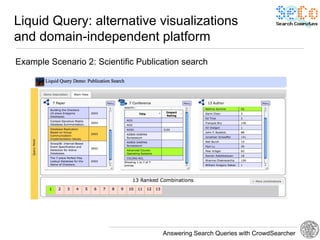
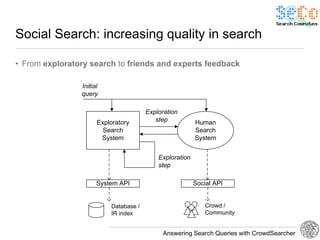
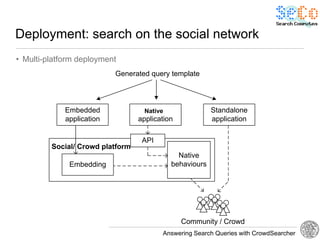
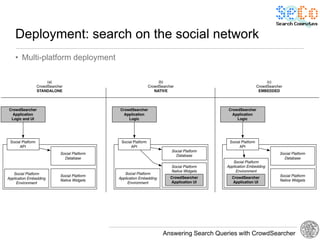
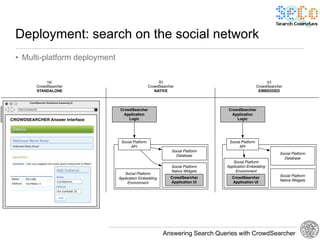
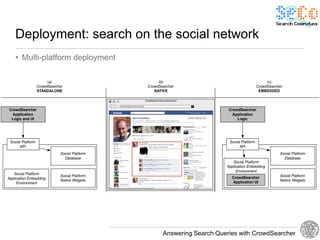
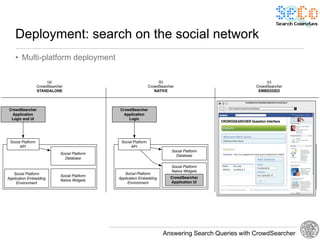
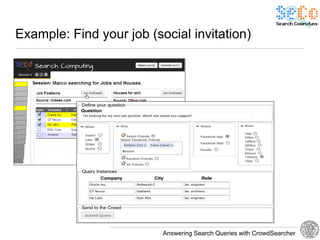
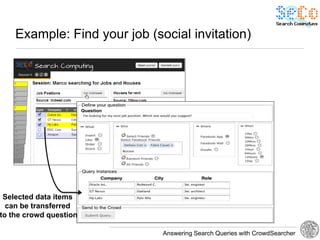
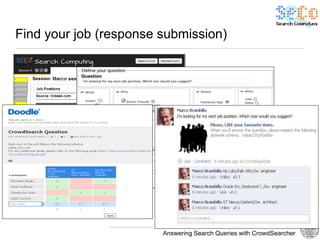
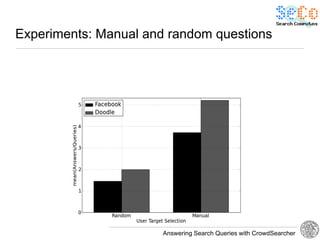
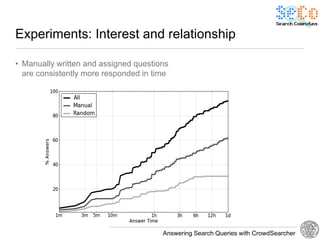
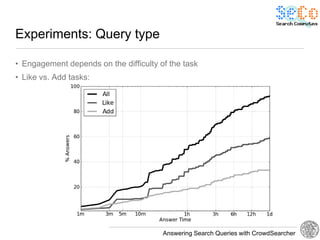
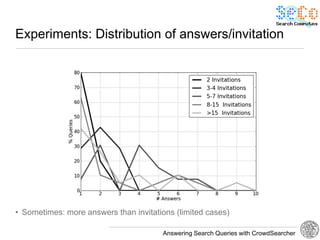
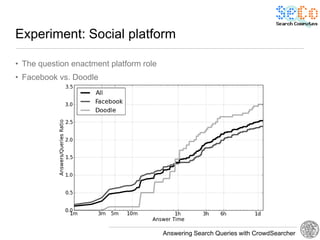
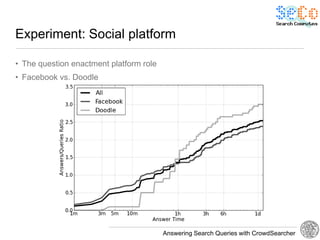
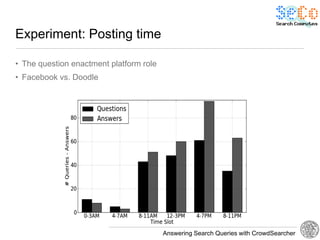
The document discusses 'CrowdSearcher', a crowdsourcing approach for addressing complex web search queries, integrating user insights and social community input. It outlines the differences between crowds and social networks, the challenges of task management in crowdsourcing, and the dynamics of engaging users through social platforms. Key findings emphasize the importance of community consistency and query management techniques in enhancing response rates for real-life problem-solving.






![Liquid Query:
Query Submission [WWW
2010]
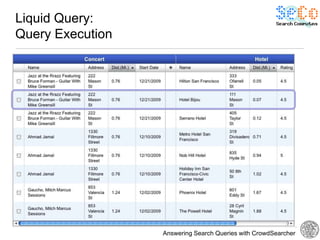
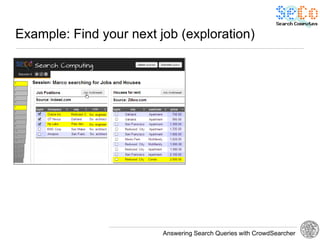
Example Scenario 1: Trip planner for events
Concert Hotels
query conditions query conditions
Answering Search Queries with CrowdSearcher](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crowdsearcher-crowdsourcing-search-engine-www2012-120420094143-phpapp02/85/Answering-Search-Queries-with-CrowdSearcher-a-crowdsourcing-and-social-network-approach-to-search-7-320.jpg)