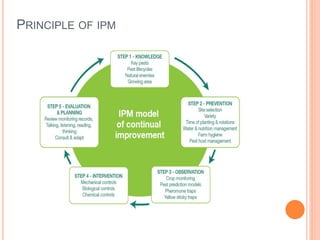
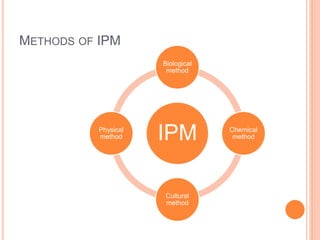
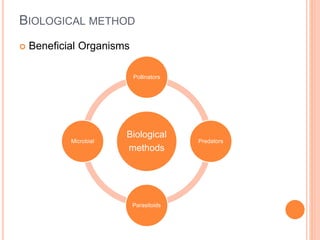
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) combines biological, cultural, physical, and chemical methods to manage pests sustainably while minimizing risks to health, the economy, and the environment. IPM aims to reduce synthetic pesticide use, ensure safe consumption of food, and provide economic returns. Various methods include biological control with beneficial organisms, cultural practices like intercropping, and the use of lower-risk chemical options such as botanical insecticides.