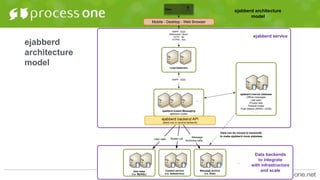
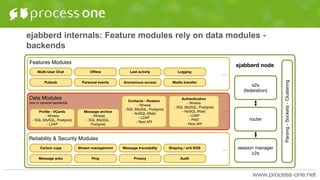
- Backends in ejabberd are pluggable modules that store data to provide to feature modules. This allows ejabberd to be more stateless. Common backends include Mnesia, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Riak, and custom backends.
- Message carbons allow messages to be copied to all connected clients so the full conversation history is visible, but they do not work in MUC rooms due to the anonymous nature of MUC chats.
- To learn XMPP, it is best to start at the protocol level by using a client like PSI that allows inspecting and crafting XMPP packets directly rather than starting from libraries that abstract the protocol.


![Example configuration
You generally need a global parameter for RDBMS:
• Example of MySQL connection:
odbc_type: mysql
odbc_server: "server.company.com"
odbc_port: 3306 # the default
odbc_database: "mydb"
odbc_username: "user1"
odbc_password: "**********"
odbc_pool_size: 5
You can then reference that back-end for authentication:
auth_method: odbc
Or in some modules configuration on a granular basis:
modules:
mod_roster: [{db_type: odbc}]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xmppacademy2-151105134735-lva1-app6892/85/XMPP-Academy-2-6-320.jpg)