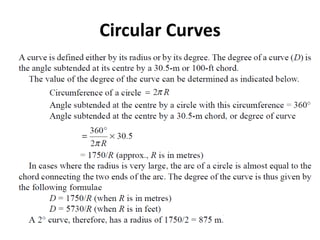
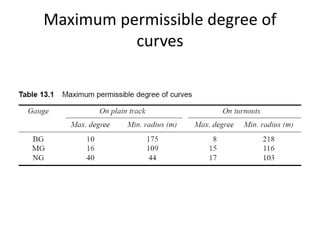
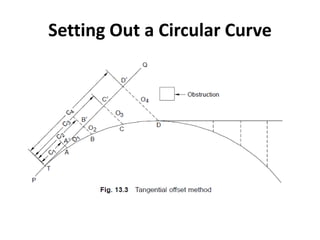
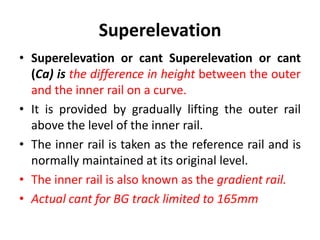
This document discusses curves and superelevation on railways. It defines horizontal and vertical curves, and explains that superelevation involves raising the outer rail on a curve to provide a comfortable ride. Superelevation counters the effects of lateral forces when negotiating a curve. The key points are:
- Superelevation is the difference in height between the inner and outer rails and helps distribute load on both rails.
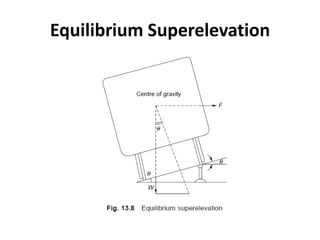
- Equilibrium speed is when the centrifugal force is balanced by the cant (superelevation), providing no unbalanced radial acceleration.
- Maximum permissible speed considers factors like radius, cant, cant deficiency/excess, and transition length.
- Examples are provided to calculate supere