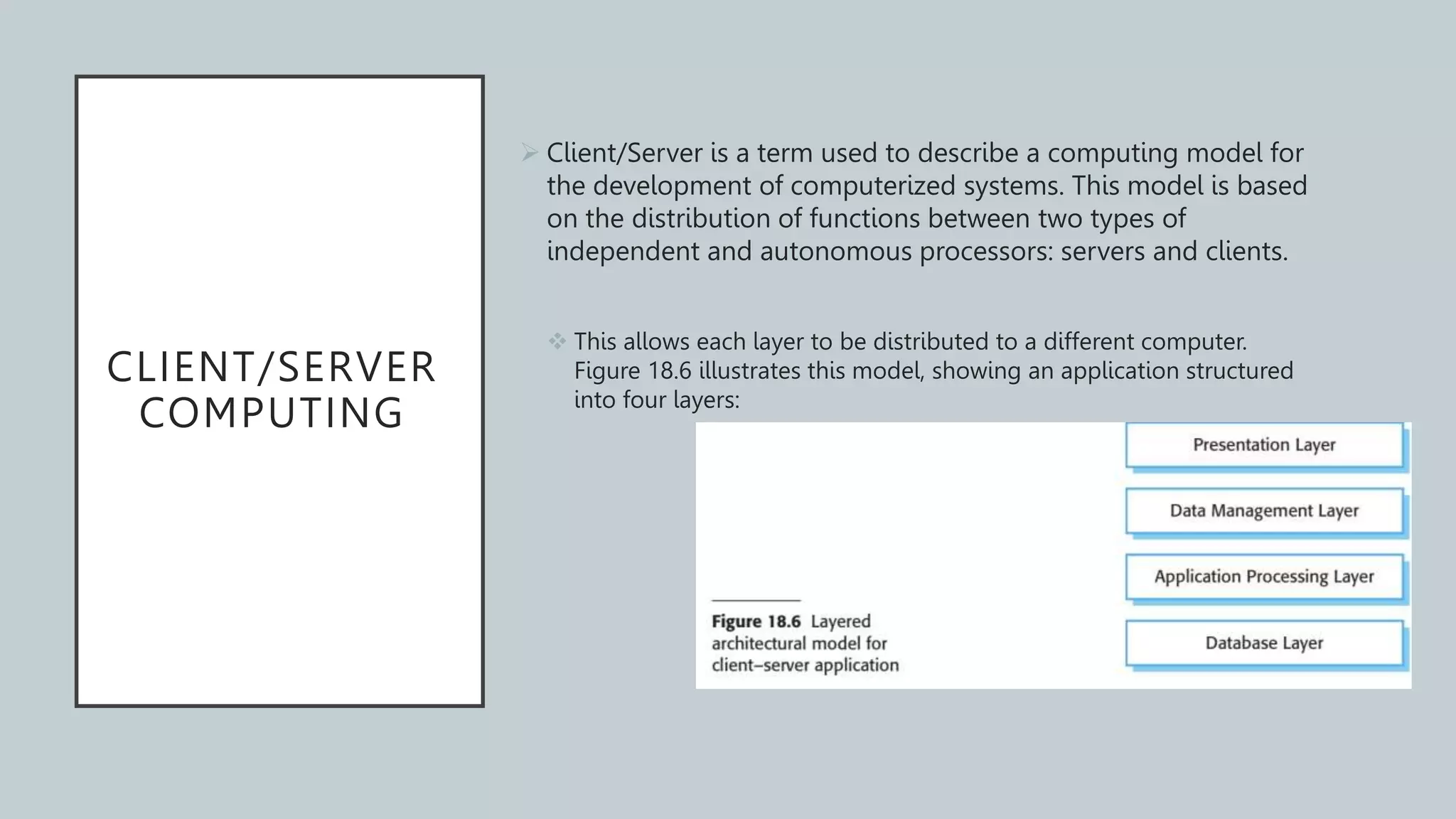
This document discusses distributed software engineering. It covers topics like distributed systems issues, client-server computing, and architectural patterns for distributed systems. Distributed systems engineering deals with systems where components are located on different computers within a network. Distributed systems have characteristics like openness, scalability, concurrency, and transparency. Client-server computing is based on distributing functions between server and client processors. Common architectural patterns include master-slave, two-tier client-server, multitier client-server, distributed component, and peer-to-peer architectures. The document also discusses software as a service (SaaS) and its multitenant architecture, easy customization, and relationship to service-oriented architecture.