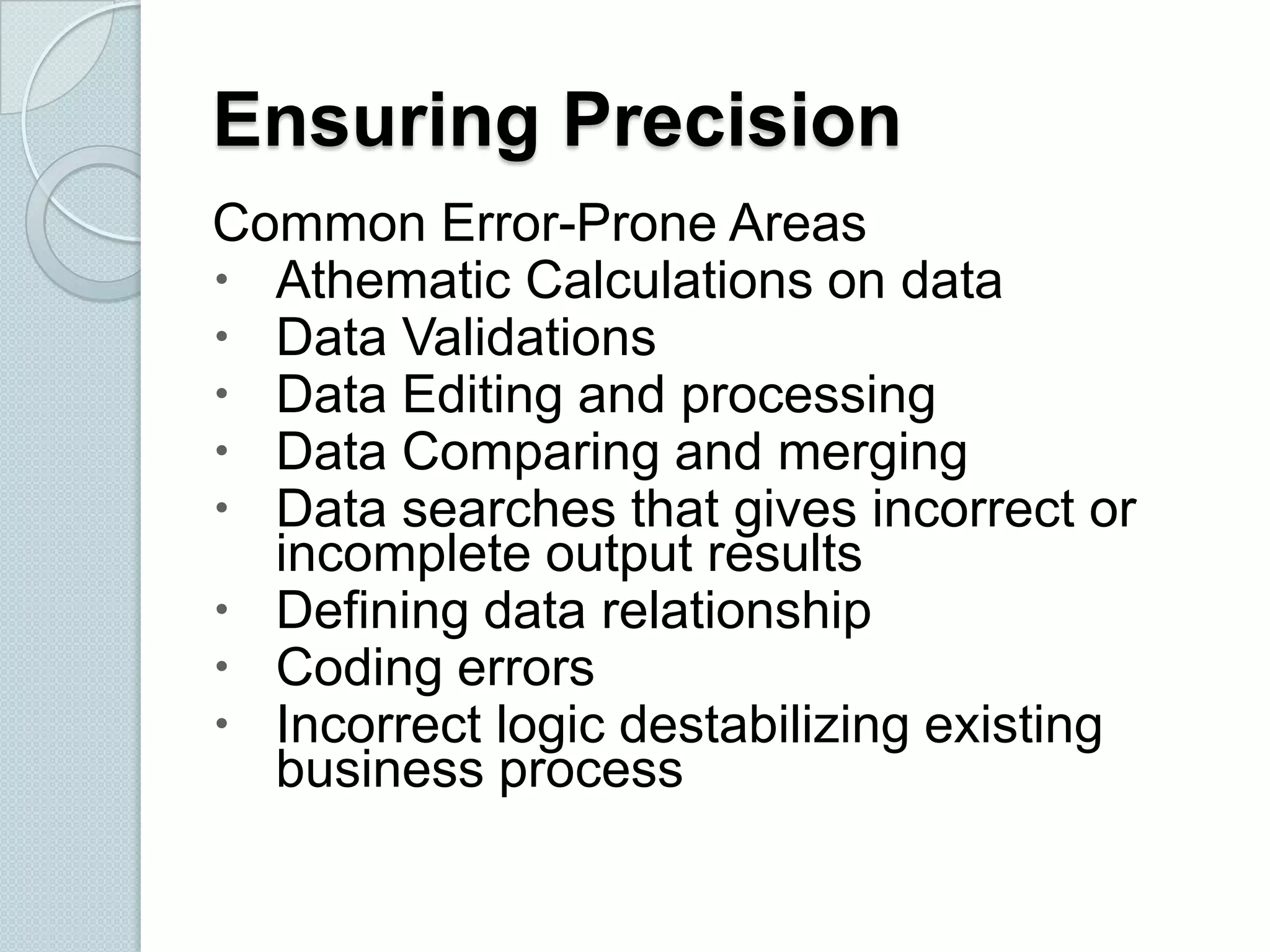
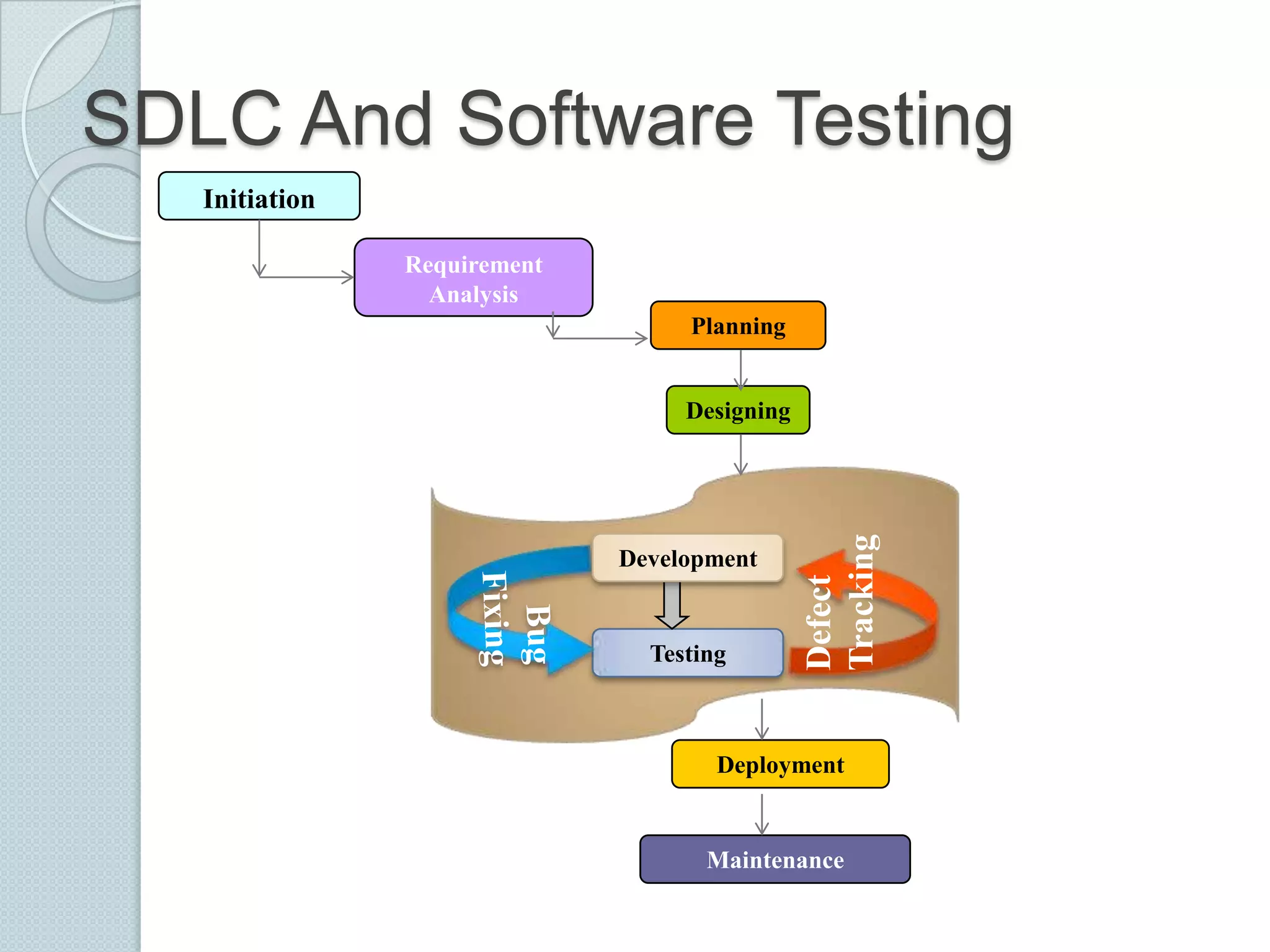
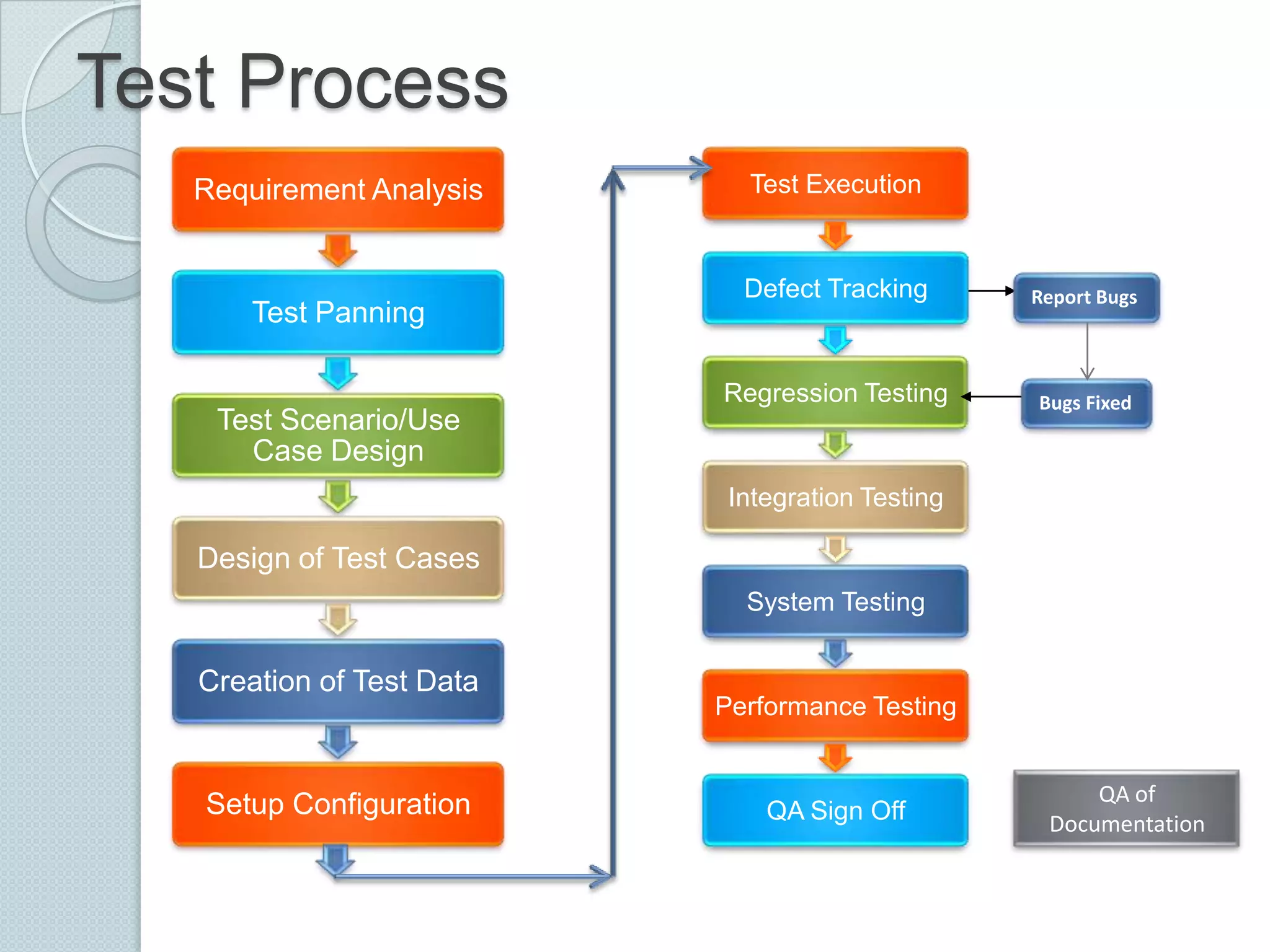
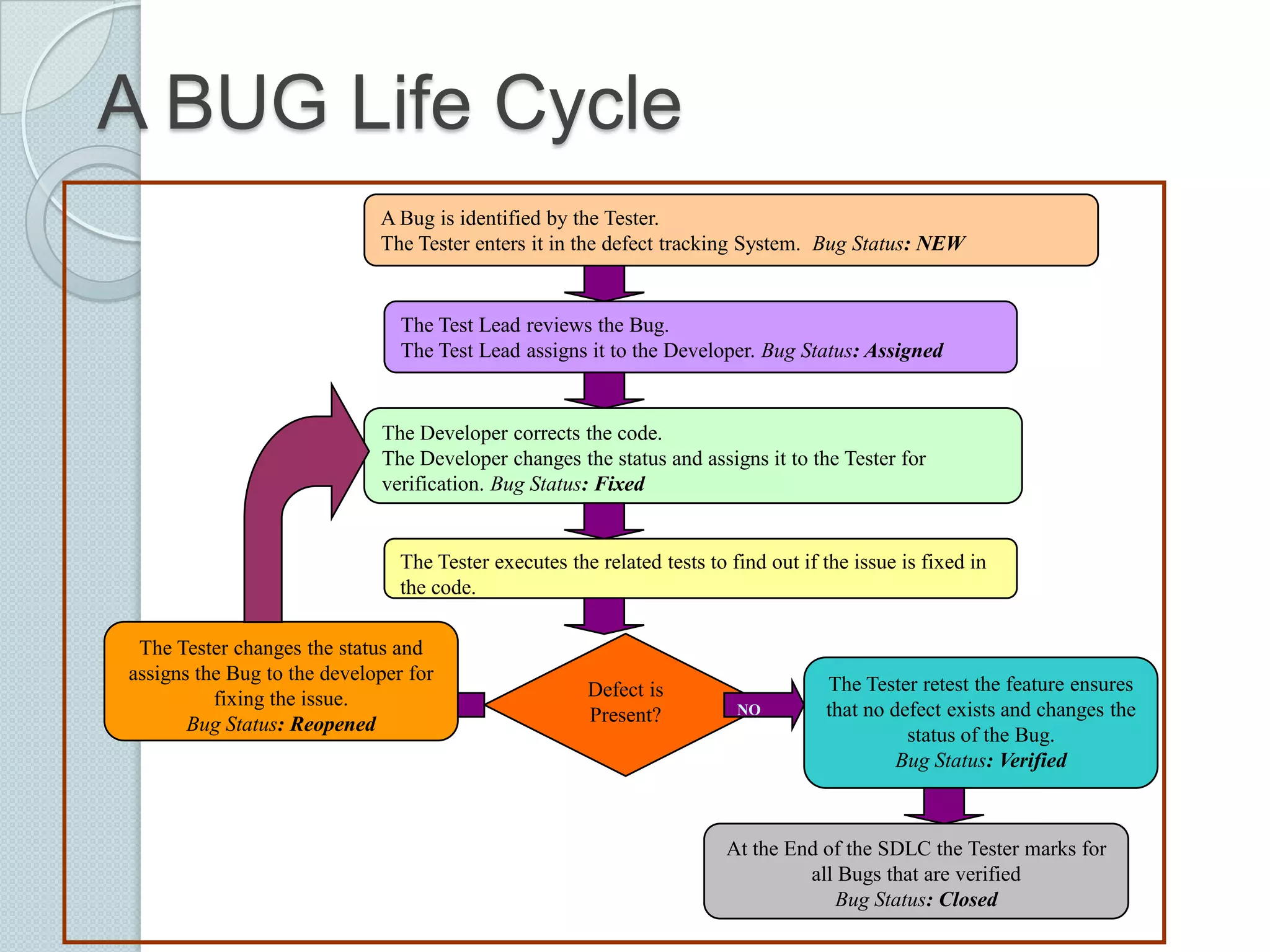
The document discusses the roles and differences between developers and testers in software development, emphasizing the importance of a proactive testing approach to ensure software quality and usability. It outlines the software testing life cycle, various testing methodologies, and provides insight into the bug life cycle, including identification, tracking, and resolution processes. Additionally, it lists common testing tools, both open-source and commercial, used for functional and performance testing.