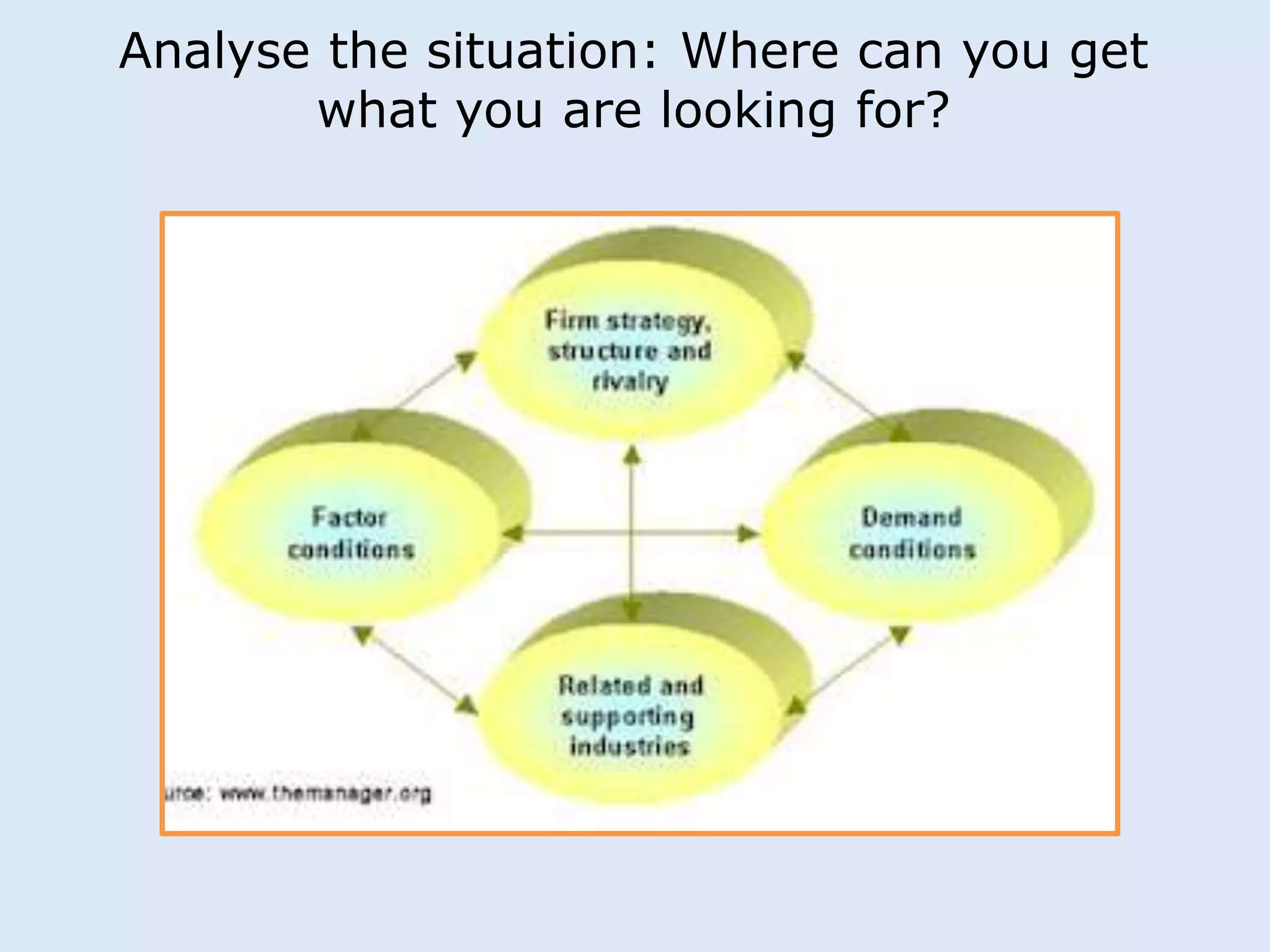
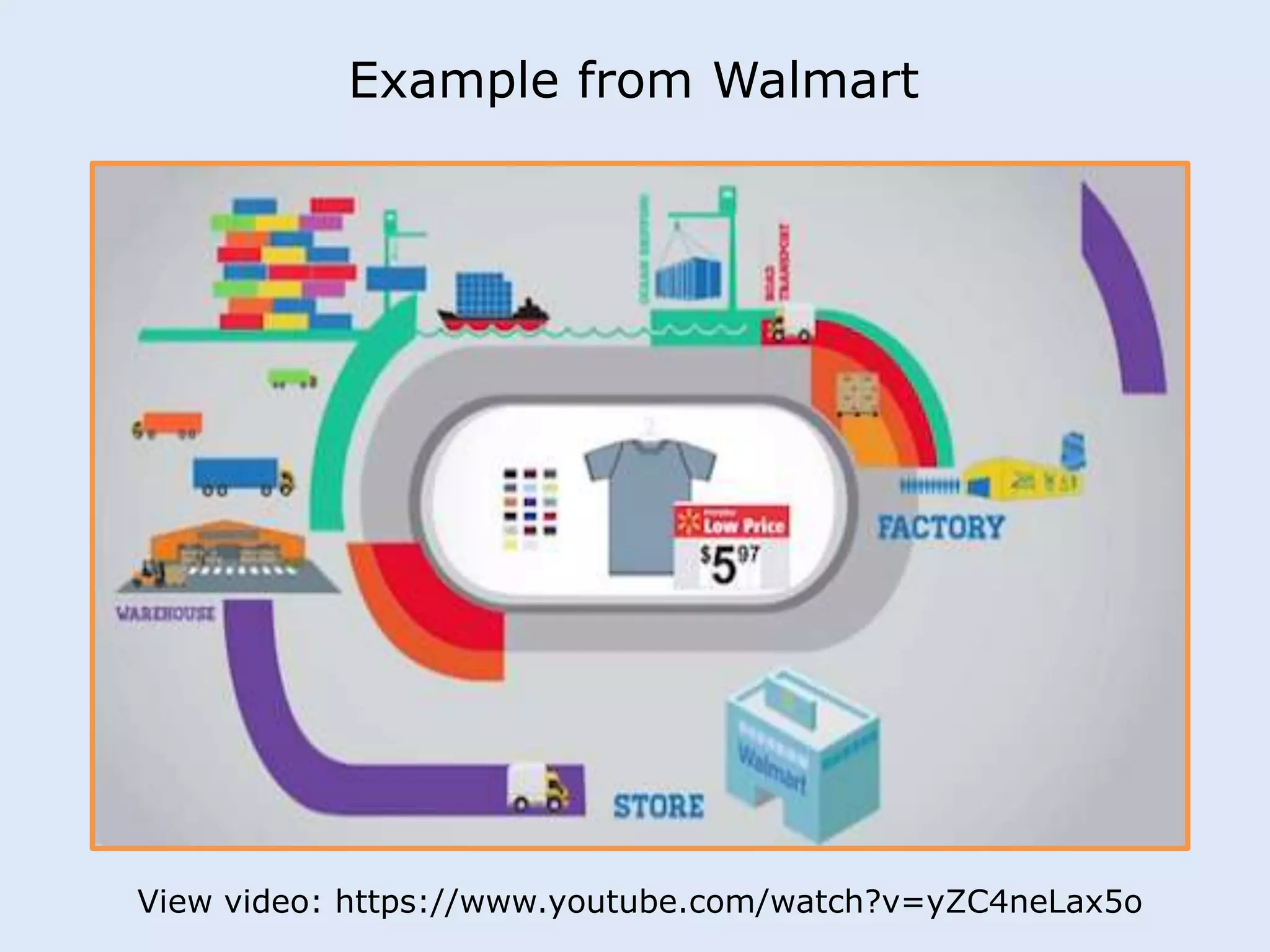
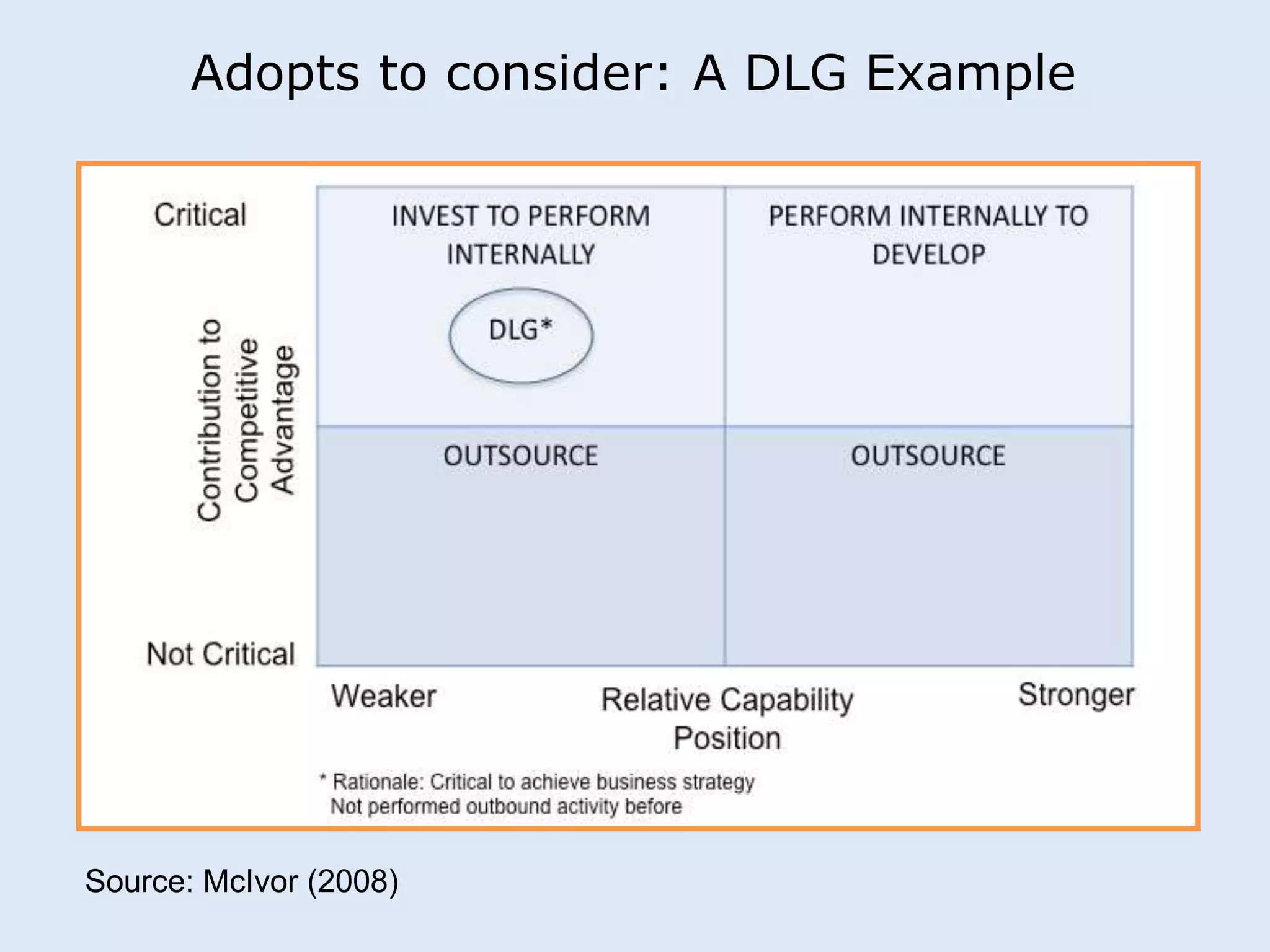
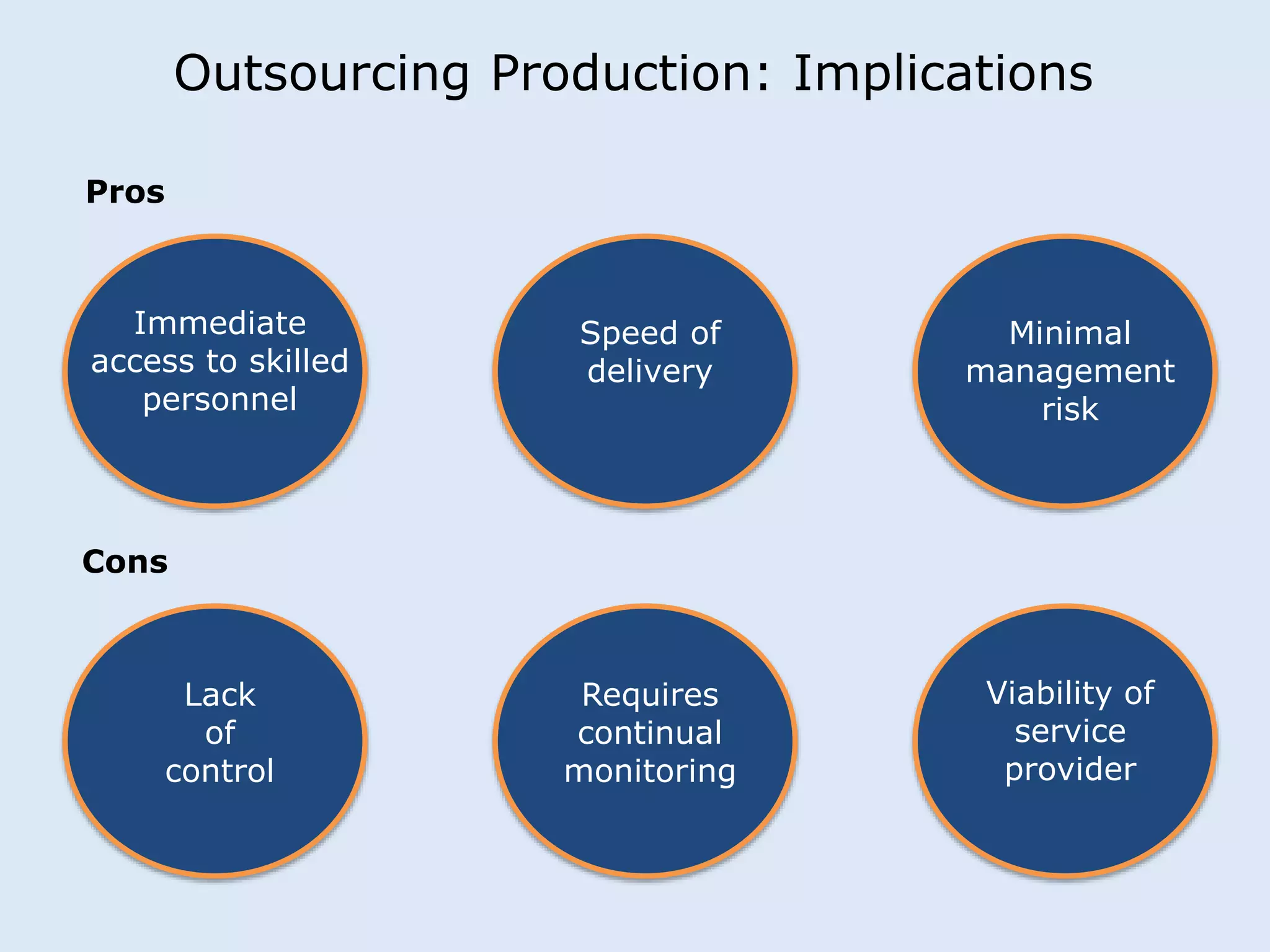
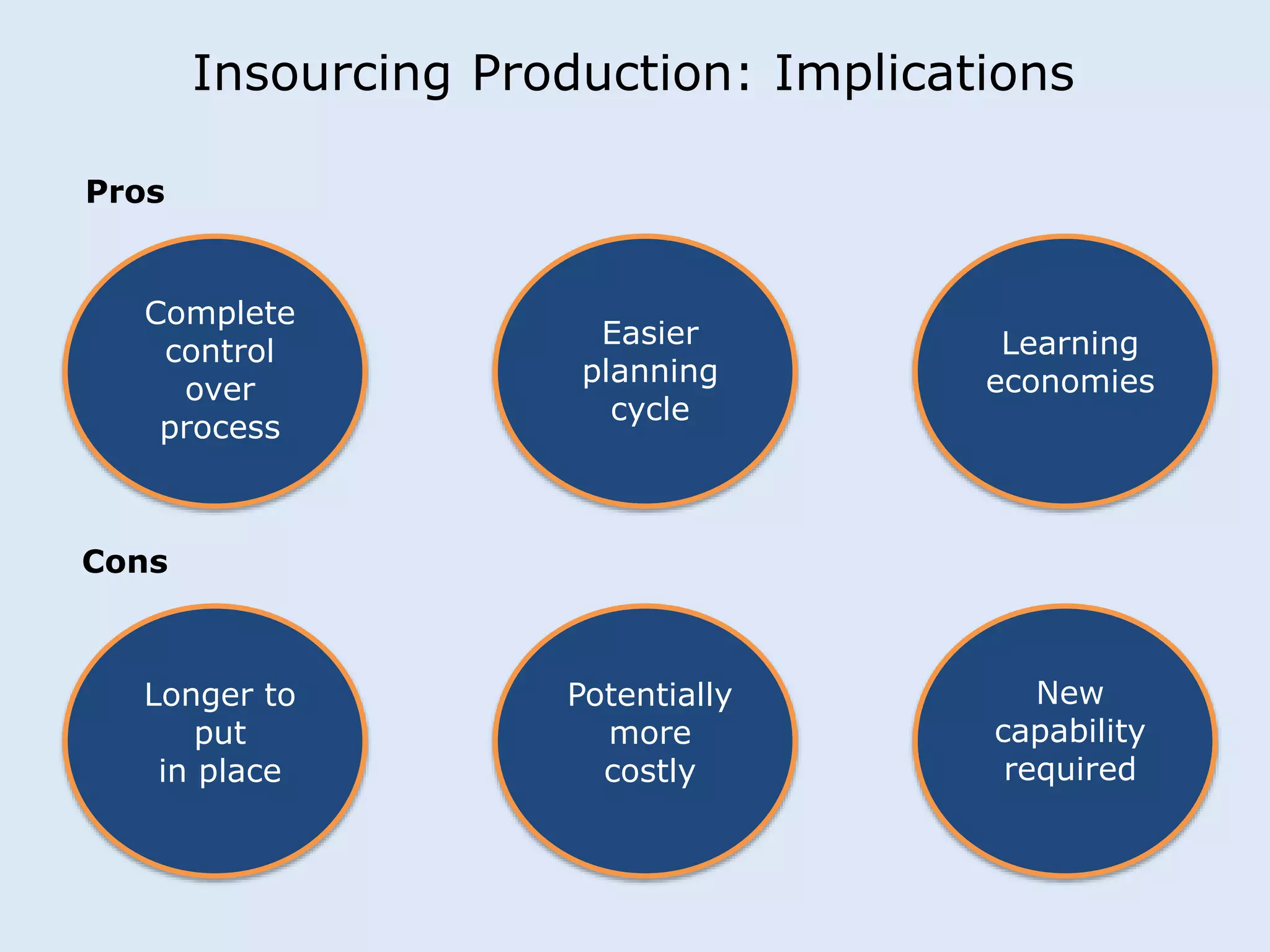
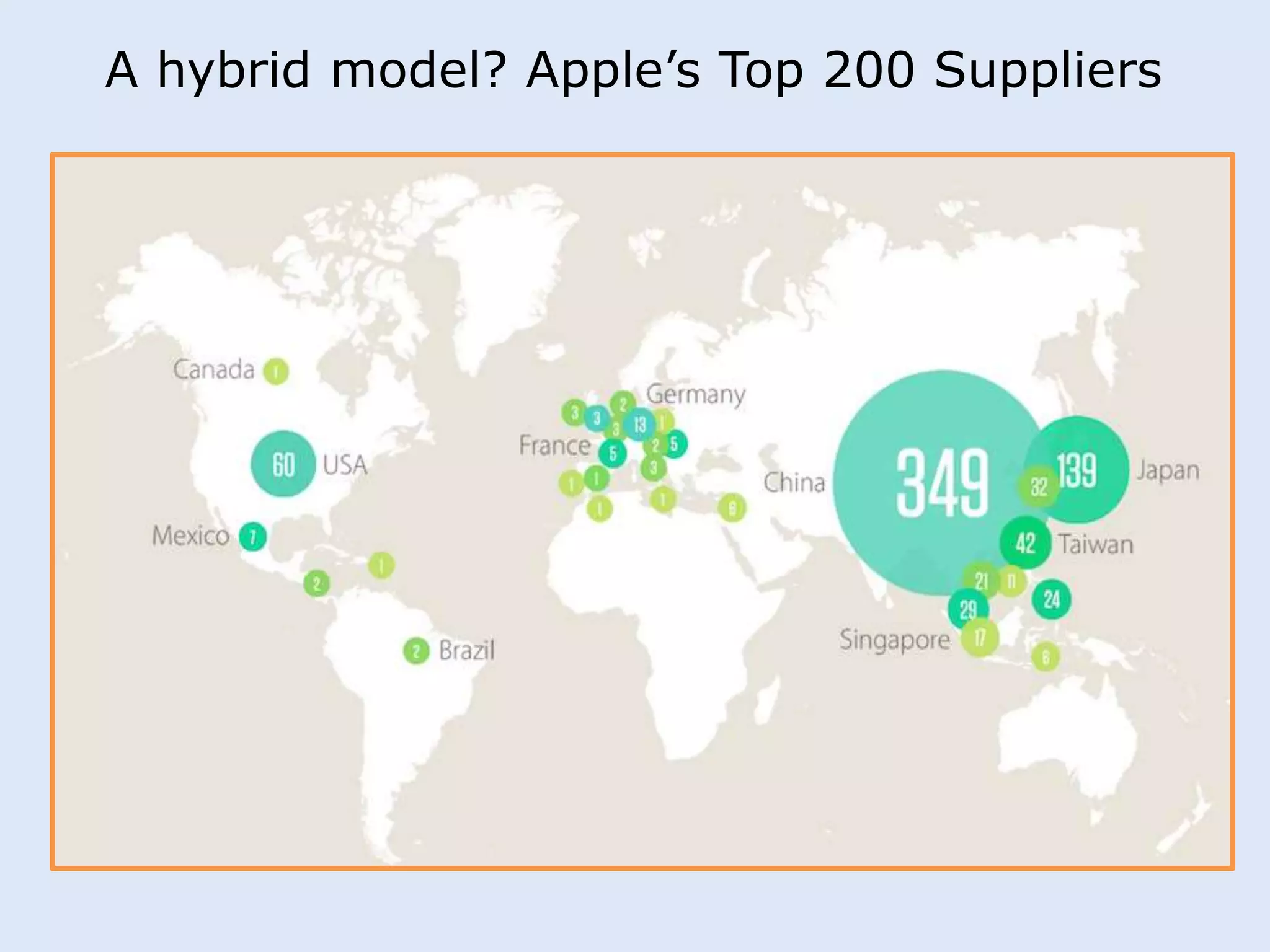
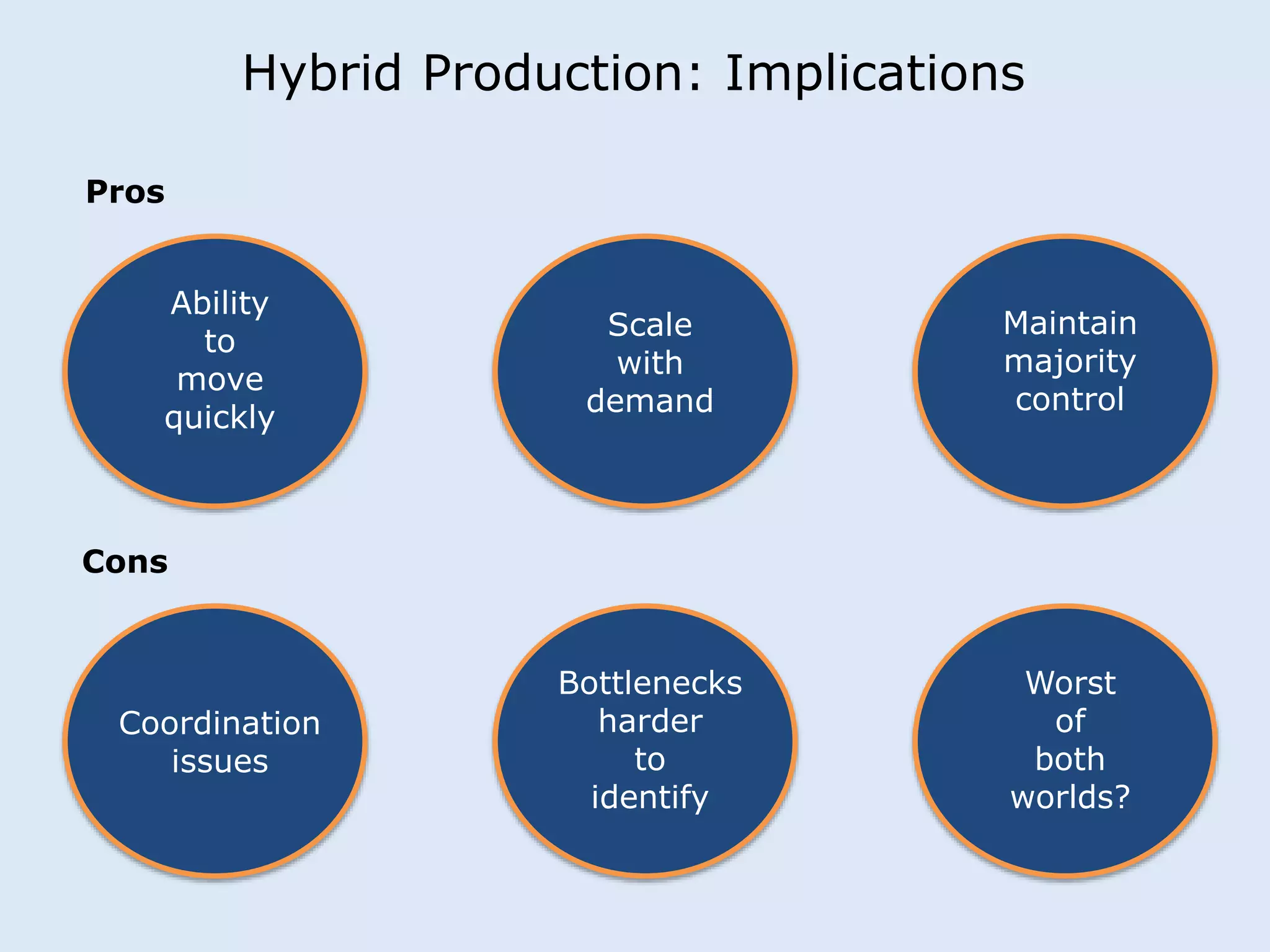
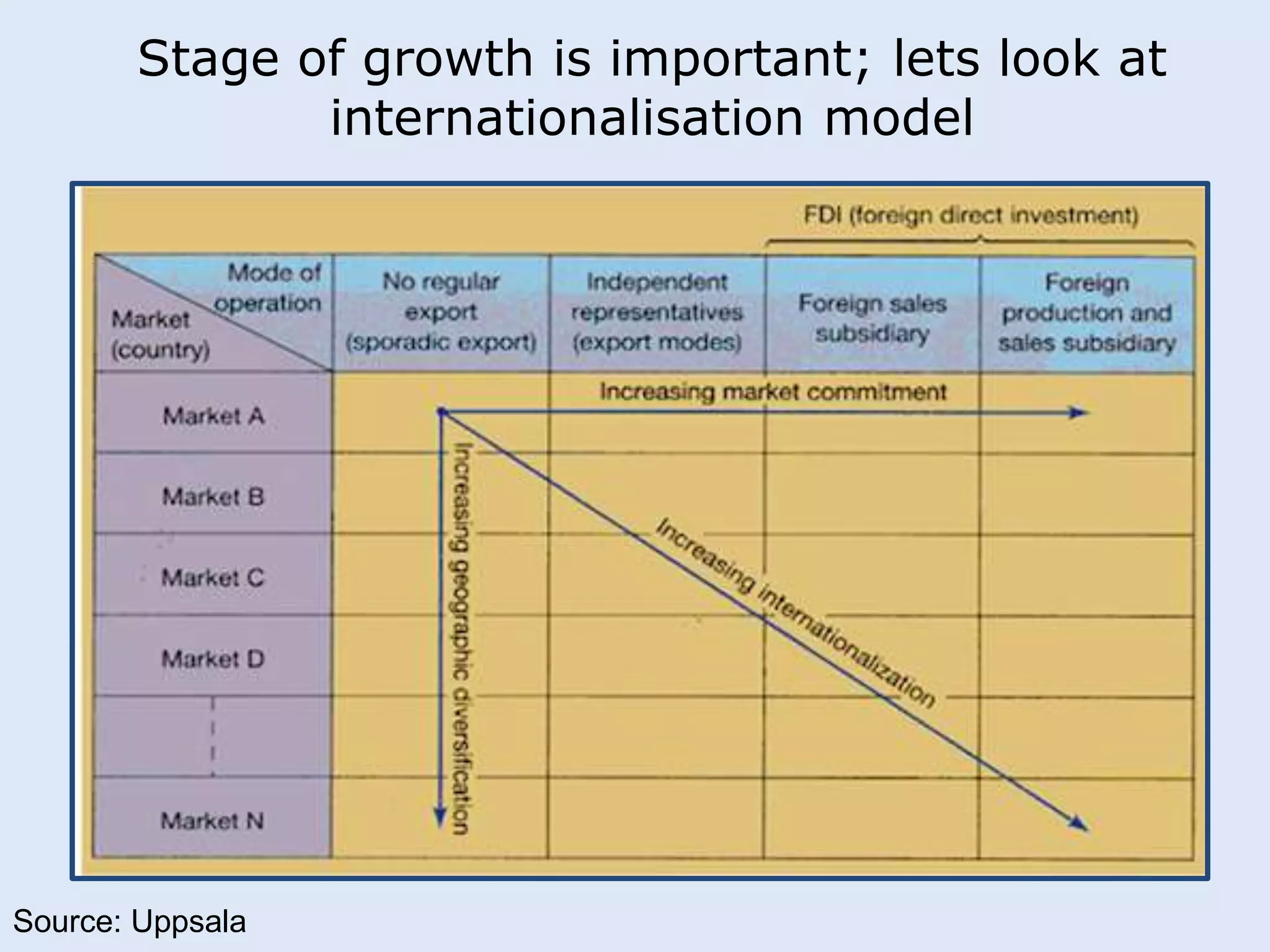
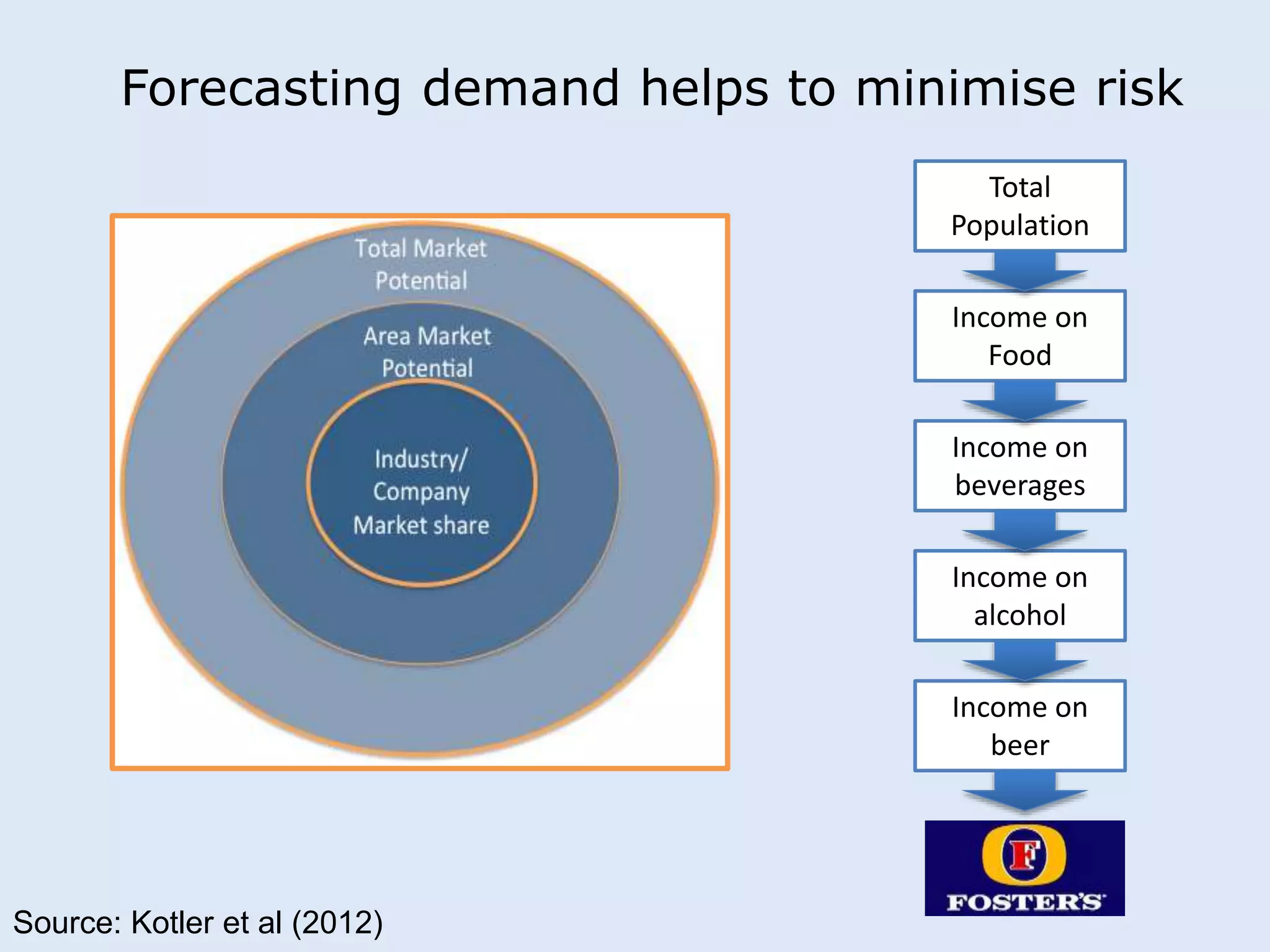
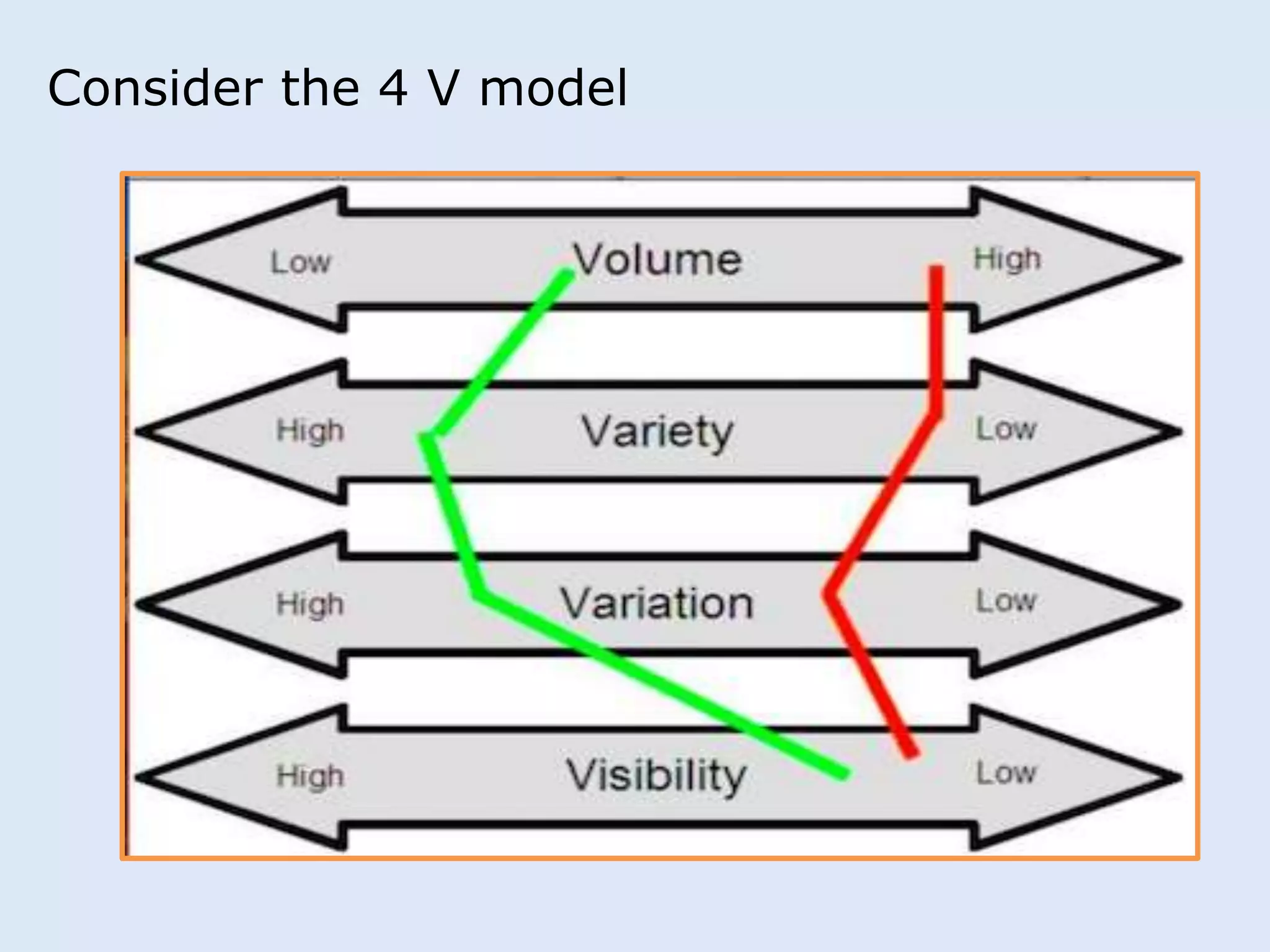
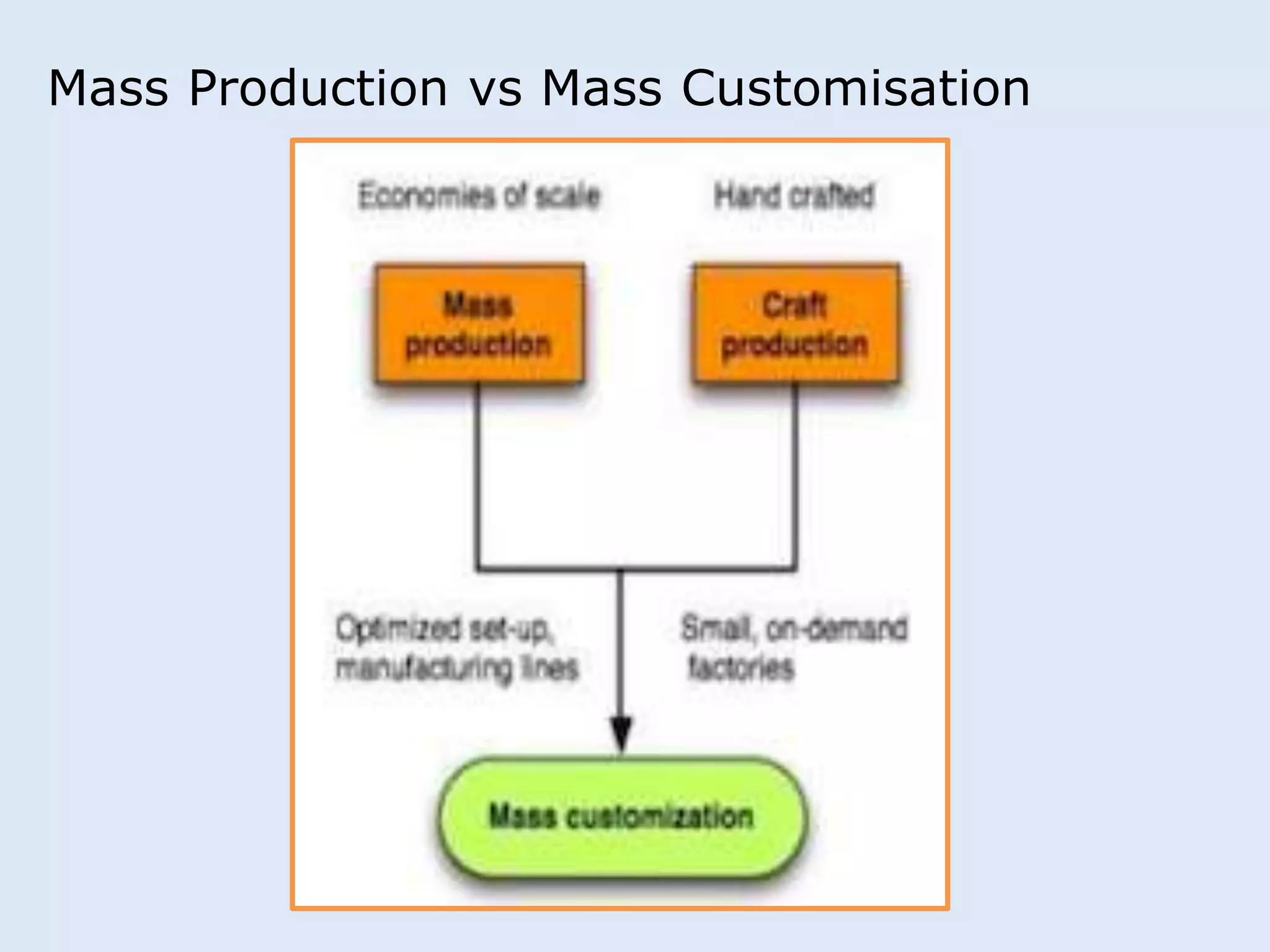
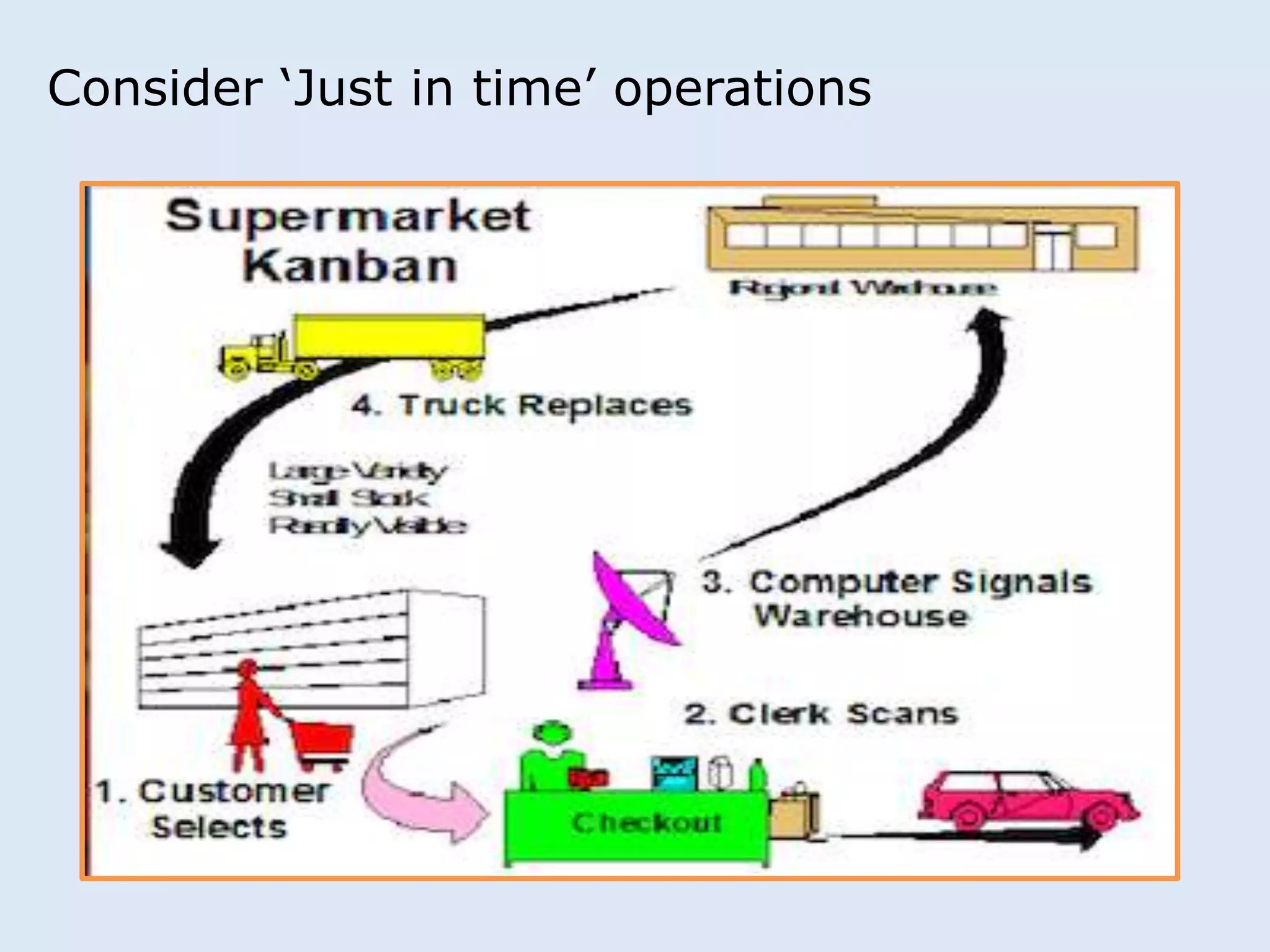
This document discusses various manufacturing considerations for organizations. It explores options for sourcing raw materials from around the world to maximize efficiencies. Manufacturing options that are evaluated include outsourcing production, insourcing production, and a hybrid model. Key factors that are examined for each option include implications, pros and cons, and examples. Additionally, considerations for whether to manufacture in the home country or host country based on stage of growth are reviewed. Tools like demand forecasting and assessing local trade barriers are also emphasized.