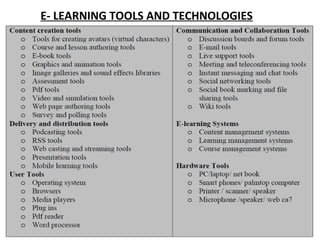
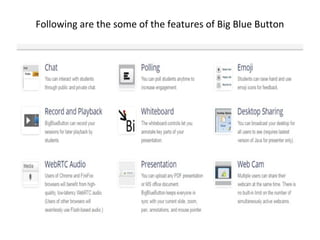
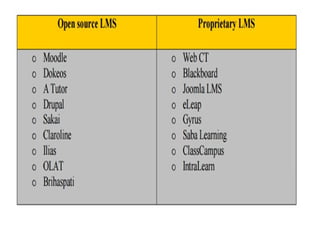
This document discusses various e-learning tools and technologies used for communication, collaboration, content creation, and delivery. Key communication tools include email, instant messaging, and blogging. Collaboration is supported by tools like wikis, social bookmarking, and social networking sites. Popular authoring tools for content creation are Adapt, LAMS, Xerte, and eXeLearning. Delivery methods include learning management systems, MOOCs, flipped learning, websites, and podcasting.