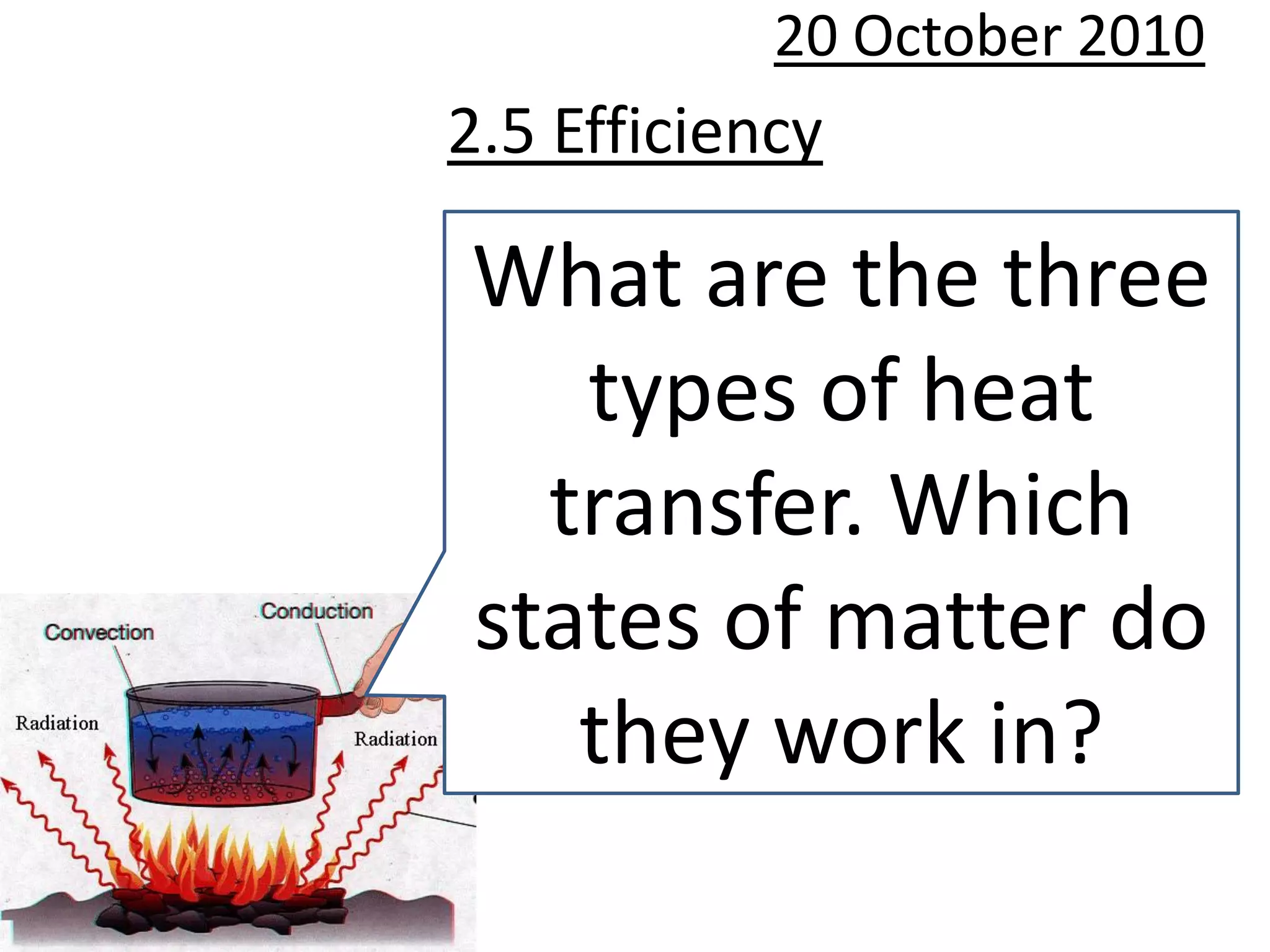
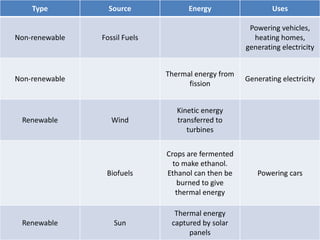
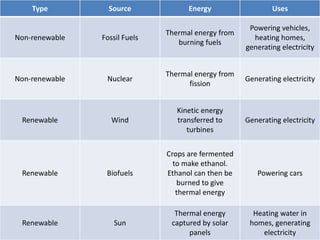
This document discusses energy efficiency and heat transfer. It defines efficiency as useful energy output divided by total energy input. It provides an example where a desk lamp has an input of 100J per second but only outputs 5J per second, giving it an efficiency of 5%. The document also discusses renewable and non-renewable energy sources, listing examples like fossil fuels, nuclear, wind, biofuels, and solar energy. It explains how each source captures and converts different forms of energy for useful applications.