The document discusses the participation of HCMUS in the MediaEval 2020 Medico Automatic Polyp Segmentation Task, focusing on two main algorithms: Pranet and Resunet++. It describes the methodology used, including data sets, training strategies, and preprocessing techniques, and reports on the performance results from both task 1 and task 2 submissions. The conclusion emphasizes the effectiveness of the proposed methods in improving both accuracy and efficiency in polyp segmentation from colonoscopy images.

![Overview
3
[1] Debesh Jha et al. “Medico Multimedia Task at MediaEval 2020: Auto-matic Polyp Segmentation”. MediaEval 2020 Workshop. 2020.
MEDICO TASK1
- Segment all types of polyps in colonoscopy images](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/047-210817190850/75/HCMUS-at-Medico-Automatic-Polyp-Segmentation-Task-2020-PraNet-and-ResUnet-for-Polyps-Segmentation-3-2048.jpg)
![Overview
4
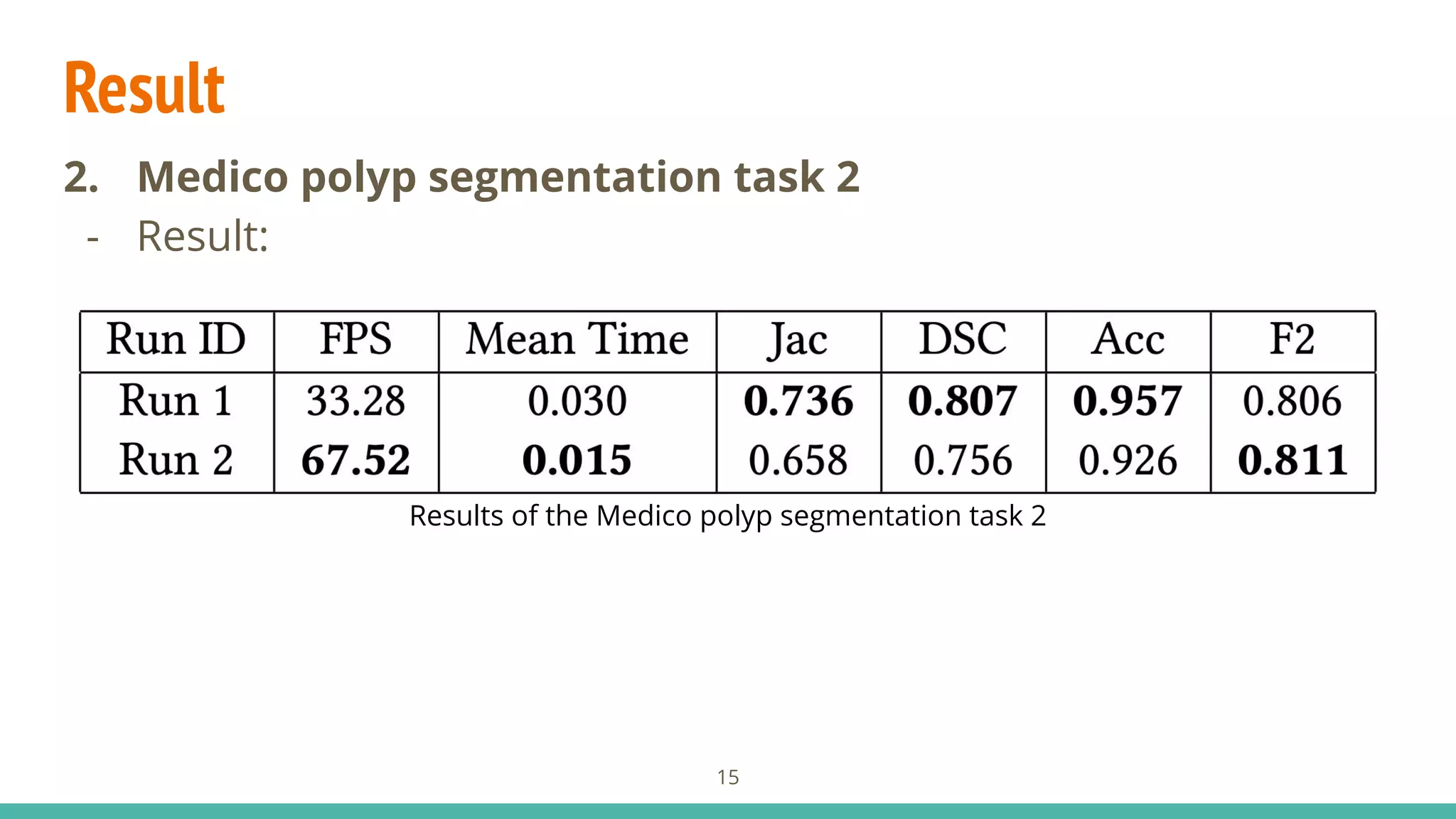
TASK 1: Polyp Segmentation
- Data:
- Training set: Kvasir-SEG1
Dataset with 1.000 images
- Test set: 160 images
- Evaluated by Jaccard index
[1] Debesh Jha et al. “Kvasir-seg: A segmented polyp dataset.” In International Conference on Multimedia Modeling. 2020.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/047-210817190850/75/HCMUS-at-Medico-Automatic-Polyp-Segmentation-Task-2020-PraNet-and-ResUnet-for-Polyps-Segmentation-4-2048.jpg)

![- PraNet1
: We use Pranet with Res2net3
backbone as the main
segmentation algorithm.
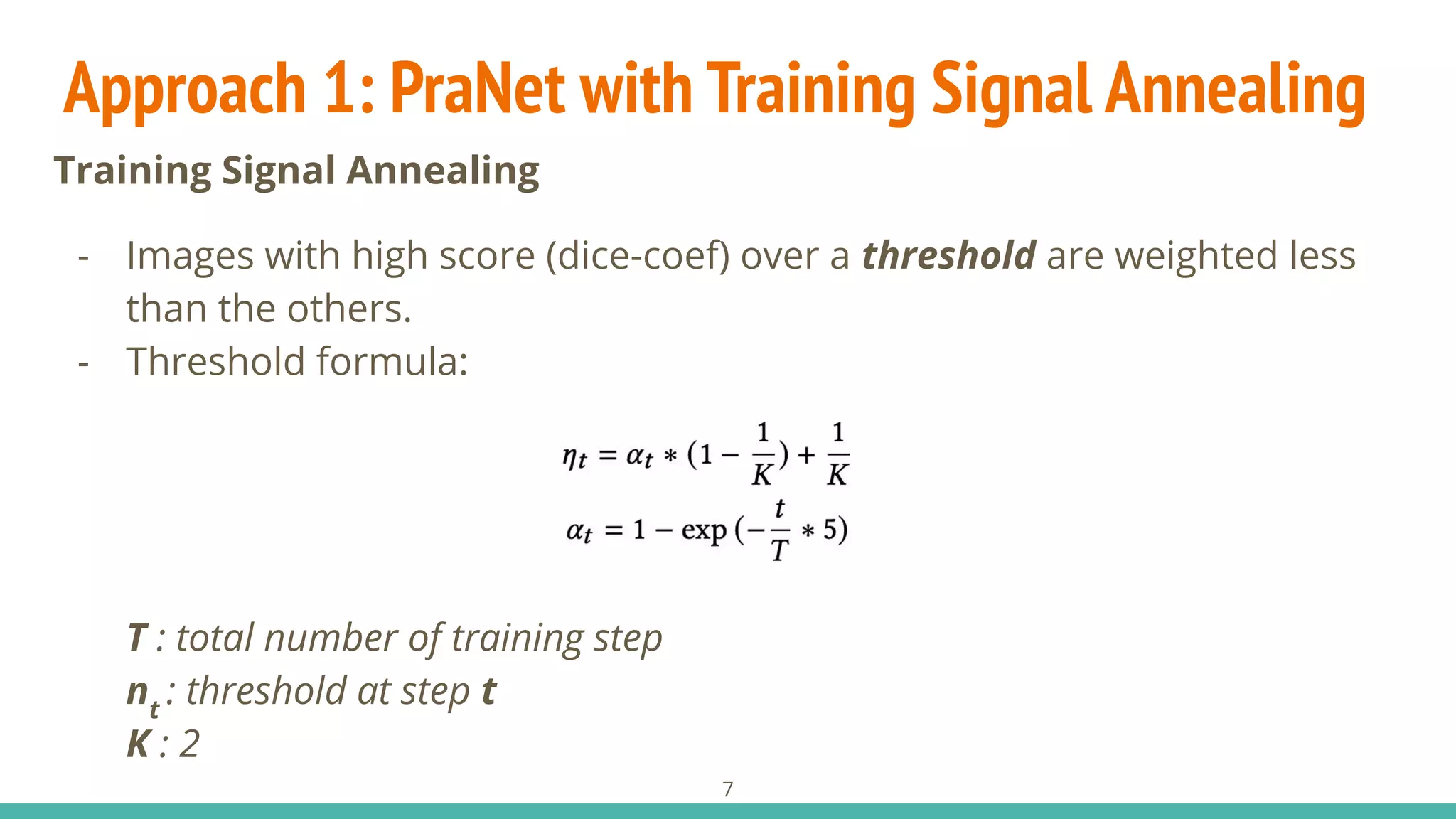
- Training Signal Annealing2
: We apply TSA strategy to prevent
overfitting in training step.
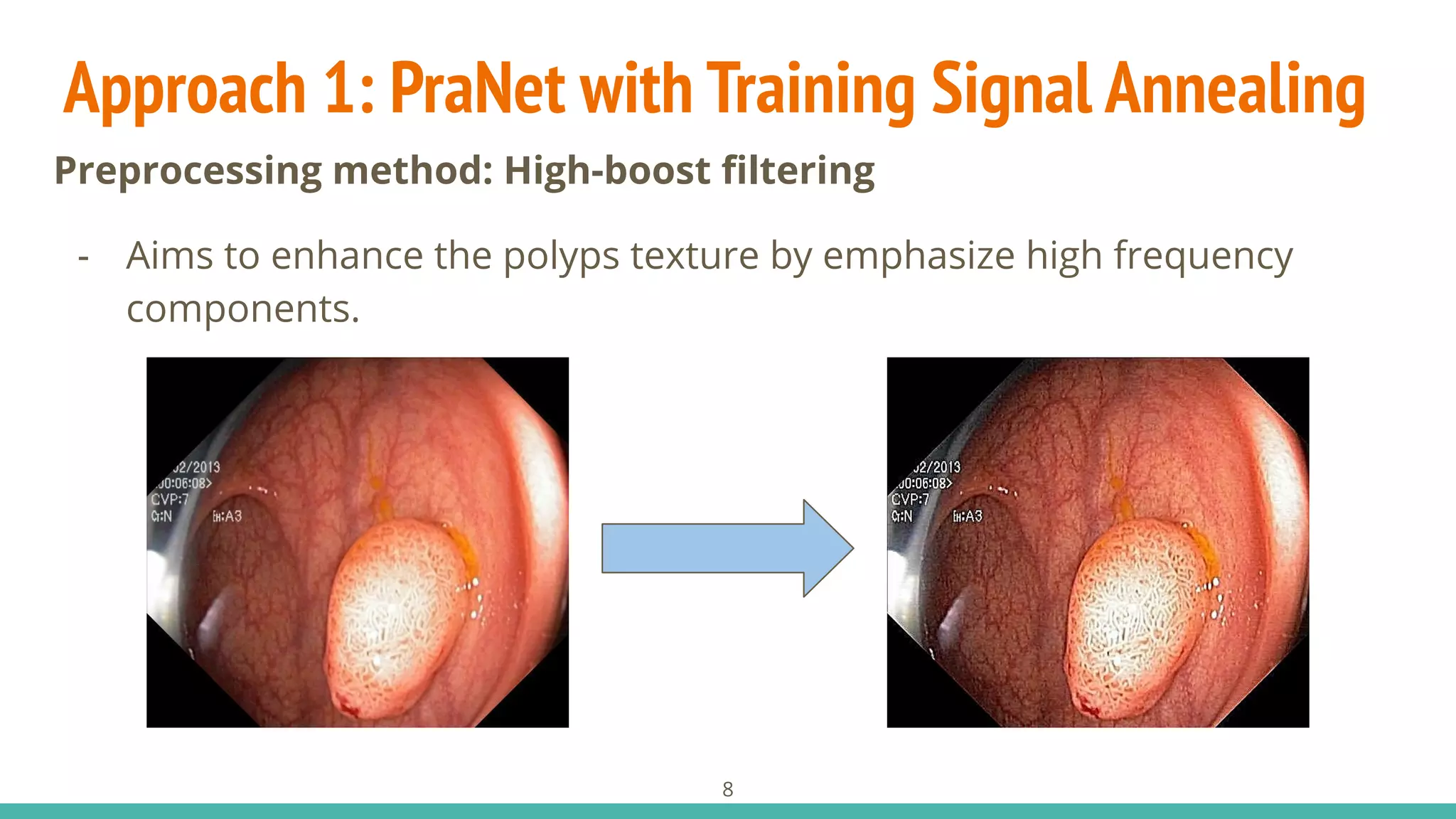
- Pre/Post-processing methods: We use random rotation and
high-boost filtering for augmentation.
Approach 1: PraNet with Training Signal Annealing
6
[1] D.-P. Fan et al. “PraNet: Parallel Reverse Attention Network for Polyp Segmentation”. MICCAI 2020
[2] Xie, Qizhe, et al. “Unsupervised data augmentation for consistency training”. (2019)
[3] Gao, Shanghua, et al. “Res2net: A new multi-scale backbone architecture”. IEEE 2019](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/047-210817190850/75/HCMUS-at-Medico-Automatic-Polyp-Segmentation-Task-2020-PraNet-and-ResUnet-for-Polyps-Segmentation-6-2048.jpg)
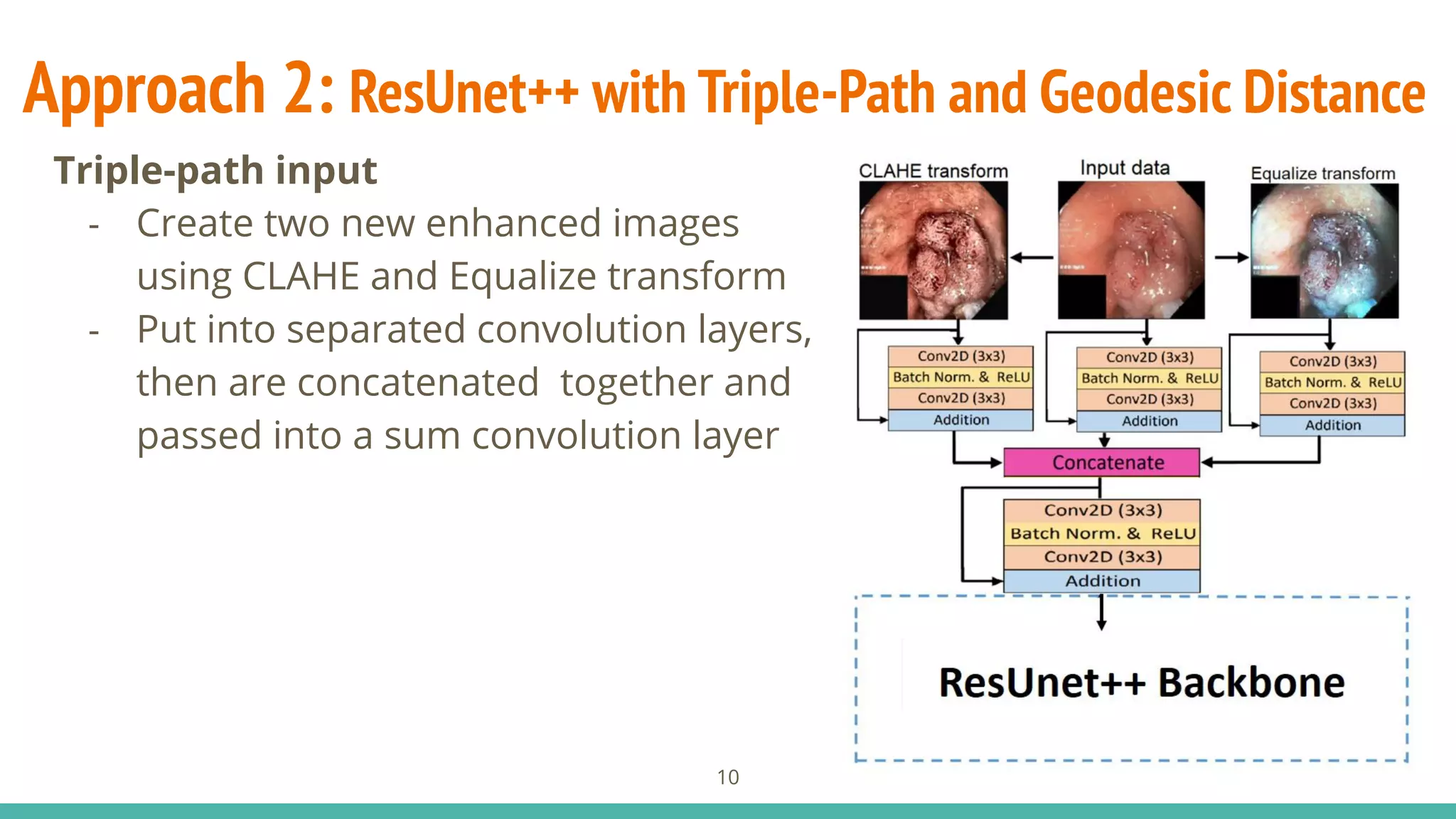
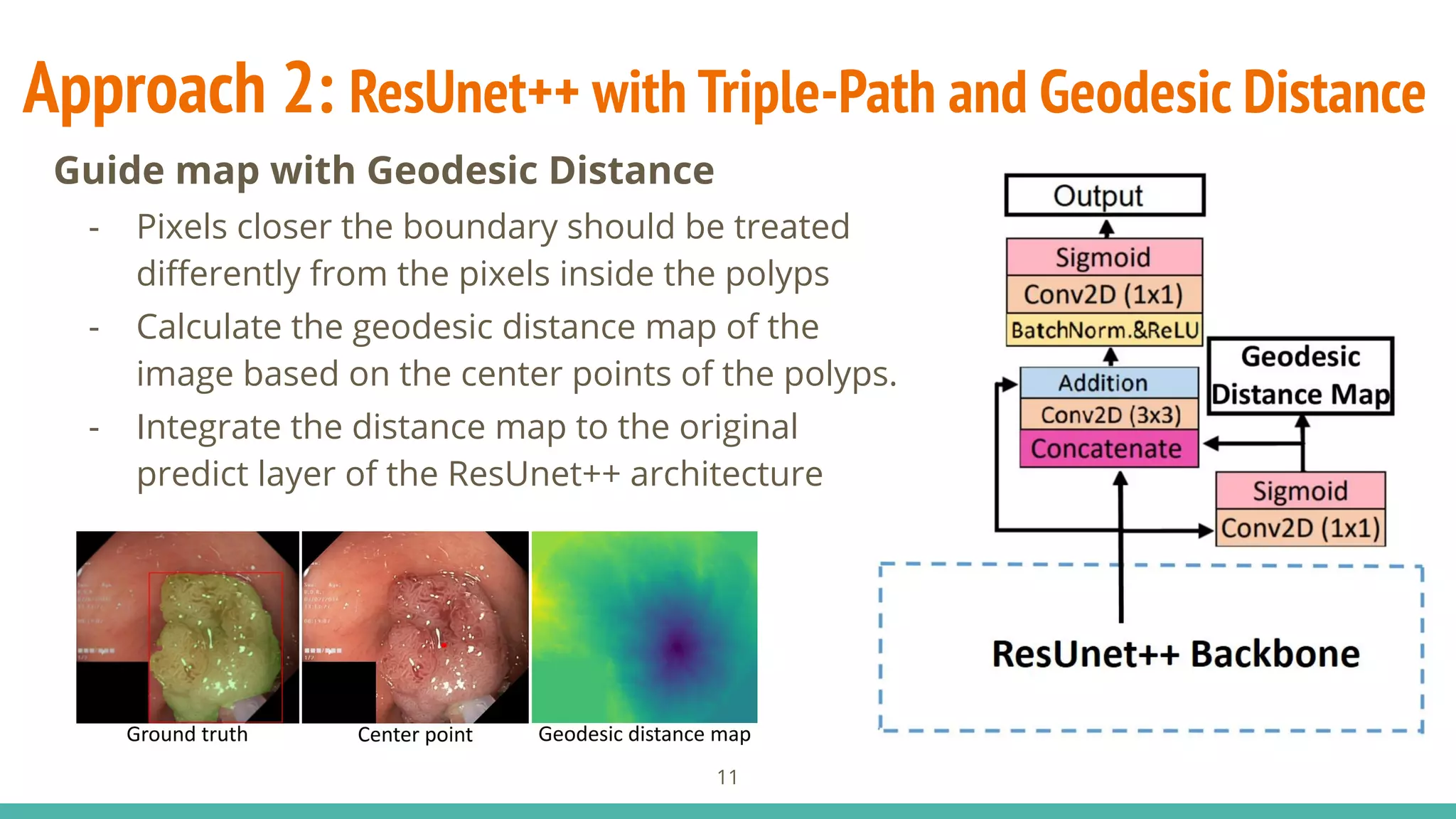
![Approach 2: ResUnet++ with Triple-Path and Geodesic Distance
- Base architecture: use ResUnet++1
- Triple-path input: aggregate three
versions of the enhanced input
image
- Guide map: integrate a distance
map layer using Geodesic Distance
Transform2
as a guide mask
9
[1] Jha, Debesh, et al. “Resunet++: An advanced architecture for
medical image segmentation.” IEEE 2020
[2] G. Wang et al. “DeepIGeoS: A Deep Interactive Geodesic Framework
for Medical Image Segmentation.IEEE 2019](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/047-210817190850/75/HCMUS-at-Medico-Automatic-Polyp-Segmentation-Task-2020-PraNet-and-ResUnet-for-Polyps-Segmentation-9-2048.jpg)