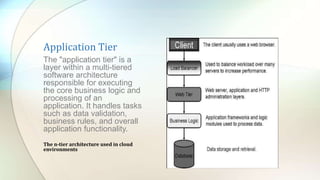
Cloud networks utilize remote servers and the internet rather than local servers or personal computers to store, manage and process data. They offer scalability, flexibility and cost savings through virtualization, resource pooling and pay-per-use billing models. Managed service providers help organizations manage their IT infrastructure through services like monitoring, support, security and compliance management. They work to fill staffing gaps and improve organizations' security, cost efficiency and business continuity. Open source software plays a key role in cloud computing through components used for web presence, databases, application servers and more.