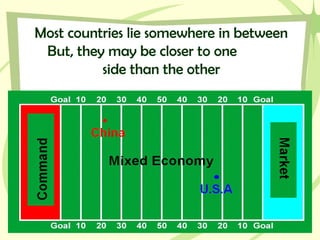
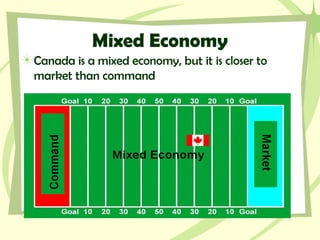
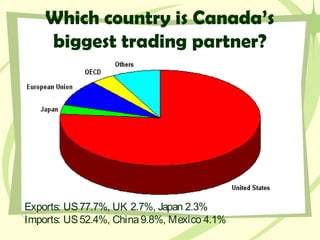
Canada has a mixed economy that is closer to a market economy, with some government regulation. It has a strong economy based on natural resources like minerals, fish, timber, and energy. Canada's largest trading partner is the United States, and it has benefited from free trade agreements like NAFTA that allow for increased trade. While Canada has a highly educated population and strong industries, it still faces challenges with unemployment, poverty, environmental issues, and providing public services.